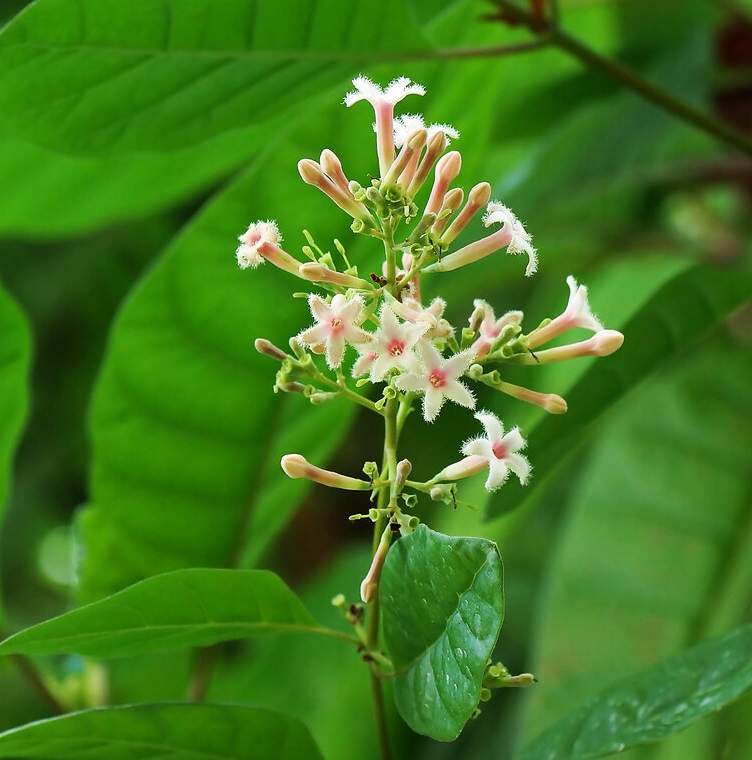
Cinchona officinalis, commonly known as Peruvian bark, is a tree native to the Andean regions of South America, particularly Peru and Ecuador. Celebrated for its historical significance and pharmacological properties, this evergreen tree belongs to the Rubiaceae family and is renowned as the primary source of quinine, a crucial compound in the treatment of malaria.
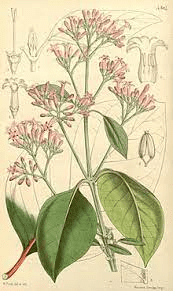
The Cinchona tree stands as an elegant specimen with glossy, dark green leaves and fragrant, tubular flowers that range in color from white to pink. Its bark, however, is the most prized part, historically sought after for its potent medicinal qualities.
The bark contains alkaloids, with quinine being the most notable. Quinine has been a vital component in the treatment of malaria, a disease caused by the Plasmodium parasite and transmitted through the bite of infected mosquitoes.
Peruvian bark’s association with malaria treatment has deep historical roots. Indigenous peoples of South America were the first to use the bark for its medicinal properties, and its knowledge was later transmitted to European colonizers in the 17th century. The use of Peruvian bark revolutionized the treatment of malaria, providing a more effective remedy compared to previous methods.
The bark of Cinchona officinalis undergoes a meticulous harvesting process to extract its medicinal compounds. After careful removal of the bark, it is dried and then ground into a powder for medicinal preparations. While quinine has been a cornerstone in malaria treatment, its application extends to other medical uses, such as alleviating symptoms of fever and muscle cramps.
Despite the development of synthetic antimalarial drugs, Cinchona officinalis remains relevant in the pharmaceutical industry. The bark’s natural properties and historical significance contribute to its continued cultivation and utilization in various regions, promoting both its cultural importance and ongoing role in global healthcare.
Cinchona officinalis stands as a botanical testament to the intersection of traditional medicine, historical exploration, and modern pharmacology, embodying the dynamic relationship between nature and human health.
The Botanical Description of Cinchona officinalis
1. Evergreen Tree: Cinchona officinalis is an evergreen tree belonging to the Rubiaceae family. It is characterized by its tall and straight stature, reaching heights of up to 15 meters.
2. Bark Features: The tree’s bark is a defining characteristic. It is smooth when young, gradually becoming rougher and fissured as the tree matures. The bark’s color varies, ranging from pale gray to dark brown.
3. Leaves: Cinchona officinalis boasts glossy, dark green leaves with a leathery texture. The leaves are arranged in opposite pairs along the branches, providing an aesthetically pleasing and symmetrical appearance.
4. Flowers: The tree produces small, tubular flowers that are typically white or pink in color. The flowers are arranged in clusters, adding a touch of elegance to the canopy.
5. Fruit Formation: The fruit of Cinchona officinalis is a capsule containing numerous seeds. The capsule, when mature, splits open to disperse the seeds, contributing to the tree’s reproductive cycle.
6. Root System: Cinchona officinalis develops a well-defined and extensive root system. The roots play a crucial role in anchoring the tree and absorbing nutrients from the soil.
