19 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Fraxinus (Ash)
Fraxinus, commonly known as ash, is a versatile and valuable tree with a rich history of medicinal use. This article will explore the various health benefits of Fraxinus, shedding light on its botanical description, traditional uses, and modern applications in healthcare.
The Botanical Description of Fraxinus
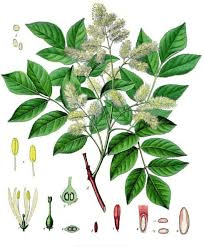
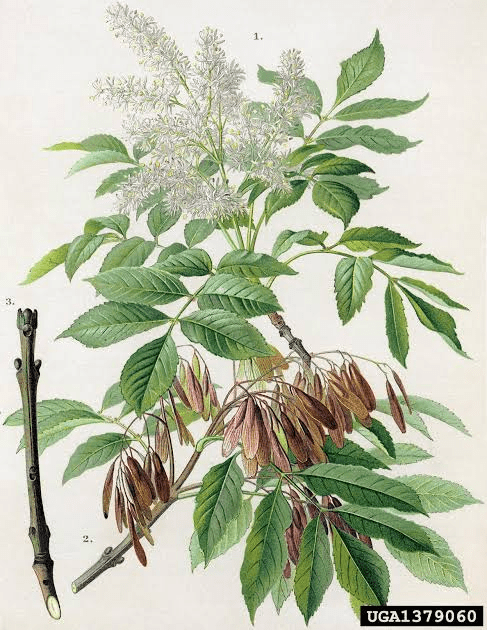
1. Life: Fraxinus trees are deciduous, meaning they shed their leaves annually. They belong to the Oleaceae family and are known for their tall, slender stature.
Fraxinus trees can reach impressive heights, often growing between 50 to 80 feet in height. They are characterized by their straight trunks and relatively narrow crowns. The tree’s leaves are typically pinnately compound, with several leaflets arranged along a central stem. These leaflets are usually serrated or toothed along the edges, giving the leaves a distinct appearance.
2. Leaves: The leaves of Fraxinus trees are pinnately compound, as mentioned earlier. Each leaf is composed of multiple leaflets, usually ranging from 5 to 11 leaflets per leaf. The leaflets are arranged in an opposite fashion, meaning they grow in pairs along the stem. The leaflets are typically lance-shaped and have serrated margins.
3. Flowers: Fraxinus trees produce small, inconspicuous flowers that are typically green or purple in color. These flowers are often arranged in clusters and appear in the spring before the leaves fully develop. The flowers are typically unisexual, with some trees bearing male flowers and others bearing female flowers. The wind plays a crucial role in pollinating these trees.
4. Fruits: The fruit of the Fraxinus tree is a distinctive winged seed commonly referred to as a “samara.” These samaras have a single seed enclosed in a winged structure, which aids in their dispersal by wind. The seeds are often flat and oblong, making them well-suited for wind dispersal. They are also a vital food source for various wildlife species.
5. Bark: The bark of Fraxinus trees is usually grayish-brown and develops distinctive diamond-shaped ridges as the tree matures. The bark’s appearance can vary slightly between different species of Fraxinus, but it generally has a rough texture and provides protection to the tree’s inner layers.
The Geographic Distribution of Fraxinus
1. Native Range: Fraxinus is a genus of trees that is widely distributed across the Northern Hemisphere. It is primarily native to temperate regions of Europe, Asia, and North America. Different species of Fraxinus have adapted to various climatic conditions, allowing them to thrive in diverse geographic areas.
2. North America: In North America, Fraxinus species are commonly found throughout the United States and Canada. Notable species include the White Ash (Fraxinus americana) and the Green Ash (Fraxinus pennsylvanica). They can be found in a variety of habitats, from forests to wetlands.
3. Europe: In Europe, various Fraxinus species are native to different countries. The European Ash (Fraxinus excelsior) is one of the most well-known and widespread species. It can be found in woodlands, hedgerows, and along riverbanks across Europe.
