The Cauliflower Stigmas: Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products
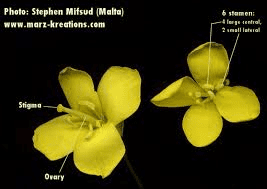
Cauliflower stigmas are an essential part of the cauliflower plant’s reproductive system. The stigma is the receptive tip of the pistil, the female reproductive organ of a flower.
In cauliflower (Brassica oleracea var. botrytis), the reproductive structures, including the stigma, are less prominent because the plant is primarily cultivated for its vegetative parts—the edible curd, which consists of tightly packed, undeveloped flower buds. However, understanding the role of the stigma and other floral components is crucial for both breeding and seed production.
The stigma is located at the top of the pistil and is designed to receive pollen during the process of pollination. In cauliflower, as in other flowering plants, successful pollination is essential for fertilization, seed development, and the continuation of the species. The stigma is typically sticky or feathery, which helps capture pollen grains from the male anthers of the flower or from other flowers via wind or insect pollinators.
Once pollen grains land on the stigma, they germinate, and pollen tubes grow down through the style, a tube-like structure connecting the stigma to the ovary. This process allows the sperm cells to travel from the pollen to the ovules within the ovary, where fertilization occurs. The fertilized ovules develop into seeds, which can be harvested for planting future cauliflower crops.
In cauliflower cultivation, flowering and seed production are usually secondary to the main goal of producing a quality curd. However, for breeding programs and seed production, ensuring successful pollination and fertilization is vital. Understanding the floral biology, including the function of stigmas, helps plant breeders develop new cauliflower varieties with desirable traits, such as disease resistance, improved yield, or specific curd characteristics.
Environmental conditions can significantly influence the reproductive success of cauliflower plants. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and the presence of pollinators affect pollen viability and stigma receptivity. For instance, extreme temperatures can hinder pollen germination or stigma function, reducing fertilization rates and seed set. Managing these conditions through controlled environments or selecting appropriate planting times can enhance reproductive success.
The anatomy of the cauliflower flower, including the stigma, is adapted to its reproductive strategy. Cauliflower flowers are typically small and clustered in inflorescences. Each flower contains both male (stamens) and female (pistil) reproductive organs, making cauliflower a predominantly self-pollinating plant. However, cross-pollination can also occur and is sometimes encouraged in breeding programs to introduce genetic diversity.
For home gardeners and small-scale farmers, understanding the reproductive parts of cauliflower, including the stigma, can improve practices related to seed saving and propagation. Allowing a few plants to flower and produce seeds can provide a sustainable source of seeds for future planting, reducing reliance on commercial seed suppliers.
Cauliflower stigmas, while not as prominent in commercial cultivation focused on curd production, are critical for the plant’s reproductive process. They play a vital role in pollination and fertilization, leading to seed development.
This understanding is essential for breeding programs, seed production, and maintaining genetic diversity within cauliflower crops. By recognizing the importance of stigmas and the conditions that affect their function, cultivators can improve both the quality and sustainability of cauliflower production.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Cauliflower Stigmas

