Lycium pallidum, commonly referred to as the Pale Wolfberry, is a remarkable and adaptable plant native to North America, particularly thriving in arid and semi-arid regions. This botanical description and other key features in this article unveils the distinctive features that define Lycium pallidum and its ability to thrive in challenging environments.
The Botanical Description of Lycium pallidum (Pale Wolfberry)
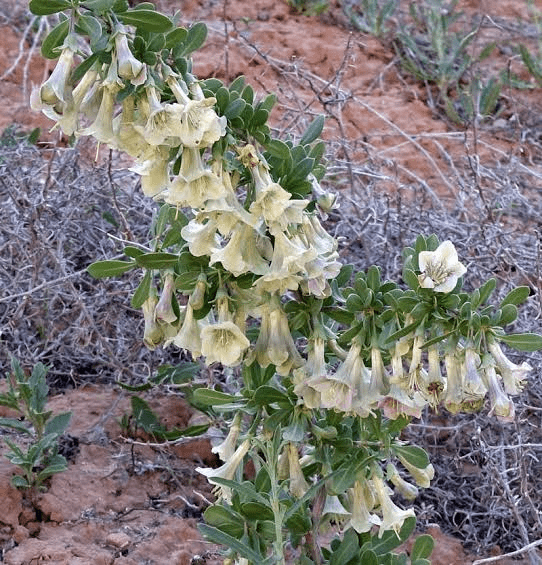
1. Plant Size and Structure: Lycium pallidum, commonly known as Pale Wolfberry, is a deciduous shrub that belongs to the Solanaceae family. It typically grows to a height ranging from 3 to 10 feet (1 to 3 meters). The plant’s structure is characterized by multiple stems arising from the base, forming a bushy and compact appearance.
2. Leaves: The leaves of Lycium pallidum are simple, arranged alternately along the stems. They are lance-shaped and have a pale green color, giving the plant its specific epithet “pallidum.” The leaves are smooth-edged and can range in size from 1 to 3 inches (2.5 to 7.6 cm) in length.
3. Flowers: Pale Wolfberry produces small, tubular flowers that are typically pale pink to lavender in color. The flowers are arranged in clusters and have a distinctive bell shape. They bloom during late spring to early summer, attracting pollinators such as bees and butterflies.
4. Fruits: The plant produces round, fleshy berries that ripen from green to orange and eventually deep red or purplish-black. These berries, often referred to as wolfberries or goji berries, are edible and have a slightly sweet taste. They are rich in nutrients and are widely used for their health benefits.
5. Habitat: Lycium pallidum is native to North America and is commonly found in arid and semi-arid regions. It thrives in well-drained soils, including sandy and rocky substrates. The plant is often spotted in desert habitats, slopes, and along roadsides.
6. Geographic Distribution: Pale Wolfberry is distributed across various states in the United States, including Arizona, California, Nevada, Utah, and New Mexico. Its adaptability to arid environments makes it a resilient species in these regions.
7. Adaptations: Lycium pallidum is well-adapted to drought conditions, with deep root systems that enable it to access water from lower soil layers. Its ability to thrive in arid environments showcases its resilience and ecological importance in fragile ecosystems.
8. Growth Cycle: As a deciduous shrub, Lycium pallidum sheds its leaves in response to changing seasons. In spring, the plant produces new leaves and flowers, followed by the development of berries in summer. During fall and winter, it enters a period of dormancy, conserving energy for the next growing season.
The Geographic Distribution of Lycium pallidum (Pale Wolfberry)
1. North American Range: Lycium pallidum, commonly known as Pale Wolfberry or goji berry, is primarily native to North America. It is distributed across several western states, including Arizona, California, Nevada, Utah, and New Mexico. These arid and semi-arid regions provide the ideal habitat for this resilient plant.
2. Arid Environments: Pale Wolfberry thrives in arid and desert environments, often growing on slopes, hillsides, and along roadsides. Its ability to adapt to dry and challenging conditions makes it a valuable species in ecosystems where water is scarce.
3. Rocky and Sandy Soils: The plant demonstrates adaptability to a variety of soil types, including rocky and sandy substrates. This adaptability allows it to colonize different habitats and contribute to soil stabilization.
4. Ecological Importance: Lycium pallidum plays a significant ecological role in arid regions by providing food and shelter for wildlife. The berries are a food source for various birds and mammals, contributing to local biodiversity.
5. Range Expansion: In addition to its native range, Pale Wolfberry has been introduced to other regions with similar climatic conditions, such as parts of Europe and Asia. Its cultivation and utilization have spread beyond its native habitat due to its valuable berries and potential health benefits.