4. Asia: Fraxinus species are also found in parts of Asia, particularly in countries like China, Japan, and Korea. The Chinese Ash (Fraxinus chinensis) is an example of a species native to China.
5. Naturalized Range: Some Fraxinus species have been introduced to regions outside their native range and have become naturalized. This includes the introduction of European Ash to North America and other parts of the world.
The Chemical Composition of Fraxinus
1. Flavonoids: Fraxinus species contain various flavonoids, which are known for their antioxidant properties. These compounds help protect the tree from oxidative stress and have potential health benefits when consumed.
2. Phenolic Compounds: Phenolic compounds, such as phenolic acids and lignans, are present in Fraxinus. They contribute to the tree’s defense mechanisms and may have anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties.
3. Triterpenoids: Some Fraxinus species produce triterpenoids, which have been studied for their potential anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory effects. These compounds are found in the bark and leaves.
4. Alkaloids: In certain species, alkaloids have been identified. These compounds can have diverse biological activities, and their presence may vary among different Fraxinus species.
5. Oleuropein: Oleuropein, a compound also found in olive trees, has been detected in Fraxinus leaves. It has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and may contribute to the tree’s medicinal uses.
The Harvesting and Processing of Fraxinus
1. Harvesting: The harvesting of Fraxinus trees typically involves cutting down mature trees or selectively pruning branches. In sustainable forestry practices, only a portion of the trees in a stand are harvested to ensure the population remains healthy.
2. Processing: Once harvested, Fraxinus wood is processed for various purposes. It is commonly used in the production of furniture, flooring, and cabinetry due to its attractive grain patterns and durability.
3. Medicinal Use: For medicinal purposes, the bark and leaves of Fraxinus trees are collected. These plant parts are dried and processed to create herbal remedies and supplements. Extraction methods may vary depending on the intended use and desired compounds.
4. Environmental Considerations: Sustainable harvesting and processing practices are essential to protect Fraxinus populations and their ecosystems. Responsible forestry management and adherence to regulations are crucial to prevent over-exploitation and habitat destruction.
5. Commercial Products: Fraxinus-based products, such as herbal teas, supplements, and topical treatments, are available in the market. Quality control and adherence to safety standards are essential in the manufacturing of such products to ensure their efficacy and safety for consumers.
The Medicinal Health Benefits Of Fraxinus (Ash)
Fraxinus, commonly known as ash, offers a range of medicinal health benefits that have been appreciated for centuries. Here are 19 of its notable advantages:
1. Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Ash has anti-inflammatory effects, making it valuable for conditions like arthritis and joint pain.
2. Analgesic Effects: It can act as a natural pain reliever, easing discomfort associated with various ailments.
3. Antioxidant Rich: Ash is rich in antioxidants, which help combat free radicals and protect cells from damage.
4. Immune Boosting: Some compounds in ash may support the immune system, aiding in illness prevention.
5. Diuretic Action: It can promote urine production, aiding in detoxification and fluid balance.
6. Gastrointestinal Health: Ash may help soothe digestive issues like indigestion and heartburn.
7. Respiratory Relief: It has been used to alleviate respiratory conditions, including coughs and bronchitis.
8. Weight Management: Some studies suggest ash may aid in weight loss efforts.
9. Liver Health: Ash has been traditionally used to support liver function and detoxification.
10. Anti-Bacterial Properties: It may possess antibacterial properties, aiding in the management of infections.
11. Anti-Viral Effects: Some compounds in ash may help combat certain viral infections.
12. Skin Health: Ash extracts may be used topically to soothe skin conditions like eczema.
13. Anti-Diabetic Potential: Research indicates it may help regulate blood sugar levels.
14. Anti-Cancer Properties: Some studies suggest ash may have anti-cancer properties, although more research is needed.
15. Cardiovascular Support: It may contribute to heart health by lowering blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
