The Carrot Stigmas: Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products
Carrot stigmas are vital components of the reproductive system of carrot plants (Daucus carota). As part of the female reproductive structure known as the pistil, the stigma plays a crucial role in the process of sexual reproduction in plants.
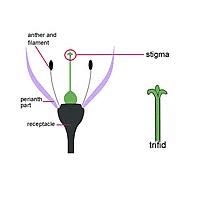
Botanically classified as part of the Apiaceae family, carrot stigmas are responsible for receiving pollen during pollination, initiating the fertilization process, and ultimately, leading to seed production. Structurally, the stigma is located at the top of the pistil and is typically positioned to intercept pollen grains carried by pollinators such as insects or wind.
The carrot stigma is characterized by its distinctive shape and surface features, which are adapted to maximize the capture and retention of pollen. It is often protruding and may have a sticky or feathery texture, allowing it to efficiently trap pollen grains as they come into contact.
The surface of the stigma is covered in microscopic structures called papillae, which increase the surface area available for pollen adhesion and germination.
The primary function of the carrot stigma is to facilitate the process of pollination by capturing pollen grains and providing a receptive surface for pollen tube growth. When a pollinator visits a carrot flower, pollen grains are transferred from the anthers of another flower onto the stigma. The sticky surface of the stigma allows the pollen grains to adhere, preventing them from being dislodged by wind or other environmental factors.
Once pollen grains have landed on the stigma, they germinate, forming pollen tubes that grow down through the style towards the ovary. This process, known as pollen tube growth, is guided by chemical signals produced by the stigma and style, ensuring that the pollen tubes reach the ovules contained within the ovary for fertilization. Once fertilization occurs, the ovules develop into seeds, which are then dispersed to propagate the next generation of carrot plants.
The development and function of the carrot stigma are influenced by various genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and light intensity can affect stigma receptivity and pollen tube growth rates. Hormonal signals, such as auxins and gibberellins, regulate stigma development and pollen tube guidance, ensuring the successful completion of the fertilization process.
From a botanical perspective, the carrot stigma exhibits structural adaptations that optimize its function in pollination and fertilization. These adaptations include specialized cell types and surface features that enhance pollen capture, adhesion, and germination. Additionally, the stigma may secrete substances that promote pollen tube growth and guidance towards the ovules within the ovary.
In conclusion, carrot stigmas are essential reproductive structures that play a critical role in the sexual reproduction of carrot plants. By facilitating pollination and fertilization, the stigma ensures the production of seeds and the continuation of the carrot plant species. Understanding the scientific description and function of carrot stigmas is essential for advancing research in plant biology, agriculture, and crop improvement strategies.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Carrot Stigmas

Carrot stigmas, though often overlooked, hold significant economic importance and serve various practical purposes. Here are 18 uses and economic implications of carrot stigmas:
1. Agriculture: Carrot stigmas play a crucial role in the reproductive process of carrot plants, contributing to seed production for agricultural purposes.
2. Seed Production: Stigmas facilitate the production of carrot seeds, which are used by farmers and gardeners for growing carrots commercially or for personal consumption.
3. Horticulture: Stigmas contribute to the cultivation and breeding of new carrot varieties with desirable traits such as improved yield, disease resistance, and flavor profile.
4. Food Industry: Carrot seeds produced by stigmas are used for planting carrot crops, which are harvested for various food products such as fresh produce, juices, and processed foods.
5. Genetic Research: Stigmas are studied by geneticists and researchers to understand the genetic basis of traits related to flowering, pollination, and seed production in carrots.
6. Plant Breeding Programs: Knowledge gained from studying carrot stigmas is applied in plant breeding programs to develop new carrot cultivars with enhanced characteristics for commercial cultivation.
7. Pollination Services: In agricultural settings, insect pollinators such as bees and butterflies assist in the pollination of carrot stigmas, ensuring the production of high-quality seeds and crops.
8. Biodiversity Conservation: Carrot stigmas contribute to the biodiversity of ecosystems by supporting pollinator populations and maintaining genetic diversity within carrot plant populations.
9. Export Industry: Carrot seeds produced from stigmas may be exported to other regions or countries, contributing to the global trade of agricultural commodities.
10. Pharmaceutical Research: Compounds extracted from carrot seeds may have potential medicinal properties, leading to research into their use in pharmaceutical formulations.
11. Animal Feed: Carrot seeds produced by stigmas can be used as a nutritious component of animal feed for livestock such as poultry and cattle.
12. Soil Conservation: Crop rotation involving carrot cultivation, supported by the production of carrot seeds by stigmas, helps improve soil structure, fertility, and nutrient balance, reducing the risk of soil degradation and erosion.
13. Landscape Beautification: Carrot plants, including their flowers and stigmas, may be used for ornamental purposes in landscaping and garden design.
14. Agroforestry: Carrot plants, including their seeds produced by stigmas, may be integrated into agroforestry systems for sustainable land use and biodiversity conservation.
15. Education: The study of carrot stigmas and their role in plant reproduction is included in agricultural and botanical education programs, contributing to students’ understanding of plant biology.
16. Culinary Arts: Carrot seeds produced by stigmas can be sprouted and used as microgreens or garnishes in culinary dishes, adding flavor and nutritional value.
17. Beekeeping: Carrot flowers, including their stigmas, provide a nectar and pollen source for honeybees and other pollinators, supporting beekeeping activities.
18. Sustainable Agriculture: By supporting the natural pollination process, carrot stigmas contribute to sustainable agricultural practices that minimize the use of synthetic pesticides and fertilizers.
Read Also: How to Use Rice Husk to Produce Electricity
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Carrot Stigmas