The Chemical Composition of Lycium pallidum (Pale Wolfberry)
1. Nutrient-Rich Berries: The most well-known feature of Lycium pallidum is its berries, which are highly nutritious. They are a rich source of essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C, vitamin A, iron, and zinc.
2. Antioxidant Compounds: Pale Wolfberry berries contain a variety of antioxidants, such as flavonoids and carotenoids. These compounds help protect cells from oxidative damage and contribute to the plant’s potential health benefits.
3. Amino Acids: Lycium pallidum berries also contain several amino acids, including essential ones like threonine and leucine. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and play a crucial role in various physiological processes.
4. Polysaccharides: Polysaccharides found in Pale Wolfberry are believed to have immunomodulatory properties, potentially enhancing the body’s immune response. These compounds have drawn interest for their potential health-promoting effects.
5. Alkaloids: Some species of Lycium, including Lycium pallidum, contain alkaloids. These bioactive compounds are known for their diverse pharmacological properties and may contribute to the plant’s medicinal applications.
6. Essential Oils: The plant’s leaves and stems may contain essential oils with distinct aromatic properties. These oils have potential applications in traditional medicine and aromatherapy.
7. Flavonoids: Flavonoids are bioactive compounds known for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. They are present in Lycium pallidum and contribute to the plant’s health benefits.
8. Terpenes: Terpenes are aromatic compounds found in various plants, including Lycium species. They may have a role in the plant’s defense mechanisms and can have potential applications in aromatherapy.
The Harvesting and Processing of Lycium pallidum (Pale Wolfberry)
1. Harvesting: Pale Wolfberry berries are typically harvested when they have ripened to a deep red or purplish-black color. This is the stage at which they are most nutrient-rich and suitable for consumption.
2. Traditional Harvesting: In traditional settings, the berries are often hand-picked from the shrubs. This method requires care to avoid damaging the plants and to ensure a sustainable harvest.
3. Commercial Harvesting: In commercial settings, mechanized methods may be employed to harvest the berries efficiently. However, sustainable practices are essential to prevent overharvesting and preserve the plant’s natural habitat.
4. Drying and Preservation: After harvesting, the berries are typically dried to extend their shelf life. This can be done using sun drying or specialized drying equipment. Once dried, they can be stored for future use.
5. Culinary Use: Lycium pallidum berries are used in various culinary applications. They can be eaten dried as a snack, added to cereals and baked goods, or used in herbal teas and infusions.
6. Herbal Remedies: The berries are also used to prepare herbal remedies and tinctures. They are valued for their potential health benefits, particularly their antioxidant and immune-boosting properties.
Understanding the geographic distribution, chemical composition, and methods of harvesting and processing of Lycium pallidum sheds light on the plant’s significance in both natural ecosystems and human culture. This knowledge sets the stage for exploring its rich history and its diverse uses in traditional and modern herbal medicine.
Read Also: How To Source For Feeds For Your Poultry Birds
The Medicinal Health Benefits of Lycium pallidum (Pale Wolfberry)
1. Antioxidant Properties: Lycium pallidum, also known as Pale Wolfberry, is celebrated for its antioxidant-rich berries. These antioxidants, including vitamin C and carotenoids, help combat oxidative stress in the body, reducing the risk of chronic diseases and promoting overall well-being.
2. Immune System Support: The immune-boosting effects of Pale Wolfberry have been well-documented. Regular consumption of its berries may enhance the body’s natural defense mechanisms, helping to ward off infections and maintain immune health.
3. Anti-Inflammatory Benefits: Some studies suggest that Pale Wolfberry possesses anti-inflammatory properties. This makes it valuable in managing conditions characterized by chronic inflammation, such as arthritis and certain skin disorders.
4. Eye Health: The carotenoids found in Pale Wolfberry are beneficial for eye health. They may help protect the eyes from age-related conditions, including macular degeneration and cataracts.
5. Cardiovascular Health: The antioxidants and nutrient content of Pale Wolfberry may support heart health. They help maintain healthy blood pressure, reduce cholesterol levels, and improve overall cardiovascular function.
6. Skin Health: Pale Wolfberry’s rich nutrient profile can benefit the skin. It may promote collagen production, improve skin elasticity, and contribute to a more youthful appearance.
7. Blood Sugar Regulation: Some studies have suggested that Pale Wolfberry may help regulate blood sugar levels, making it potentially beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk.
8. Liver Health: Traditional herbal medicine has employed Pale Wolfberry to support liver health. It may help in detoxifying the liver and improving its overall function.
9. Weight Management: The berries’ high fiber content can aid in weight management by promoting a feeling of fullness and supporting healthy digestion.
10. Cognitive Function: Some research indicates that the antioxidants in Pale Wolfberry may have a protective effect on the brain, potentially reducing the risk of cognitive decline.
