The Maize/Corn Pedicels: Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products
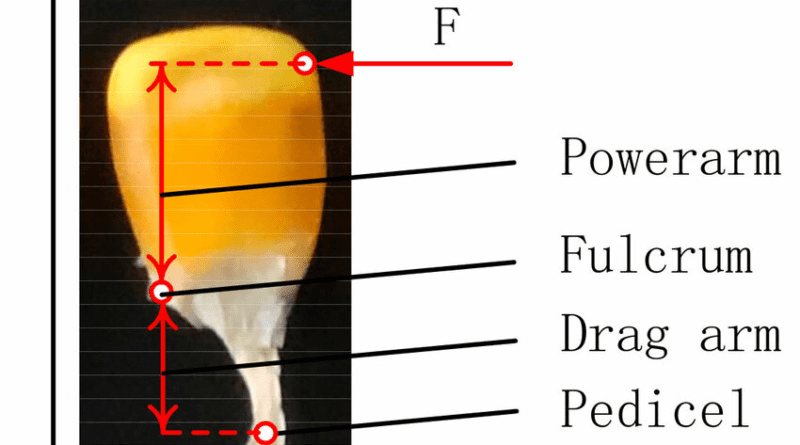
The Maize/Corn Pedicels is the stalk that attaches each kernel to the cob, playing a vital role in nutrient transport and kernel development.
The pedicel of maize is anatomically and physiologically significant. Structurally, it is a short, thick stalk that connects the kernel to the rachis, which is the central axis of the cob. The pedicel is composed of several tissue types, including vascular bundles, parenchyma, and sclerenchyma. The vascular bundles are particularly important because they contain the xylem and phloem, which are responsible for the transport of water, nutrients, and photosynthates between the cob and the kernels.
During the development of maize, the pedicel undergoes significant changes. Initially, it forms as part of the spikelet, a small inflorescence unit that later differentiates into the cob and the kernels. As the kernels develop, the pedicels grow in length and diameter to accommodate the increasing demand for nutrients and water. This growth is driven by the activity of the meristematic cells in the pedicel, which divide and differentiate to form the various tissues.
Functionally, the pedicel is critical for the successful development of the maize kernel. It acts as a conduit for the transport of essential substances. The xylem vessels in the pedicel transport water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the kernels, while the phloem carries photosynthetically produced sugars and other organic compounds from the leaves to the developing kernels. This transport system ensures that the kernels receive the necessary nutrients for growth and maturation.
Moreover, the pedicel also plays a role in the mechanical support of the kernel. The sclerenchyma tissue, composed of thick-walled cells, provides structural strength to the pedicel, helping to support the weight of the kernels as they develop. This mechanical support is crucial, especially as the kernels mature and increase in weight.
Another important aspect of the pedicel is its role in the physiological processes that determine the quality and yield of the maize crop. The efficiency of nutrient and water transport through the pedicel can affect the size, weight, and overall health of the kernels. Researchers have found that variations in pedicel structure and function can lead to differences in kernel size and yield, making it a key focus in maize breeding programs.
In addition to its direct role in kernel development, the pedicel also interacts with various environmental factors. For instance, drought stress can impact the function of the pedicel by reducing the availability of water for transport, leading to smaller kernels and lower yields. Similarly, nutrient deficiencies in the soil can affect the composition and efficiency of the vascular bundles, further influencing kernel development.
In conclusion, the pedicel of maize is a small but vital structure that plays multiple roles in the plant’s growth and development. Its anatomical features, including the vascular bundles and supportive tissues, facilitate the transport of nutrients and water to the developing kernels. This transport system is essential for the proper growth and maturation of the kernels, ultimately affecting the yield and quality of the maize crop. Understanding the structure and function of the maize pedicel can provide valuable insights for improving crop performance and addressing agricultural challenges.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Maize/Corn Pedicels
1. Nutrient Transport: The pedicels are essential for transporting nutrients from the cob to the kernels, ensuring healthy kernel development and higher yields.
2. Structural Support: Pedicels provide structural support to the kernels, maintaining their attachment to the cob, which is crucial for mechanical harvesting.
3. Breeding Programs: Pedicel traits are considered in maize breeding programs aimed at improving kernel size, weight, and yield.
4. Crop Resilience: Robust pedicels can contribute to the plant’s resilience against environmental stresses like wind and heavy rain, reducing crop losses.
5. Water Regulation: Pedicels help regulate water transport to the kernels, which is vital for kernel hydration and development.
6. Nutrient Efficiency: Efficient nutrient transport through the pedicels can enhance the overall nutrient use efficiency of the maize plant, contributing to better growth.
