The Carrot Ovary: Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products
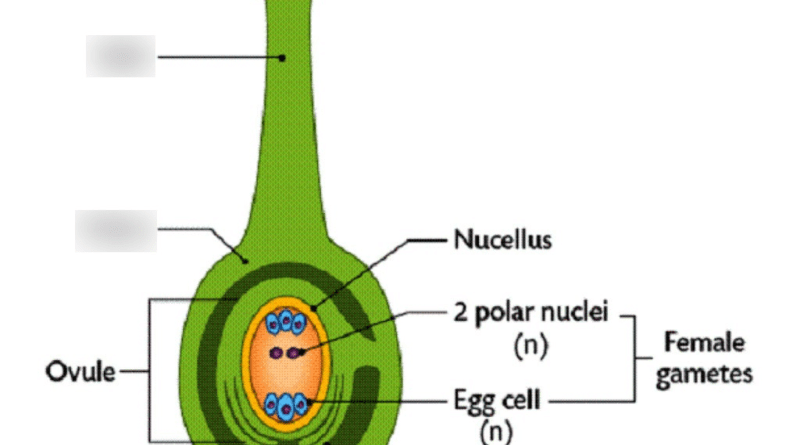
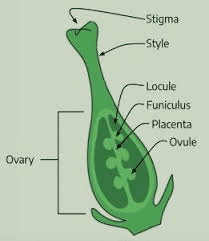
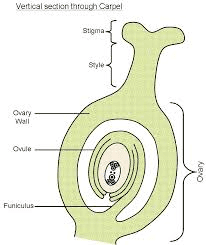
The carrot ovary is a crucial component of the carrot plant’s reproductive system, playing a vital role in the process of sexual reproduction. Scientifically known as the ovary, this structure is located at the base of the pistil within the carrot flower. Botanically classified as part of the Apiaceae family, the carrot ovary is a specialized organ that houses the ovules, which are the female reproductive cells or gametes.
The ovary is typically situated at the center of the flower, surrounded by the stamens, petals, and sepals, forming the innermost part of the floral structure.
The primary function of the carrot ovary is to protect and nurture the developing ovules, facilitate fertilization, and ultimately, produce seeds for the next generation of carrot plants. Each ovary contains one or more ovules, which are enclosed within protective layers of tissue called integuments. These integuments serve to shield the ovules from external threats such as pests, pathogens, and adverse environmental conditions.
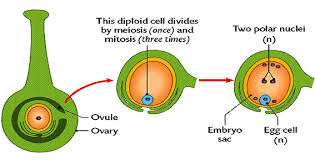
Within the ovary, the ovules undergo a series of developmental stages, culminating in the formation of seeds upon successful fertilization. The process begins with ovule initiation, during which specialized cells within the ovary differentiate and develop into ovules. These ovules then mature and become receptive to pollen, which is transferred from the stamens to the stigma of the pistil during pollination.
Once pollination occurs, pollen grains germinate on the stigma, forming pollen tubes that grow down through the style and into the ovary. The male gametes contained within the pollen tubes fertilize the female gametes within the ovules, resulting in the formation of zygotes. These zygotes develop into embryos, and the ovules develop into seeds, each containing a new generation of carrot plants.
The development and maturation of the ovary and its contents are regulated by a complex interplay of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. Factors such as temperature, light, moisture, and nutrient availability can influence ovary development and seed production in carrot plants. Additionally, the genetic makeup of the plant, including traits inherited from parental plants, can impact the quality and quantity of seeds produced by the ovary.
In addition to its role in seed production, the carrot ovary also serves as a source of genetic diversity and variability within carrot populations. Through sexual reproduction and seed dispersal, genetic traits and characteristics are passed on to subsequent generations, contributing to the adaptability and resilience of carrot plants in diverse environments.
From a botanical perspective, the carrot ovary exhibits structural adaptations that optimize its function in seed production. These adaptations include specialized tissues and cells, such as the ovular integuments, which provide protection and support to the developing ovules. The ovary is also equipped with vascular tissues that facilitate nutrient transport and hormone signaling, ensuring proper ovule development and seed maturation.
In conclusion, the carrot ovary is a vital reproductive structure that plays a central role in the sexual reproduction and propagation of carrot plants. Through the production of seeds, the ovary ensures the continuation of the carrot plant species and contributes to the genetic diversity and adaptability of carrot populations. Understanding the scientific description and function of the carrot ovary is essential for advancing research in plant biology, agriculture, and crop improvement strategies.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Carrot Ovary
1. Seed Production: Carrot ovary produces seeds essential for commercial carrot cultivation, contributing to the agricultural industry’s seed market.
2. Crop Improvement: Genetic traits encoded in carrot ovary seeds are utilized for breeding programs, leading to the development of improved carrot varieties with desirable traits like disease resistance and high yield.
3. Agriculture: Seeds from carrot ovary are crucial for establishing carrot crops, supporting agricultural activities and food production.
4. Horticulture: Carrot ovary seeds are used by horticulturists and home gardeners for growing carrots in gardens and greenhouses.
5. Export Industry: Carrot ovary seeds may be exported to international markets, contributing to the global trade of agricultural commodities.
6. Research: Carrot ovary seeds are utilized by researchers for studying plant genetics, reproductive biology, and crop improvement strategies.
7. Food Security: Carrot ovary seeds play a role in ensuring food security by providing a sustainable source of seeds for carrot production.