11. Stress Reduction: Traditional herbal uses of Pale Wolfberry include its potential to reduce stress and improve mood. It may have adaptogenic properties that help the body cope with stress.
12. Digestive Health: The fiber content of Pale Wolfberry can promote digestive health by regulating bowel movements and supporting a healthy gut microbiome.
13. Bone Health: The plant’s nutrient profile includes minerals like calcium, which can contribute to bone health and reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
14. Fertility and Reproductive Health: Some cultures have historically associated Pale Wolfberry with fertility and reproductive health. While more research is needed, it remains a topic of interest.
The Methods of Usage to Achieve the Provided Health Benefits of Lycium pallidum (Pale Wolfberry)
1. Fresh Consumption: One of the most direct ways to benefit from Pale Wolfberry is by consuming its fresh berries. You can eat them as a nutritious snack or add them to your daily meals, such as salads or yogurt.
2. Dried Berries: Dried Pale Wolfberry berries are widely available and can be enjoyed as a convenient and nutritious snack. They can also be used in various recipes, including trail mixes and baked goods.
3. Herbal Teas: You can prepare a herbal tea using dried Pale Wolfberry berries. Simply steep a handful of berries in hot water, and enjoy the health benefits of the infused tea.
4. Tinctures and Extracts: Tinctures and extracts made from Pale Wolfberry are available in many health stores. They offer a concentrated form of the plant’s benefits and can be added to beverages or taken sublingually.
5. Supplements: Dietary supplements in the form of capsules or powders are available for those who prefer a convenient way to incorporate Pale Wolfberry into their daily routine.
6. Topical Products: Some skin and cosmetic products contain Pale Wolfberry extracts, promoting its potential benefits for skin health. These products can include creams, serums, and lotions.
The Side Effects of Using Lycium pallidum Medicinal Plant
1. Allergies: While rare, some individuals may be allergic to Pale Wolfberry. If you experience symptoms like itching, rash, or swelling after consumption, discontinue use and seek medical advice.
2. Digestive Discomfort: Excessive consumption of Pale Wolfberry may lead to digestive discomfort, including diarrhea or stomach cramps. It’s essential to consume them in moderation.
3. Blood Sugar Interactions: If you have diabetes or are taking medications to regulate blood sugar, consult your healthcare provider before adding Pale Wolfberry to your diet. It may interact with these medications.
4. Drug Interactions: Some medications, such as anticoagulants or antihypertensive drugs, may interact with Pale Wolfberry. It’s crucial to discuss any potential interactions with your healthcare provider.
5. Photosensitivity: There is some evidence to suggest that certain compounds in Pale Wolfberry may increase sensitivity to sunlight. While this is not a common side effect, take precautions if you are exposed to direct sunlight after consumption.
6. Pregnancy and Nursing: Pregnant and nursing individuals should use Pale Wolfberry with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare provider. Limited safety data are available for these groups.
Understanding the health benefits, methods of usage, and potential side effects of Pale Wolfberry provides individuals with valuable information to make informed decisions about its incorporation into their wellness routines. As we delve deeper into the scientific research and safety precautions, we will uncover a holistic perspective on the plant’s role in health and well-being.
Read Also: 19 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Juniperus Scopulorum (Rocky Mountain Juniper)
The Scientific Research and Studies of Lycium pallidum (Pale Wolfberry)

1. Antioxidant Studies: Numerous scientific studies have explored the antioxidant properties of Lycium pallidum. Researchers have investigated the plant’s ability to combat oxidative stress, which is linked to various chronic diseases. These studies have found that the plant’s berries are rich in antioxidants, particularly carotenoids and vitamin C, which contribute to its health benefits.
2. Immunomodulatory Effects: Some scientific research has focused on the potential immunomodulatory effects of Pale Wolfberry. Studies suggest that regular consumption of its berries may enhance the immune system’s function, leading to increased resistance to infections and improved overall health.
3. Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Research has examined the anti-inflammatory properties of Lycium pallidum. Inflammation is associated with a wide range of health conditions, and the plant’s ability to reduce inflammation has garnered interest in the field of natural medicine.
4. Eye Health Studies: The carotenoid content of Pale Wolfberry has led to studies on its benefits for eye health. Some research has indicated that carotenoids like those found in the plant may help protect the eyes from age-related conditions such as macular degeneration and cataracts.
5. Cardiovascular Research: Several scientific investigations have explored the cardiovascular benefits of Pale Wolfberry. The antioxidants and nutrients present in the plant’s berries have been studied for their potential to support heart health, including maintaining healthy blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
6. Skin Health Studies: Research has looked into the potential benefits of Pale Wolfberry for skin health. Some studies have examined its role in promoting collagen production, improving skin elasticity, and contributing to a more youthful appearance.