7. Disease Resistance: Healthy pedicels can reduce the risk of disease transmission from the cob to the kernels, protecting the crop yield.
8. Biofuel Production: Maize pedicels, along with other plant parts, can be used in biofuel production, providing a renewable energy source.
9. Animal Feed: Ground pedicels can be included in animal feed, providing additional fiber and nutrients.
10. Compost Material: Pedicels can be composted, enriching the soil with organic matter and nutrients.
11. Industrial Uses: Pedicels can be processed to extract cellulose, which is used in the production of various industrial products like paper and textiles.
12. Carbon Sequestration: Maize pedicels contribute to carbon sequestration, helping mitigate climate change by storing carbon in plant biomass.
13. Soil Improvement: When left in the field after harvest, pedicels decompose and improve soil structure and fertility.
14. Biochar Production: Pedicels can be converted into biochar, which is used as a soil amendment to enhance soil fertility and water retention.
15. Pharmaceutical Uses: Extracts from maize pedicels are studied for potential pharmaceutical applications due to their bioactive compounds.
16. Craft Materials: Dried maize pedicels can be used in traditional crafts and decorations.
17. Mushroom Substrate: Pedicels serve as a substrate for mushroom cultivation, providing a growth medium for various mushroom species.
18. Bioplastic Production: Pedicels are researched as a raw material for bioplastic production, offering a biodegradable alternative to conventional plastics.
Read Also Scrapie in Sheep and Goats: Description, Damages Caused, Control and Preventive Measures
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Maize/Corn Pedicels
1. Bioethanol: Pedicels are fermented to produce bioethanol, a renewable biofuel used as an alternative to gasoline.
2. Animal Feed: Ground pedicels are mixed into livestock feed, providing fiber and nutrients.
3. Cellulose: Extracted from pedicels, cellulose is used in making paper, textiles, and other industrial products.
4. Compost: Pedicels are composted to produce organic fertilizer that enriches soil.
5. Biochar: Pedicels are pyrolyzed to create biochar, used to improve soil fertility and sequester carbon.
6. Mushroom Substrate: Pedicels serve as a substrate for mushroom farming, promoting mushroom growth.
7. Bioplastic: Pedicel-derived cellulose is used in manufacturing biodegradable plastics.
8. Dietary Fiber: Processed pedicels are added to food products as a source of dietary fiber.
9. Organic Mulch: Shredded pedicels are used as mulch in gardening and agriculture to retain soil moisture.
10. Erosion Control: Pedicels are used in erosion control mats to prevent soil erosion.
11. Bio-based Adhesives: Extracts from pedicels are used in making environmentally friendly adhesives.
12. Textiles: Cellulose from pedicels is used to create sustainable textiles.
13. Particleboard: Pedicels are combined with other materials to produce particleboard for construction.
14. Bio-composites: Pedicels are incorporated into bio-composites for manufacturing various products.
15. Soil Amendment: Composted pedicels improve soil structure and fertility.
16. Craft Items: Dried pedicels are used in crafting traditional and decorative items.
17. Pharmaceutical Extracts: Bioactive compounds from pedicels are researched for medicinal uses.
Read Also Management of Breeding Stock in Sheep and Goats
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Maize/Corn Pedicels
1. What are maize/corn pedicels? Maize/corn pedicels are the small stalks that attach each kernel to the cob, facilitating nutrient and water transport.
2. Why are maize/corn pedicels important? They play a crucial role in nutrient transport, structural support, and overall kernel development, impacting yield and quality.
3. Can maize/corn pedicels be used in animal feed? Yes, ground pedicels are included in animal feed as a source of fiber and nutrients.
4. How do maize/corn pedicels contribute to biofuel production? Pedicels can be fermented to produce bioethanol, a renewable energy source.
5. Are there industrial uses for maize/corn pedicels? Yes, they are used to extract cellulose for paper, textiles, and bioplastic production.
6. Can maize/corn pedicels improve soil health? Pedicels can be composted or converted into biochar, both of which enhance soil fertility and structure.
7. What is the role of maize/corn pedicels in crop resilience? They help the plant withstand environmental stresses like wind and heavy rain by providing structural support.
8. Are maize/corn pedicels used in any pharmaceutical applications? Extracts from pedicels are being studied for potential medicinal uses due to their bioactive compounds.
9. How do maize/corn pedicels affect kernel quality? Efficient nutrient transport through pedicels ensures healthy kernel development, impacting size, weight, and overall quality.
10. What are the environmental benefits of maize/corn pedicels? They contribute to carbon sequestration, improve soil health, and can be used to produce eco-friendly products like bioplastics.
Read Also How to Make an Avocado Tree Bear Fruit