1. Seed Production: The primary role of stigmas in capturing pollen is vital for seed production, ensuring the propagation of cauliflower plants.
2. Plant Breeding: Knowledge of stigma function helps in plant breeding programs, aiming to produce hybrids with desired traits.
3. Pollination Efficiency: Efficient stigma function ensures successful pollination, leading to better crop yields and quality.
4. Hybrid Varieties: Stigmas play a crucial role in creating hybrid varieties through controlled pollination, leading to improved cauliflower strains.
5. Genetic Research: Studying stigmas provides insights into genetic compatibility and fertilization processes, aiding genetic research.
6. Biodiversity: Healthy stigma function supports genetic diversity within cauliflower crops, contributing to overall biodiversity.
7. Crop Improvement: Understanding stigma function can lead to improvements in crop quality, including taste, texture, and nutritional value.
8. Disease Resistance: Breeding programs focusing on stigma health can produce disease-resistant cauliflower varieties.
9. Environmental Adaptation: Knowledge of stigma response to environmental factors helps develop climate-resilient cauliflower varieties.
10. Seed Industry: Stigma function is critical for the commercial seed industry, ensuring the production of high-quality seeds.
11. Agricultural Practices: Farmers can optimize pollination practices by understanding stigma biology, improving overall yield.
12. Ecosystem Services: Stigmas play a role in supporting pollinator species, contributing to ecosystem health.
13. Educational Value: Stigmas serve as a model for teaching plant reproductive biology and pollination mechanisms.
14. Biotechnology: Stigmas are a focus in biotechnological applications, such as genetic modification and tissue culture.
15. Sustainable Farming: Healthy stigma function supports sustainable farming practices by enhancing crop resilience and yield.
16. Food Security: Effective stigma function ensures reliable seed production, contributing to food security.
17. Economic Value: High-quality seeds produced through effective stigma function add economic value to the cauliflower market.
18. Horticultural Practices: Innovations in understanding and manipulating stigmas lead to new horticultural techniques and practices.
Read Also: Mulching: Meaning and Benefits of Mulching
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Cauliflower Stigmas

1. Seeds: The primary product derived from successful pollination involving stigmas, used for planting new crops.
2. Hybrid Seeds: Produced through controlled pollination, offering improved traits and higher yields.
3. Genetic Material: DNA extracted from stigmas for genetic research and breeding programs.
4. Plant Tissue Cultures: Stigmas used in tissue culture techniques to propagate new plants.
5. Seed Oils: Oils extracted from seeds produced through stigma-mediated fertilization for culinary and industrial applications.
6. Nutritional Supplements: Seeds processed into supplements due to their high nutrient content.
7. Biofuels: Seeds and pods used in the production of biofuels.
8. Animal Feed: Residual plant material from stigma processing used as animal feed.
9. Compost: Organic matter from stigmas used to enrich soil as compost.
10. Biodegradable Plastics: Seed by-products processed into biodegradable plastics.
11. Cosmetics: Seed oils and extracts used in cosmetic products for their beneficial properties.
12. Pharmaceuticals: Compounds extracted from seeds used in pharmaceutical applications.
13. Dietary Fibers: Seeds processed into dietary fibers for food products.
14. Agricultural Inputs: By-products used as inputs for organic farming practices.
15. Pest Control: Extracts from stigmas used in natural pest control solutions.
16. Research Tools: Stigmas used as models in scientific research to study plant reproduction.
17. Educational Kits: Stigmas included in educational kits for teaching plant biology and pollination.
Read Also: Rabbit Housing Requirements
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Cauliflower Stigmas

1. What is the function of the cauliflower stigma?
The stigma is the part of the female reproductive organ that captures pollen, enabling fertilization and seed production.
2. How does the stigma contribute to seed production?
The stigma captures pollen grains, which germinate and grow pollen tubes to fertilize the ovules in the ovary, leading to seed development.
3. Can stigmas be used in plant breeding?
Yes, understanding stigma function is crucial for plant breeding to create hybrids with improved traits.
4. What products are derived from cauliflower stigmas?
Products include seeds, hybrid seeds, genetic material, seed oils, nutritional supplements, biofuels, and more.
5. How does stigma health impact agricultural practices?
Healthy stigmas ensure successful pollination, leading to better crop yields and quality, which improves agricultural practices.
6. Are there industrial uses for the products derived from stigmas?
Yes, seeds and their by-products are used in biofuels, biodegradable plastics, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
7. How do stigmas contribute to sustainable agriculture?
Efficient stigma function enhances crop yields and resource use, supporting sustainable agricultural practices.
8. What role do stigmas play in biodiversity preservation?
Healthy stigma function supports genetic diversity within cauliflower crops, contributing to overall biodiversity.
9. Can cauliflower stigmas be used in biotechnology?
Yes, stigmas are a focus in biotechnological applications such as genetic engineering and tissue culture.
10. Why is the cauliflower stigma important for food security?
Effective stigma function ensures reliable seed production, contributing to food security by supporting consistent crop yields.
Read Also: Sustainable Development: Building a Better Future for All