The Beans Ovary: Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products
The Beans Ovary, scientifically known as Phaseolus vulgaris, is a crucial reproductive structure responsible for seed production. Beans are dicotyledonous plants, belonging to the legume family Fabaceae. The ovary is a part of the female reproductive organ of the flower, situated at the base of the pistil. It plays a central role in the process of sexual reproduction in plants.
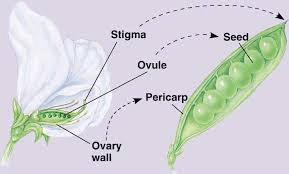
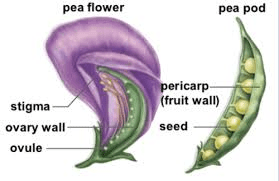
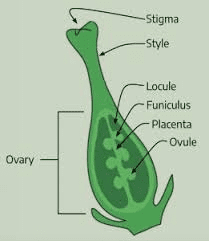
The ovary typically consists of three main parts: the ovary wall (pericarp), ovules, and placenta. The ovary wall, or pericarp, is the outermost layer and protects the developing seeds within. It can vary in thickness and texture depending on the specific bean species. Inside the ovary wall are one or more ovules, which are small structures that contain the female gametes (egg cells). These ovules are attached to the ovary wall by a stalk-like structure called the funiculus.
At the center of the ovary is the placenta, a tissue that connects the ovules to the ovary wall. It serves as a support structure and also facilitates the transport of nutrients and water to the developing seeds. The placenta is crucial for the development and maturation of the seeds.
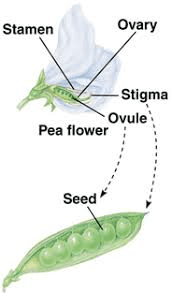
The process of seed development begins with pollination, where pollen grains containing male gametes (sperm cells) land on the stigma, the receptive part of the pistil. From there, the pollen tube grows down through the style and reaches the ovary. Fertilization occurs when the sperm cells unite with the egg cells within the ovules.
After fertilization, the ovules develop into seeds, and the ovary begins to undergo changes to support seed maturation. The ovary wall, or pericarp, often undergoes thickening and transformation into the fruit, which surrounds and protects the seeds. In beans, the fruit is typically a pod that develops from the ovary and matures to contain several seeds.
Throughout seed development, the ovary provides a protective environment for the developing seeds and ensures they receive the necessary nutrients and water for growth. The placenta continues to play a vital role in nutrient transport and support.
Once seeds are fully matured, the pod of the bean plant ripens and dries out, preparing for seed dispersal. This process ensures the continuation of the plant species by dispersing seeds to new locations where they can germinate and grow into new bean plants.
In conclusion, the ovary of a bean plant is a crucial structure in the process of sexual reproduction and seed production. It consists of the ovary wall (pericarp), ovules, and placenta, all of which play specific roles in supporting seed development and maturation. Through pollination, fertilization, and seed formation, the ovary ensures the continuation of the bean plant species by producing mature seeds within protective pods. Understanding the anatomy and function of the ovary provides insights into the reproductive strategies and life cycle of bean plants in their natural environment.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Beans Ovary
1. Seed Production: The ovary develops into pods containing seeds, which are essential for growing new bean plants.
2. Food Source: The ovary produces the beans, a staple food rich in protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, important for human nutrition.
3. Agricultural Yield: A healthy ovary leads to higher bean production, contributing to increased agricultural yield and food security.
4. Animal Feed: Bean pods and seeds are used as nutritious feed for livestock, supporting the animal husbandry industry.
5. Biodiversity: Beans ovaries contribute to the genetic diversity of bean plants, allowing for the development of new varieties with desirable traits.
6. Crop Rotation: Beans, through their ovaries, play a key role in crop rotation systems, enriching the soil with nitrogen and improving its fertility.
7. Soil Improvement: Bean plants enhance soil quality through nitrogen fixation, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
8. Biofuel Production: Biomass from bean plants, including ovaries, can be converted into biofuels, providing a renewable energy source.
9. Medicinal Research: Compounds in beans are studied for their potential health benefits, such as antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties.
10. Horticultural Uses: Bean ovaries are integral in ornamental gardening for their aesthetic appeal and contribution to plant diversity.