7. Blood Sugar Regulation: The plant’s potential to regulate blood sugar levels has been a subject of scientific interest, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk. Research in this area aims to elucidate the mechanisms behind this potential effect.
8. Cognitive Function Research: Certain studies have explored the plant’s impact on cognitive function and brain health. The antioxidants in Pale Wolfberry may have a protective effect on the brain, potentially reducing the risk of cognitive decline.
9. Stress Reduction Investigations: The traditional use of Pale Wolfberry to reduce stress and improve mood has prompted scientific inquiries into its adaptogenic properties. Research aims to better understand how the plant may help the body cope with stress.
10. Digestive Health Studies: Research has examined how the fiber content of Pale Wolfberry promotes digestive health by regulating bowel movements and supporting a healthy gut microbiome.
11. Bone Health Investigations: The potential benefits of Pale Wolfberry for bone health have attracted scientific attention. Some studies aim to determine the impact of the plant’s nutrient content, including minerals like calcium, on bone health.
12. Reproductive Health Research: The traditional association of Pale Wolfberry with fertility and reproductive health has sparked scientific curiosity. While more research is needed, these studies explore the plant’s potential effects in this area.
The Safety Precautions and Recommendations in Using Lycium pallidum (Pale Wolfberry) Medicinal Plant
1. Allergy Precautions: While allergic reactions to Pale Wolfberry are rare, it’s essential to be cautious, especially if you have known allergies to plants in the Solanaceae family. If you experience any signs of an allergic reaction, such as itching, rash, or swelling, discontinue use and seek medical attention.
2. Digestive Care: Moderate your consumption of Pale Wolfberry to avoid digestive discomfort, including diarrhea or stomach cramps. Excessive consumption can lead to such issues.
3. Consultation for Medical Conditions: If you have diabetes or are taking medications to regulate blood sugar, consult your healthcare provider before incorporating Pale Wolfberry into your diet. It may interact with these medications, necessitating adjustments.
4. Medication Interactions: Certain medications, such as anticoagulants or antihypertensive drugs, may interact with Pale Wolfberry. It is crucial to discuss any potential interactions with your healthcare provider to ensure your safety.
5. Sun Sensitivity Precautions: Although not common, there is evidence to suggest that some compounds in Pale Wolfberry may increase sensitivity to sunlight. Take precautions if you are exposed to direct sunlight after consumption.
6. Pregnancy and Nursing: Pregnant and nursing individuals should exercise caution and consult a healthcare provider before using Pale Wolfberry, as limited safety data are available for these groups.
FAQs About Lycium pallidum (Pale Wolfberry) Medicinal Plant
Q1: Can I eat Pale Wolfberry raw?
A1: Yes, you can eat Pale Wolfberry raw. Its fresh berries are a nutritious snack and can be added to salads or consumed as a whole.
Q2: Are there any known drug interactions with Pale Wolfberry?
A2: Some medications, such as anticoagulants or antihypertensive drugs, may interact with Pale Wolfberry. Consult your healthcare provider if you have concerns.
Q3: Is Pale Wolfberry safe for children to consume?
A3: In general, Pale Wolfberry is considered safe for children when consumed in moderation. However, consult a healthcare provider for specific recommendations.
Q4: Can I use Pale Wolfberry topically for skin health?
A4: Some skincare products contain Pale Wolfberry extracts. These products may promote skin health and can be used in topical applications.
Q5: Is it safe to take Pale Wolfberry supplements daily?
A5: Pale Wolfberry supplements are generally safe when used as directed. Follow the recommended dosage on the product label.
Q6: How can I store dried Pale Wolfberry berries?
A6: Store dried Pale Wolfberry berries in an airtight container in a cool, dry place to maintain their quality and shelf life.
Q7: Can I grow Pale Wolfberry at home?
A7: Yes, it is possible to grow Pale Wolfberry in your garden. It is a hardy and drought-resistant plant, making it suitable for home cultivation in appropriate climates.
Understanding the scientific research, safety precautions, and frequently asked questions related to Pale Wolfberry provides a comprehensive overview of its use, safety, and potential benefits. As we continue to explore its geographical distribution and delve into its historical and cultural significance, we gain a deeper appreciation for this versatile plant.
Do you have any questions, suggestions, or contributions? If so, please feel free to use the comment box below to share your thoughts. We also encourage you to kindly share this information with others who might benefit from it. Since we can’t reach everyone at once, we truly appreciate your help in spreading the word. Thank you very much for your support and for sharing!
Disclaimer: This article is for educational and informational purposes only. The health benefits described are based on scientific research and traditional knowledge. They are not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a healthcare professional before using any herb or natural remedy for medical purposes.