8. Culinary Arts: Carrot ovary seeds are used in culinary practices for sprouting into nutritious microgreens or as garnishes in dishes.
9. Sustainable Agriculture: The production of carrot ovary seeds supports sustainable agriculture practices by promoting crop diversity and resilience.
10. Livelihoods: The cultivation and sale of carrot ovary seeds provide livelihood opportunities for seed producers, farmers, and agricultural workers.
11. Education: Carrot ovary seeds are used in educational settings for teaching students about plant biology, reproduction, and agriculture.
12. Biosecurity: Maintaining a diverse gene pool through carrot ovary seeds helps safeguard against crop diseases and pests, enhancing biosecurity in agriculture.
13. Soil Health: Crop rotation involving carrot cultivation, facilitated by ovary seed production, contributes to soil health and fertility.
14. Environmental Conservation: Carrot ovary seeds support biodiversity conservation efforts by preserving genetic diversity within carrot plant populations.
15. Rural Development: Carrot ovary seed production can stimulate rural development through income generation and employment opportunities in rural areas.
16. International Trade: Carrot ovary seeds contribute to international trade relationships, as they are traded between countries for agricultural purposes.
17. Botanical Gardens: Carrot ovary seeds are utilized by botanical gardens and seed banks for conservation and preservation of plant genetic resources.
18. Seed Banking: Conservation of carrot ovary seeds in seed banks ensures their availability for future use in breeding programs and research endeavors.
Read Also: The Most Lucrative between Production of Fish Fingerlings or Raising them to Table Size
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Carrot Ovary
1. Carrot Seeds: Seeds produced by carrot ovary are used for planting and propagating carrot crops in agriculture and horticulture.
2. Seedlings: Carrot seeds germinate into seedlings, which are transplanted into fields or containers for further growth and development.
3. Culinary Ingredients: Carrot seeds produced by ovary are ground into a powder and used as a culinary spice or flavoring agent in food products.
4. Sprouts: Carrot seeds can be sprouted and used as nutritious microgreens for salads, sandwiches, and garnishes.
5. Botanical Research: Carrot ovary seeds are utilized by researchers for studying plant genetics, reproductive biology, and crop improvement strategies.
6. Seed Oil: Oil extracted from carrot seeds produced by ovary is used in culinary, cosmetic, and industrial applications.
7. Animal Feed: Carrot seeds are used as a nutritious component of animal feed for livestock such as poultry and cattle.
8. Herbal Medicine: Compounds extracted from carrot seeds may have potential medicinal properties and are used in herbal medicine formulations.
9. Essential Oils: Carrot seed essential oil, extracted from seeds produced by ovary, is used in aromatherapy and skincare products.
10. Biodegradable Packaging: Carrot seed oil can be used as a sustainable alternative for biodegradable packaging materials.
11. Botanical Extracts: Carrot ovary seeds are used in the formulation of botanical extracts for cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and food applications.
12. Soil Enrichment: Carrot seeds produced by ovary can be used as a cover crop to improve soil health and fertility.
13. Biodiesel Production: Oil extracted from carrot seeds can be used in biodiesel production as a renewable fuel source.
14. Nutritional Supplements: Carrot seed oil and extracts are used in the formulation of dietary supplements for their potential health benefits.
15. Fertilizers: Carrot seed meal, a by-product of oil extraction from seeds produced by ovary, can be used as organic fertilizer.
16. Horticultural Use: Carrot seeds produced by ovary are used for growing carrot plants in home gardens, farms, or commercial nurseries.
17. Plant Propagation: Carrot seeds produced by ovary are used for propagating carrot plants through seedlings or direct seeding methods.
Read Also: The Best Stage to Start Raising your Catfishes (Fingerlings or Juveniles)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Carrot Ovary
1. What is carrot ovary?
Carrot ovary is the reproductive organ of the carrot plant responsible for producing seeds.
2. How does carrot ovary contribute to agriculture?
Carrot ovary produces seeds that are essential for planting and propagating carrot crops, supporting agricultural activities and food production.
3. Can carrot ovary seeds be stored for future use?
Yes, carrot ovary seeds can be stored in dry, cool conditions for extended periods, allowing them to be used for planting in subsequent growing seasons.
4. Are carrot ovary seeds edible?
No, carrot ovary seeds are not typically consumed as they are used for planting and propagating carrot crops.
5. How long does it take for carrot ovary seeds to germinate?
The time it takes for carrot ovary seeds to germinate varies depending on factors such as temperature, moisture, and soil conditions.
6. Can carrot ovary seeds be genetically modified?
Research into genetic modification of carrot ovary seeds is ongoing, with the aim of improving crop yield, resilience, and nutritional content.
7. Are there any environmental benefits associated with carrot ovary?
Yes, carrot ovary seeds support biodiversity conservation efforts by preserving genetic diversity within carrot plant populations.
8. What is the role of carrot ovary in sustainable agriculture?
Carrot ovary seeds contribute to sustainable agriculture practices by promoting crop diversity, resilience, and soil health.
9. Can carrot ovary seeds be used for culinary purposes?
While carrot ovary seeds are not commonly used for culinary purposes, they can be sprouted and used as nutritious microgreens or garnishes in dishes.
10. Are there any economic opportunities associated with carrot ovary?
Yes, carrot ovary seeds provide economic opportunities for seed producers, farmers, agricultural workers, and industries involved in agriculture, h
Read Also: What to Know About Kokedama