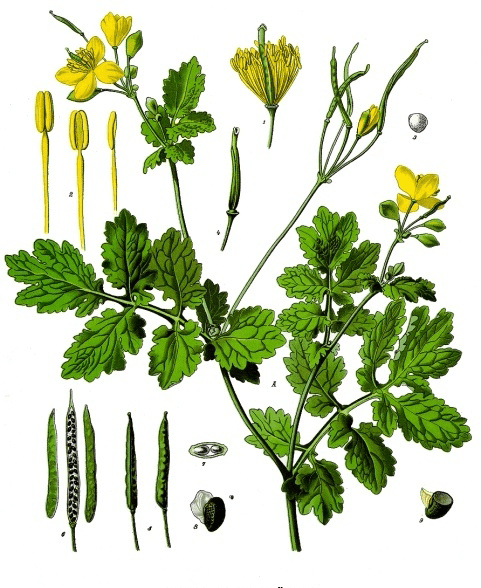
Chelidonium majus, commonly known as greater celandine, is a perennial herbaceous plant that belongs to the Papaveraceae family. This plant is known for its distinctive appearance and vibrant yellow sap, which has earned it several common names, including swallowwort and devil’s milk.
Greater celandine typically reaches a height of 30 to 120 centimeters (12 to 47 inches). The leaves of Chelidonium majus are deeply lobed and pinnately compound, giving them a fern-like appearance. They are bright green and can grow up to 30 centimeters (12 inches) in length.
The plant produces bright yellow flowers with four petals, each measuring around 1 to 2 centimeters (0.4 to 0.8 inches) in diameter. The flowers have a delicate appearance and are borne in clusters.
After flowering, Chelidonium majus forms long, slender seed pods that contain small seeds. These pods resemble elongated capsules and split open when mature to release the seeds.
Greater celandine is native to Europe and parts of Asia, but it has naturalized in various regions around the world. It thrives in temperate climates and is often found in disturbed areas, such as roadsides, gardens, and waste places. This plant has adapted well to a range of soil types and can grow in both sunny and partially shaded environments.
Perhaps the most distinctive feature of Chelidonium majus is its bright yellow, latex-like sap. When the stem or leaves are cut, this sap exudes, and it has historically been used for various purposes, including treating skin issues. The lobed and pinnately compound leaves of greater celandine make it easily recognizable, especially during its growing season.
Chelidonium majus is a perennial plant, which means it can live for several years. It typically flowers in late spring to early summer, producing its characteristic yellow blooms. After flowering and seed production, the plant may die back in the fall and winter, only to regrow from its root system in the following spring.
Read Also: Causes of Egg Production Reduction in Poultry Farms and Ways to prevent them
The Medicinal Health Benefits of Chelidonium majus (Greater Celandine)
1. Liver Health: Chelidonium majus is known for its hepatoprotective properties, supporting liver health and aiding in detoxification processes.
2. Jaundice Treatment: It has been traditionally used to alleviate symptoms of jaundice due to its potential to improve liver function.
3. Skin Conditions: The plant’s sap can be applied topically to treat skin conditions like warts, eczema, and fungal infections.
4. Antispasmodic: Chelidonium majus may help relax muscles and alleviate muscle spasms.
5. Respiratory Health: It has been used to address respiratory issues such as coughs, bronchitis, and asthma.
6. Analgesic Properties: The herb may offer pain relief, making it useful for managing mild pain and discomfort.
7. Anti-Inflammatory: Chelidonium majus has anti-inflammatory effects, potentially beneficial for inflammatory conditions.
8. Antioxidant: Its constituents may have antioxidant properties, helping to protect cells from oxidative stress.
9. Antimicrobial: The plant may have antimicrobial properties, aiding in the management of infections.
10. Immune Support: It could help boost the immune system, increasing the body’s resistance to illnesses.
11. Digestive Aid: Chelidonium majus may improve digestion, reducing issues like indigestion and bloating.
12. Blood Pressure: Some studies suggest it may have a mild hypotensive effect, potentially assisting in blood pressure management.
13. Analgesic: It has been used traditionally to relieve pain associated with conditions like arthritis.
14. Wound Healing: The sap may promote wound healing, making it useful for minor cuts and abrasions.
Read Also: Poultry Disease Prevention and Management
The Methods of Usage to Achieve the Provided Health Benefits of Chelidonium majus (Greater Celandine)
1. Herbal Infusion: To make an herbal infusion, steep dried Chelidonium majus leaves or roots in hot water for about 10-15 minutes. This infusion can be consumed as a tea to support digestive health and relieve mild respiratory discomfort.
2. Tincture: Chelidonium majus tinctures are available and can be taken orally. Follow the recommended dosage instructions provided on the product’s label or consult a healthcare professional.
3. Topical Application: The sap or an ointment made from Chelidonium majus can be applied topically to treat skin conditions such as warts, eczema, and fungal infections. Apply a small amount to the affected area and monitor for any adverse reactions.
4. Poultice: Create a poultice by mashing fresh Chelidonium majus leaves and applying them directly to the affected area, such as a wound or skin irritation. Secure the poultice with a bandage and replace it as needed.
5. Inhalation: Inhaling the steam from an infusion of Chelidonium majus can help alleviate respiratory issues. Pour hot water over the dried herb, cover your head with a towel, and inhale the steam for relief from congestion or coughs.
6. Capsules or Tablets: Chelidonium majus supplements in capsule or tablet form are available for oral consumption. Follow the recommended dosage on the product’s packaging or consult a healthcare provider.
7. Salve: Create a salve by combining Chelidonium majus sap or extract with a carrier oil or beeswax. Apply this salve topically to soothe skin irritations or wounds.
