The Carrot Taproots: Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products
The carrot taproots are fascinating organ from both a botanical and nutritional perspective, playing a crucial role in the plant’s growth, storage of nutrients, and reproduction. Understanding the scientific aspects of the carrot taproot provides insights into its development, structure, and significance in agriculture and human nutrition.
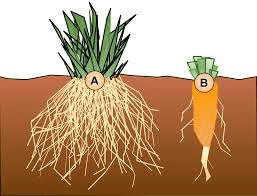
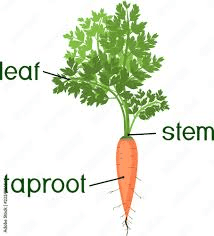
The carrot taproot is a specialized storage organ that develops from the primary root. It is characterized by its conical shape, which varies in size, length, and color depending on the carrot variety. Common colors include orange, yellow, purple, red, and white, each containing different pigments and nutrients. The orange carrot, for example, is rich in beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A.
The development of the carrot taproot begins with the germination of the seed. The primary root elongates and thickens as it grows downward into the soil, forming the taproot. This process is regulated by genetic factors and environmental conditions, such as soil quality, moisture, and temperature. Carrots prefer well-drained, sandy loam soils that are free from stones, which allows the taproot to grow straight and uniform.
The carrot taproot is composed of several distinct tissue layers. The outermost layer is the epidermis, which protects the root from physical damage and pathogen invasion. Beneath the epidermis lies the cortex, which contains parenchyma cells that store starch, sugars, and other nutrients.
The innermost layer is the stele, which includes the vascular tissues: the xylem and phloem. The xylem transports water and minerals from the soil to the rest of the plant, while the phloem distributes the photosynthates produced in the leaves to the taproot for storage.
The primary function of the carrot taproot is to store carbohydrates and other essential nutrients during the vegetative growth phase. These reserves provide energy for the plant during unfavorable growing conditions and support reproductive processes, such as flowering and seed production. The stored nutrients also make carrots a highly nutritious food source for humans and animals.
Carrots are a rich source of dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals. The high beta-carotene content in orange carrots is particularly noteworthy, as it is converted into vitamin A in the human body, supporting vision, immune function, and skin health. Additionally, carrots contain vitamins K, C, and B6, as well as potassium, which contributes to cardiovascular health.
The cultivation of carrots requires careful management of growing conditions to ensure the development of high-quality taproots. Factors such as planting depth, spacing, and irrigation practices must be optimized to promote uniform root growth and prevent issues like forked or twisted roots. Harvesting carrots at the right time is also crucial, as over-mature roots can become woody and less palatable.
The carrot taproot is a vital organ that serves as a storage reservoir for nutrients, enabling the plant to survive and reproduce. Its development and structure are influenced by both genetic and environmental factors, making it a subject of interest in agricultural science.
The nutritional benefits of carrots, derived from their taproots, make them an important component of the human diet, contributing to overall health and well-being. Understanding the biology and cultivation of carrot taproots is essential for maximizing their agricultural productivity and nutritional value.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Carrot Taproot
1. Nutritional Value: Carrot taproots are rich in essential nutrients, including vitamins A, K, and C, dietary fiber, and antioxidants, making them a valuable component of a healthy diet.
2. Culinary Uses: Carrots are widely used in cooking, from raw snacks and salads to soups, stews, and baked goods, adding flavor, color, and nutrition to meals.
3. Juice Production: Carrot juice is popular for its health benefits and is produced commercially, providing a nutritious beverage option rich in beta-carotene.
4. Animal Feed: Carrot taproots and by-products are used in animal feed, providing a nutritious supplement for livestock such as cattle, pigs, and poultry.
5. Food Coloring: Carrots are used as a natural food coloring agent due to their vibrant orange pigment, derived from beta-carotene.
6. Pharmaceutical Industry: Carrot extract is used in pharmaceuticals for its health benefits, including improved vision, skin health, and immune function.
7. Cosmetic Industry: Carrot oil and extract are used in skincare products for their antioxidant properties and ability to promote healthy skin.
8. Seed Production: Carrot taproots are crucial for producing seeds for future crops, ensuring the continued cultivation and availability of carrots.
9. Agricultural Economy: The cultivation of carrots supports local economies by providing jobs and income for farmers and workers in the agricultural sector.
10. Export Market: Carrots are a significant export commodity for many countries, contributing to their trade balance and economic growth.
