The Okra Ovary: Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products
The okra ovary is a pivotal part of the reproductive anatomy of the Abelmoschus esculentus plant, commonly known as okra. It is within the ovary that the transformation from flower to fruit, specifically the okra pod, takes place.
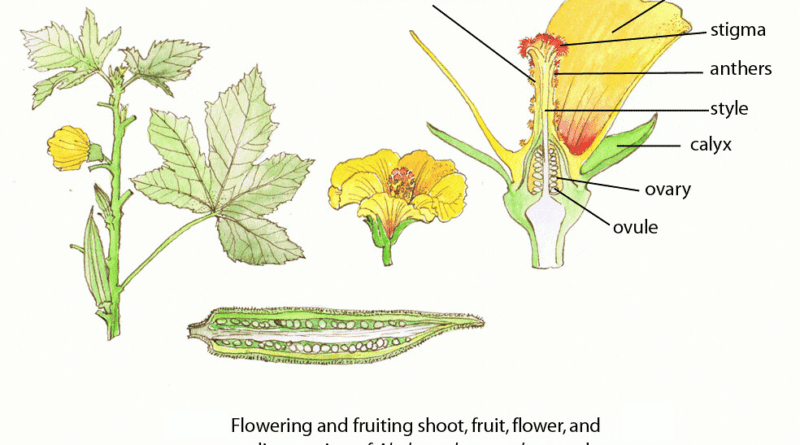
Botanically, the ovary is the enlarged basal portion of the female reproductive organ of the flower, known as the pistil. In the case of okra, each flower contains a single pistil composed of three distinct parts: the stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is the receptive surface that receives pollen, the style is the slender tube connecting the stigma to the ovary, and the ovary is the swollen base where ovules develop and eventually mature into seeds.
After successful pollination and fertilization, the okra ovary undergoes significant changes. The fertilized ovule within the ovary develops into a seed, while the ovary itself expands and matures into the characteristic elongated pod that is harvested for consumption. Okra pods are typically green and cylindrical, with a ridged texture and tapering ends. They contain multiple seeds embedded in a mucilaginous pulp, which is a defining characteristic of okra and contributes to its culinary appeal.
Culturally and culinarily, the okra ovary (or pod) is highly valued for its versatility in cooking. It is a staple ingredient in various cuisines around the world, appreciated for its unique texture and ability to thicken soups and stews. Okra pods can be prepared in numerous ways, including frying, steaming, sautéing, and adding to dishes like gumbo, curries, and salads. They are prized not only for their taste but also for their nutritional benefits, as they are rich in vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber.
In agriculture, the development of the okra ovary into mature pods is a key stage in the plant’s life cycle. Farmers monitor the growth and maturation of pods closely to determine the optimal time for harvest, ensuring the pods are tender and flavorful. Harvesting at the right stage also helps maintain the plant’s productivity and ensures a continuous supply of fresh okra throughout the growing season.
The okra ovary represents a critical link between the reproductive biology of the plant and its culinary significance. It exemplifies the transformation from flower to fruit, showcasing nature’s process of seed production and providing a nutritious and versatile ingredient for human consumption.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Okra Ovary