16. Anti-Anxiety Effects: Ash may have calming properties, benefiting individuals dealing with anxiety.
17. Cognitive Enhancement: Some compounds may support cognitive function and memory.
18. Anti-Arthritic Benefits: Ash has been used to alleviate symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
19. Anti-Allergic Effects: It may help reduce allergic reactions and symptoms.
The Methods of Usage to Achieve the Provided Health Benefits Of Fraxinus (Ash)
To harness the health benefits of Fraxinus, various methods of usage can be employed. Here are 11 common approaches:
1. Herbal Teas: Prepare ash leaf or bark tea by steeping dried plant parts in hot water.
2. Tinctures: Alcohol-based extracts are available for precise dosing.
3. Capsules: Ash supplements come in capsule form for convenient consumption.
4. Topical Applications: Ash extracts can be applied to the skin for conditions like eczema or joint pain.
5. Decoctions: Boil ash plant parts to make concentrated liquid extracts.
6. Poultices: Create a paste using ash plant material for external applications.
7. Infused Oils: Soak ash leaves or bark in carrier oils for massage or skin care.
8. Inhalation: Inhale steam from ash-infused water to alleviate respiratory issues.
9. Dietary Inclusion: Include ash leaves or seeds in culinary preparations.
10. Ash Bark Chewing: Chewing ash bark has been used traditionally for oral health.
11. Ash Bath: Add ash-infused water to baths for skin and muscle relaxation.
The Side Effects Of Using Fraxinus Medicinal Plant
While Fraxinus offers numerous health benefits, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects. Here are 10 side effects associated with its use:
1. Gastrointestinal Upset: Some individuals may experience stomach discomfort when using ash.
2. Allergic Reactions: Allergic responses, such as skin rashes or itching, can occur in sensitive individuals.
3. Diarrhea: Excessive consumption of ash may lead to diarrhea.
4. Nausea: Some people may feel nauseous after ingesting ash-based products.
5. Dizziness: In rare cases, ash usage may cause dizziness or lightheadedness.
6. Headaches: Headaches can occur as a side effect of ash consumption.
7. Kidney Issues: Prolonged or excessive use of ash can impact kidney function.
8. Blood Sugar Changes: Individuals with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar levels when using ash.
9. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Ash usage is not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women due to potential risks.
10. Drug Interactions: Ash may interact with certain medications, so consult a healthcare provider before use, especially if taking other medications.
Read Also: 15 Medicinal Health Benefits of Barringtonia Macrostachya (Powder-puff Mangrove)
The Scientific Research and Studies of Fraxinus
Scientific research and studies on Fraxinus have uncovered various aspects of its properties and potential benefits. Here are 10 key findings from scientific investigations:
1. Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Research has demonstrated the anti-inflammatory properties of compounds found in Fraxinus, particularly in the context of arthritis and inflammatory diseases.
2. Antioxidant Activity: Fraxinus extracts have shown strong antioxidant activity, which can help protect cells from oxidative damage.
3. Anti-Diabetic Potential: Some studies suggest that Fraxinus may help regulate blood sugar levels, making it a potential aid for individuals with diabetes.
4. Anti-Cancer Properties: Preliminary research has explored the potential anti-cancer effects of certain compounds in Fraxinus, although more studies are needed.
5. Analgesic Effects: Fraxinus has been studied for its pain-relieving properties, with promising results for conditions like osteoarthritis.
6. Immune Modulation: Some compounds in Fraxinus may modulate the immune system, which could have implications for autoimmune diseases.
7. Antiviral Activity: Research has examined the antiviral potential of Fraxinus extracts, particularly in the context of viral infections.
8. Cardiovascular Benefits: Studies suggest that Fraxinus may contribute to heart health by lowering blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
9. Neuroprotective Effects: Research on animal models has indicated that certain Fraxinus compounds may have neuroprotective properties.
10. Wound Healing: Topical applications of Fraxinus extracts have been studied for their potential in wound healing and skin conditions.