11. Food Processing Industry: Carrots are processed into various products such as canned carrots, frozen carrots, and carrot powder, extending their shelf life and availability.
12. Culinary Innovation: Carrot taproots inspire culinary innovation, leading to new recipes and food products that cater to diverse consumer preferences.
13. Nutraceuticals: Carrot-derived supplements are used in the nutraceutical industry for their potential health benefits, including eye health and antioxidant support.
14. Soil Health: Carrot cultivation improves soil health through crop rotation practices, reducing soil erosion, and enhancing soil fertility.
15. Ethnobotanical Uses: Carrot taproots have been used traditionally in various cultures for medicinal purposes, including digestive health and as a natural remedy for certain ailments.
16. Organic Farming: Carrots are a popular crop in organic farming due to their adaptability and the growing demand for organic produce.
17. Climate Adaptability: Carrot taproots can be cultivated in a variety of climates, making them a versatile crop that supports food security in different regions.
18. Research and Development: Carrot taproots are used in agricultural research to develop improved varieties with enhanced nutritional content, disease resistance, and yield potential.
Read Also Processing of Pig Products and Record Keeping
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Carrot Taproot

1. Fresh Carrots: The most direct product is the fresh carrot taproot, which is consumed as a vegetable in numerous culinary applications.
2. Carrot Juice: Produced by extracting juice from fresh carrots, it is a popular health drink rich in vitamins and minerals.
3. Carrot Puree: Made by blending cooked carrots, it is used in baby foods, soups, sauces, and baked goods.
4. Carrot Powder: Created by drying and grinding carrots, it is used as a natural food coloring and flavoring agent in various products.
5. Carrot Oil: Extracted from carrot seeds or taproots, it is used in cosmetics and skincare products for its nourishing properties.
6. Carrot Chips: Dehydrated carrot slices are marketed as a healthy snack alternative to traditional potato chips.
7. Canned Carrots: Processed and preserved in cans, they provide a convenient, long-lasting option for consumers.
8. Frozen Carrots: Flash-frozen to preserve nutrients, they are a staple in the frozen food aisle.
9. Carrot Cake: A popular dessert, carrot taproot is a key ingredient, adding moisture and sweetness to the cake.
10. Animal Feed: By-products such as carrot tops and peels are used in animal feed, reducing waste and providing nutritional benefits to livestock.
11. Bioactive Compounds: Carrot taproots are a source of beta-carotene, used in dietary supplements and nutraceuticals for their antioxidant properties.
12. Carrot Extracts: Used in pharmaceutical and cosmetic products for their health and skin benefits.
13. Carrot Fiber: Extracted from the taproot, it is used as a dietary supplement to promote digestive health.
14. Pickled Carrots: Fermented or pickled carrots offer a tangy, preserved vegetable option.
15. Carrot Wine: Produced by fermenting carrot juice, it is an innovative product in the beverage industry.
16. Carrot Syrup: Made by reducing carrot juice with sugar, it is used as a natural sweetener and flavoring agent.
17. Carrot Flour: Produced by milling dried carrots, it is used in gluten-free baking and as a thickening agent in soups and sauces.
Read Also Poultry Records Keeping Books, Types and Benefits
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Carrot Taproot

1. What is a carrot taproot?
The carrot taproot is the primary root of the carrot plant, which grows downward and stores nutrients.
2. Why are carrot taproots orange?
Carrot taproots are orange due to the high concentration of beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A.
3. How are carrot taproots used in cooking?
Carrot taproots are used in various culinary applications, including salads, soups, stews, and baked goods.
4. Are carrot taproots good for health?
Yes, carrot taproots are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which contribute to overall health and wellness.
5. Can carrot taproots be used in animal feed?
Yes, carrot taproots and their by-products are used in animal feed, providing essential nutrients for livestock.
6. What products can be made from carrot taproots?
Products include fresh carrots, carrot juice, carrot puree, carrot powder, and more.
7. How do carrot taproots contribute to agriculture?
Carrot taproots support agriculture by providing a versatile crop that enhances soil health and offers economic benefits.
8. Are there industrial uses for carrot taproots?
Yes, carrot taproots are used in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food processing industries.
9. How do carrot taproots benefit the environment?
Carrot cultivation improves soil health and supports sustainable agricultural practices.
10. Can carrot taproots be used in organic farming?
Yes, carrot taproots are popular in organic farming due to their adaptability and consumer demand for organic produce.
Read Also Best Organic Fertilizer for Vegetables