11. Economic Stability: Bean cultivation, driven by productive ovaries, supports the livelihoods of farmers and agricultural workers, contributing to economic stability.
12. Culinary Uses: Beans from the ovary are used in a variety of culinary applications, from soups and stews to salads and side dishes.
13. Industrial Applications: Bean plant residues, including ovaries, can be used in the production of biodegradable plastics and other eco-friendly materials.
14. Nutritional Supplements: Extracts from beans are used in dietary supplements for their high protein and nutrient content.
15. Genetic Research: The ovary is crucial in plant breeding programs aimed at improving bean varieties for disease resistance and yield.
16. Soil Erosion Control: Bean plants, including ovaries, help prevent soil erosion through their extensive root systems and ground cover.
17. Organic Farming: Beans are essential in organic farming practices, improving soil health and reducing reliance on synthetic inputs.
18. Cultural Significance: Beans and their ovaries hold cultural and traditional importance in various societies, often featured in festivals and rituals.
Read Also: Ordering Honey Bees: A Comprehensive Guide
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Beans Ovary
1. Beans: The primary product, beans are harvested from the pods developed from the ovary and used as a staple food worldwide.
2. Bean Flour: Beans can be ground into flour, used in baking and cooking to make bread, cakes, and other dishes.
3. Bean Sprouts: Bean seeds from the ovary can be sprouted and used in salads and stir-fries, providing a nutritious addition to meals.
4. Bean Oil: Oil can be extracted from beans for cooking, as well as for use in cosmetics and industrial applications.
5. Bean Meal: The by-product of oil extraction, bean meal is used as animal feed due to its high protein content.
6. Bean Paste: Beans can be processed into paste, which is used in various culinary applications, including sauces and spreads.
7. Tofu: Made from bean curd, tofu is a versatile protein-rich food used in many cuisines.
8. Tempeh: A fermented bean product, tempeh is used as a meat substitute in vegetarian and vegan diets.
9. Bean Milk: Beans can be processed into milk, providing a dairy-free alternative for lactose-intolerant individuals.
10. Bean Protein Isolate: Extracted from beans, this protein isolate is used in dietary supplements and food products to enhance protein content.
11. Biofertilizer: Bean plant residues, including ovaries, can be composted to produce biofertilizer, enriching the soil.
12. Biochar: Bean plant biomass, including ovaries, can be converted into biochar, a form of charcoal used to improve soil health and sequester carbon.
13. Biogas: Bean plant waste can be anaerobically digested to produce biogas, a renewable energy source.
14. Fiber: Bean plant fibers, including those from the ovary, can be used to make biodegradable textiles and ropes.
15. Green Manure: Bean plants, including their ovaries, are used as green manure to enhance soil fertility.
16. Medicinal Extracts: Compounds from beans are extracted for their potential health benefits and used in pharmaceuticals.
17. Natural Dyes: Pigments from beans can be used to produce natural dyes for fabrics and crafts.
Read Also: Best Flowers for Honey Bees
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Beans Ovary
1. What is the beans ovary?
The beans ovary is the part of the flower that develops into the pod containing seeds.
2. Why is the beans ovary important?
It is essential for seed production, leading to the growth of new bean plants and ensuring crop yields.
3. Can beans ovary be used in animal feed?
Yes, bean pods and seeds are nutritious feed for livestock.
4. How does the beans ovary contribute to soil fertility?
Bean plants enhance soil quality through nitrogen fixation, improving fertility and reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
5. Are there medicinal uses for beans ovary?
Compounds in beans are studied for potential health benefits, such as antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties.
6. What products can be derived from beans ovary?
Products include beans, bean flour, bean sprouts, bean oil, bean meal, bean paste, tofu, tempeh, and bean milk.
7. How is bean oil extracted from beans?
Bean oil is extracted through pressing or solvent extraction processes, separating the oil from the bean solids.
8. Can beans ovary be converted into biofuel?
Yes, bean plant residues, including ovaries, can be processed into biofuels.
9. What is the role of beans ovary in crop rotation?
Beans improve soil health and fertility, making them ideal for use in crop rotation systems.
10. How does the beans ovary benefit genetic research?
The ovary is crucial in plant breeding programs aimed at improving bean varieties for disease resistance and yield.
Read Also: What Are People Looking For in Online Fitness Classes?