8. Herbal Bath: Infuse a warm bath with Chelidonium majus leaves or extract. Soak in the herbal bath to relieve muscle tension or skin issues.
The Side Effects of Using Chelidonium majus Medicinal Plant
1. Gastrointestinal Distress: Chelidonium majus may cause gastrointestinal discomfort, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea in some individuals.
2. Allergic Reactions: Allergic reactions to Chelidonium majus are possible and may manifest as skin rashes, itching, or swelling. Individuals with known allergies to plants in the Papaveraceae family should exercise caution.
3. Photosensitivity: Some individuals may become more sensitive to sunlight (photosensitivity) when using Chelidonium majus, potentially leading to sunburn or skin reactions upon sun exposure.
4. Liver Toxicity: In rare cases, excessive or prolonged use of Chelidonium majus may lead to liver toxicity. This can result in jaundice, elevated liver enzymes, and other liver-related issues.
5. Stomach Ulcers: Chelidonium majus may exacerbate stomach ulcers or gastritis in some people due to its potential irritant effect on the gastrointestinal lining.
6. Dizziness and Headaches: A few individuals have reported experiencing dizziness and headaches as side effects when using Chelidonium majus.
7. Interaction with Medications: Chelidonium majus may interact with certain medications, such as blood thinners, antiplatelet drugs, and medications that affect the liver. Consult a healthcare professional before use if you are taking any medications.
8. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid Chelidonium majus due to the lack of sufficient safety data. It is not recommended for use during these periods.
Nutritional Value of Chelidonium majus (Greater Celandine)

1. Alkaloids: Greater celandine contains alkaloids like chelidonine and sanguinarine, which contribute to its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, used traditionally for medicinal purposes.
2. Flavonoids: These antioxidant compounds, such as quercetin, help neutralize free radicals, supporting cellular health and reducing oxidative stress.
3. Phenolic Compounds: Phenolic acids in the plant provide antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits, potentially protecting against chronic diseases.
4. Saponins: These compounds may enhance immune function and have potential cholesterol-lowering effects, though present in small amounts.
5. Terpenoids: Volatile terpenoids contribute to antimicrobial activity, supporting traditional uses for skin infections and wound healing.
6. Vitamin C: The aerial parts contain trace amounts of vitamin C, aiding immunity and collagen synthesis, though not a primary dietary source.
7. Minerals: Includes minerals like potassium and calcium, supporting electrolyte balance and bone health in herbal preparations.
8. Carbohydrates: The plant provides minimal carbohydrates, used for energy in medicinal decoctions rather than as a staple food.
9. Amino Acids: Trace amino acids support protein synthesis, contributing to the plant’s nutritional profile in traditional remedies.
10. Coumarins: These compounds offer anticoagulant and anti-inflammatory properties, potentially aiding blood circulation and reducing swelling.
Chelidonium majus is primarily a medicinal herb rather than a food source, valued in traditional European and Asian medicine for its bioactive compounds, typically used in teas, tinctures, or topical applications to support health, but caution is needed due to potential toxicity.
Scientific Evidence and Case Studies on Chelidonium majus
1. Biswas et al. (2011): This study investigated the hepatoprotective effects of Chelidonium majus ethanolic extract in carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage in rats, showing reduced liver enzyme levels and oxidative stress, supporting its traditional use for liver disorders (Biswas, S. J., et al., 2011).
2. Zielińska et al. (2018): Researchers evaluated the antimicrobial activity of Chelidonium majus extracts, finding strong inhibition against Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans due to alkaloids like sanguinarine, validating its use for infections (Zielińska, S., et al., 2018).
3. Kujawska et al. (2017): This ethnobotanical review documented Chelidonium majus’s use in Eastern European folk medicine for warts and skin conditions, with alkaloids like chelidonine showing cytotoxic effects on HPV-infected cells in vitro, supporting topical applications (Kujawska, M., et al., 2017).
Frequently Asked Questions About Chelidonium majus
1. What is Chelidonium majus used for?
It is used in traditional medicine for liver and gallbladder issues, skin conditions like warts, and as an antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory remedy.
2. Is Chelidonium majus safe to consume?
Small amounts in teas or tinctures may be safe under medical guidance, but it is toxic in high doses, potentially causing liver damage or nausea.
3. Can Chelidonium majus treat warts?
Yes, its latex sap is traditionally applied topically to remove warts, with studies supporting its cytotoxic effects on HPV-infected cells.
4. What are the active compounds in Chelidonium majus?
Key components include alkaloids (chelidonine, sanguinarine), flavonoids, phenolics, saponins, and coumarins.
5. How is Chelidonium majus prepared?
Aerial parts or roots are dried for teas or tinctures; fresh sap is used topically for skin issues, with caution.
6. Where does Chelidonium majus grow?
Native to Europe and western Asia, it thrives in temperate regions, often in disturbed soils, gardens, or near human settlements.
7. Are there side effects of Chelidonium majus?
Possible side effects include nausea, liver toxicity, or skin irritation; avoid during pregnancy or with liver conditions.
8. Can Chelidonium majus support liver health?
Studies suggest its extracts protect against chemical-induced liver damage, supporting traditional uses for liver and gallbladder health.
Do you have any questions, suggestions, or contributions? If so, please feel free to use the comment box below to share your thoughts. We also encourage you to kindly share this information with others who might benefit from it. Since we can’t reach everyone at once, we truly appreciate your help in spreading the word. Thank you very much for your support and for sharing!
Disclaimer: This article is for educational and informational purposes only. The health benefits described are based on scientific research and traditional knowledge. They are not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a healthcare professional before using any herb or natural remedy for medical purposes.
Read Also: 7 Amazing Health Benefits of Cherries