1. Culinary Use: The ovary of the okra plant matures into the okra pod, widely used in cooking for dishes like gumbo and stews.
2. Nutritional Supplements: Okra ovaries are rich in vitamins and minerals, making them useful in dietary supplements.
3. Herbal Medicine: Okra ovaries are used in traditional medicine for their potential to aid digestion and manage blood sugar levels.
4. Animal Feed: Fresh or dried okra ovaries can be used as feed for livestock, providing essential nutrients.
5. Organic Fertilizer: Okra ovaries can be composted to create organic fertilizer, improving soil health.
6. Biofuel Production: The fibrous nature of okra ovaries makes them suitable for biofuel production, such as biogas.
7. Mulch: Shredded okra ovaries can be used as mulch in gardens to retain soil moisture and prevent weed growth.
8. Pickling: Okra ovaries are commonly pickled, creating a popular and tasty snack.
9. Food Thickener: The mucilage from okra ovaries can be used as a natural thickener in soups and sauces.
10. Skin Care: Extracts from okra ovaries are used in skincare products for their moisturizing and anti-aging properties.
11. Natural Pesticide: Extracts from okra ovaries can be used as a natural pesticide, helping control pests without harmful chemicals.
12. Green Manure: Okra ovaries can be used as green manure, enriching the soil with nutrients when plowed back into the field.
13. Medicinal Extracts: Extracts from okra ovaries are used in traditional medicine for their health benefits.
14. Composting: Okra ovaries can be composted to create rich, nutrient-dense compost.
15. Erosion Control: When used as mulch or in erosion control mats, okra ovaries help prevent soil erosion.
16. Craft Materials: Dried okra ovaries can be used in various crafts, such as making decorative items.
17. Soil Amendment: Okra ovaries can be added to the soil to improve its structure and nutrient content.
18. Biomass Energy: Okra ovaries can be used as biomass for generating electricity, providing a sustainable energy source.
Read Also: Honey Bees: A Closer Look
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Okra Ovary

1. Okra Pods: The mature ovaries, widely used in cooking for dishes like gumbo, stews, and stir-fries.
2. Pickled Okra: Okra ovaries pickled in vinegar and spices, creating a popular snack and side dish.
3. Herbal Tea: Dried okra ovaries brewed to make a nutritious herbal tea with potential health benefits.
4. Nutritional Supplements: Powdered okra ovaries used in dietary supplements for their rich vitamin and mineral content.
5. Food Thickener: Mucilage extracted from okra ovaries used as a natural thickener in soups and sauces.
6. Organic Fertilizer: Okra ovaries composted to create organic fertilizer, enhancing soil fertility.
7. Animal Feed: Fresh or dried ovaries processed into feed for livestock, providing essential nutrients.
8. Biofuel: Okra ovaries used in anaerobic digestion to produce biogas, a renewable energy source.
9. Mulch: Shredded okra ovaries used as mulch to retain soil moisture and suppress weeds.
10. Cosmetic Ingredients: Extracts from okra ovaries used in skincare products for their moisturizing effects.
11. Natural Pesticide: Extracts from okra ovaries used as a natural pesticide to control pests.
12. Green Manure: Okra ovaries plowed into the soil to add nutrients and improve soil structure.
13. Craft Materials: Dried ovaries used in making decorative items and eco-friendly packaging.
14. Compost: Okra ovaries composted to create nutrient-rich compost for gardening.
15. Soil Amendment: Ovaries added to the soil to improve its structure and nutrient content.
16. Biomass Pellets: Okra ovaries compressed into pellets for use as a sustainable fuel source.
17. Erosion Control Mats: Ovaries woven into mats used to control soil erosion.
Read Also: How Do Honey Bees Reproduce
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Okra Ovary

1. What is the okra ovary?
The okra ovary is the part of the okra plant that develops into the edible okra pod.
2. Can you eat the okra ovary?
Yes, the ovary matures into the okra pod, which is widely consumed in various dishes.
3. How are okra ovaries used in cooking?
Okra ovaries, or pods, are used in soups, stews, stir-fries, and can be pickled.
4. What are the medicinal uses of okra ovaries?
Okra ovaries are used in traditional medicine to aid digestion and manage blood sugar levels.
5. Can okra ovaries be used in skincare products?
Yes, extracts from okra ovaries are used in skincare products for their moisturizing and anti-aging properties.
6. How are okra ovaries used as animal feed?
Okra ovaries can be fed fresh or dried to livestock, providing essential nutrients and fiber.
7. Can okra ovaries be used in composting?
Yes, okra ovaries can be composted to create organic fertilizer, improving soil health and fertility.
8. How are okra ovaries used as a natural pesticide?
Extracts from okra ovaries can be used to control pests naturally without harmful chemicals.
9. What is okra mucilage?
Okra mucilage is a gelatinous substance extracted from okra ovaries, used as a natural thickener in foods.
10. How do okra ovaries contribute to biofuel production?
Okra ovaries can be used in anaerobic digestion to produce biogas, a renewable energy source.
Read Also: Waste To Fertilizer: What You Need to Know