1. Carrot Seeds: Produced by stigmas, carrot seeds are used for planting and propagating carrot crops in agricultural settings.
2. Pollen: Carrot pollen collected from stigmas may be used in research studies, beekeeping activities, or dietary supplements.
3. Herbal Medicine: Compounds extracted from carrot stigmas may be used in herbal medicine formulations for their potential health benefits.
4. Essential Oils: Carrot seed essential oil, extracted from seeds produced by stigmas, is used in aromatherapy and skincare products.
5. Animal Feed: Carrot seeds produced by stigmas can be used as a nutritious component of animal feed for livestock.
6. Seed Oil: Oil extracted from carrot seeds produced by stigmas may be used in culinary applications, cosmetics, or industrial products.
7. Biodegradable Packaging: Carrot seed oil can be used as a sustainable alternative for biodegradable packaging materials.
8. Botanical Extracts: Carrot stigma extracts may be used in the formulation of botanical extracts for cosmetic, pharmaceutical, or food applications.
9. Plant Breeding: Knowledge gained from studying carrot stigmas may be applied in plant breeding programs to develop new carrot cultivars.
10. Soil Enrichment: Carrot seeds produced by stigmas can be used as a cover crop to improve soil health and fertility.
11. Biodiesel Production: Oil extracted from carrot seeds produced by stigmas can be used in biodiesel production as a renewable fuel source.
12. Nutritional Supplements: Carrot seed oil and extracts may be used in the formulation of dietary supplements for their potential health benefits.
13. Culinary Ingredients: Carrot seeds produced by stigmas can be ground into a powder and used as a culinary spice or flavoring agent.
14. Fertilizers: Carrot seed meal, a by-product of oil extraction from seeds produced by stigmas, can be used as organic fertilizer.
15. Horticultural Use: Carrot seeds produced by stigmas are used for growing carrot plants in home gardens, farms, or commercial nurseries.
16. Plant Propagation: Carrot seeds produced by stigmas are used for propagating carrot plants through seedlings or direct seeding methods.
17. Herbal Teas: Carrot stigma extracts may be used in the formulation of herbal teas or dietary supplements for their potential health benefits.
Read Also: 5 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Meriandra dianthera (Mint Marjoram)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Carrot Stigmas

1. What are carrot stigmas?
Carrot stigmas are reproductive structures found within the flowers of the carrot plant, playing a crucial role in the process of sexual reproduction.
2. How do carrot stigmas contribute to agriculture?
Carrot stigmas facilitate the production of carrot seeds, which are essential for planting and propagating carrot crops in agricultural settings.
3. Can carrot stigmas be used for culinary purposes?
While carrot stigmas themselves are not commonly consumed, the seeds produced by stigmas can be used in culinary applications for their flavor and nutritional value.
4. Are there any environmental benefits associated with carrot stigmas?
Yes, carrot stigmas support biodiversity conservation efforts by promoting pollinator populations and maintaining genetic diversity within carrot plant populations.
5. Can carrot seeds produced by stigmas be stored for future use?
Yes, carrot seeds produced by stigmas can be stored in dry, cool conditions for extended periods, allowing them to be used for planting in subsequent growing seasons.
6. Are carrot stigmas genetically modified for agricultural purposes?
Currently, there are no genetically modified carrot stigmas approved for commercial use. However, research into genetic modification of carrot plants, including their reproductive structures like stigmas, is ongoing, aiming to improve crop yield, pest resistance, and nutritional content.
Read Also: Understanding the Basics of Environmental Law