The Safety Precautions and Recommendations In Using Fraxinus Medicinal Plant
When using Fraxinus as a medicinal plant, it’s essential to take safety precautions and follow recommendations to ensure a positive and safe experience. Here are 12 important precautions and recommendations:
1. Consult a Healthcare Provider: Before using Fraxinus for medicinal purposes, consult with a healthcare provider, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
2. Dosage: Follow recommended dosages provided on product labels or by a qualified herbalist to avoid overconsumption.
3. Allergies: Be aware of potential allergies to Fraxinus or related plants, and discontinue use if you experience allergic reactions.
4. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Avoid using Fraxinus during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as its safety during these periods is not well-established.
5. Children: Keep Fraxinus products out of reach of children, as they may be more sensitive to its effects.
6. Drug Interactions: Be cautious if you are taking medications, as Fraxinus may interact with certain drugs. Discuss potential interactions with your healthcare provider.
7. Side Effects: Monitor for any side effects, such as gastrointestinal discomfort, and discontinue use if they occur.
8. Quality Control: Purchase Fraxinus products from reputable sources to ensure quality and purity.
9. Long-Term Use: Avoid prolonged or excessive use of Fraxinus without professional guidance.
10. Topical Use: Perform a patch test when applying Fraxinus extracts topically to check for skin sensitivity.
11. Safe Storage: Store Fraxinus products in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
12. Withdrawal: If you decide to stop using Fraxinus products, do so gradually to minimize potential withdrawal effects.
FAQs About Fraxinus Medicinal Plant
Here are 20 frequently asked questions about Fraxinus as a medicinal plant, along with informative answers:
1. What is Fraxinus?
Fraxinus is a genus of trees commonly known as ash, used for various medicinal purposes.
2. What are the health benefits of Fraxinus?
Fraxinus offers benefits such as anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, pain relief, and potential support for various health conditions.
3. How can I use Fraxinus for health benefits?
Fraxinus can be consumed as tea, supplements, or used topically in various forms.
4. Is Fraxinus safe for long-term use?
Long-term use should be supervised by a healthcare provider to ensure safety.
5. Are there any side effects of using Fraxinus?
Possible side effects include gastrointestinal upset and allergic reactions.
6. Can Fraxinus be used during pregnancy?
It’s best to avoid using Fraxinus during pregnancy due to limited safety data.
7. Does Fraxinus interact with medications?
Fraxinus may interact with certain medications; consult a healthcare provider if you are taking drugs.
8. What precautions should I take when using Fraxinus topically?
Perform a patch test to check for skin sensitivity before applying Fraxinus extracts.
9. Can children use Fraxinus products?
Keep Fraxinus products out of reach of children, as they may be more sensitive to its effects.
10. Where can I purchase high-quality Fraxinus products?
Look for reputable herbal stores or consult a qualified herbalist.
11. How does Fraxinus taste when brewed as tea?
Fraxinus tea typically has a slightly bitter and earthy taste.
12. Can I combine Fraxinus with other herbs for enhanced benefits?
Yes, but consult an herbalist for guidance on safe combinations.
13. Is Fraxinus effective for arthritis pain?
Fraxinus has been traditionally used for arthritis pain, but individual results may vary.
14. What research supports the use of Fraxinus for diabetes management?
Some studies suggest Fraxinus may help regulate blood sugar levels, but more research is needed.
15. Are there any known drug interactions with Fraxinus?
Fraxinus may interact with anticoagulants and medications for blood pressure or diabetes.
16. Can I use Fraxinus for skin conditions like eczema?
Topical applications of Fraxinus extracts have been explored for skin conditions, but consult a dermatologist for guidance.
17. Are there any age restrictions for using Fraxinus products?
While generally safe for adults, consult a pediatrician before giving Fraxinus products to children.
18. How should I store Fraxinus products?
Store them in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight to maintain quality.
19. Can Fraxinus be used to alleviate respiratory conditions?
Fraxinus has been used traditionally to alleviate respiratory issues like coughs and bronchitis.
20. Is Fraxinus recommended for weight loss?
Some studies suggest it may aid in weight management, but a balanced diet and exercise are essential for sustainable weight loss.
Read Also: Benefits of Automated Farming