7. Growth Habit: This species exhibits a pyramidal growth habit, with a conical or cylindrical crown. The shape of the crown contributes to the overall aesthetics and structure of the tree.
8. Adaptations to Altitude: Cinchona officinalis is well-adapted to thrive in mountainous regions. Its ability to grow at varying altitudes makes it a resilient and versatile species.
9. Medicinal Bark: The most notable feature of Cinchona officinalis is its medicinal bark, historically renowned for containing quinine. Quinine is a compound with antimalarial properties, making the tree of significant importance in traditional medicine.
10. Cultivation Characteristics: Cultivation of Cinchona officinalis requires specific environmental conditions, including a tropical climate with well-drained soils. The tree is primarily cultivated for the extraction of quinine, contributing to pharmaceutical applications.
The Geographic Distribution of Cinchona officinalis

1. Native to South America: Cinchona officinalis is native to the Andes region of South America, where it thrives in the mountainous terrain of countries such as Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Bolivia.
2. Altitudinal Range: The geographic distribution of Cinchona officinalis is closely tied to altitude. It is commonly found at elevations ranging from 1,000 to 3,000 meters above sea level, thriving in the cool and temperate conditions of mountainous landscapes.
3. Global Cultivation: While native to South America, Cinchona officinalis has been introduced and cultivated in various tropical regions worldwide. Plantations can be found in countries with suitable climates, including India, Indonesia, and parts of Africa.
4. Specific Growing Conditions: The tree prefers regions with well-defined wet and dry seasons. The combination of cool temperatures and consistent rainfall in its native habitat and cultivated areas contributes to optimal growth.
5. Biodiversity Impact: The introduction of Cinchona officinalis to non-native regions has had ecological implications. The tree’s cultivation for quinine extraction has influenced local biodiversity and, in some cases, led to the displacement of native flora.
6. Conservation Efforts: Due to its historical and medicinal significance, there have been conservation efforts to protect natural populations of Cinchona officinalis. Conservation initiatives focus on preserving the genetic diversity of this valuable species.
7. Role in Malaria Treatment: The global distribution of Cinchona officinalis aligns with regions where malaria is prevalent. The tree’s bark, containing quinine, has played a crucial role in the treatment of malaria, especially in areas where the disease is endemic.
8. Economic Importance: The geographic distribution of Cinchona officinalis is closely tied to its economic importance. Regions cultivating the tree contribute significantly to the pharmaceutical industry by supplying quinine for antimalarial medications.
9. Challenges in Non-Native Regions: In regions where Cinchona officinalis is not native, challenges include potential invasiveness and the need for sustainable cultivation practices to balance economic benefits with environmental considerations.
10. Research and Global Collaboration: Ongoing research and global collaboration aim to enhance the cultivation practices of Cinchona officinalis, ensuring sustainable production and preserving its geographic distribution while addressing ecological concerns.
The Chemical Composition of Cinchona officinalis
1. Quinine Content: The primary and most significant chemical component of Cinchona officinalis is quinine. The bark of the tree contains varying concentrations of quinine, with medicinal properties recognized for its antimalarial effects.
2. Alkaloids: Apart from quinine, Cinchona officinalis bark contains a range of alkaloids. These alkaloids contribute to the tree’s medicinal properties and are of interest in pharmaceutical research.
3. Cinchonine and Cinchonidine: Alongside quinine, cinchonine and cinchonidine are notable alkaloids found in Cinchona officinalis. These compounds have pharmacological significance, influencing the tree’s medicinal applications.
4. Tannins: The bark also contains tannins, contributing to its astringent properties. Tannins have been studied for their potential antioxidant effects and role in traditional medicine.
5. Flavonoids: Cinchona officinalis contains flavonoids, which are known for their antioxidant properties. These compounds may play a role in the overall health benefits associated with the consumption of Cinchona officinalis extracts.
6. Terpenes and Essential Oils: The tree’s bark contains terpenes and essential oils, adding to its complex chemical composition. These compounds contribute to the distinct aroma and flavor of Cinchona officinalis.
7. Anthraquinones: Some varieties of Cinchona officinalis may contain anthraquinones, which are compounds known for their laxative effects. However, the concentrations of anthraquinones can vary among different Cinchona species.
8. Research on Secondary Metabolites: Ongoing research explores the secondary metabolites present in Cinchona officinalis, aiming to uncover additional bioactive compounds with potential medicinal applications.
9. Extraction Methods: The chemical composition of Cinchona officinalis is harnessed through various extraction methods. Extraction techniques, including decoction and maceration, are employed to obtain the valuable compounds from the bark.
10. Pharmaceutical Applications: The unique chemical composition of Cinchona officinalis, especially its quinine content, has made it a cornerstone in the pharmaceutical industry. Quinine is utilized in the production of antimalarial drugs, showcasing the practical significance of the tree’s chemical profile.
Read Also: 18 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Alchornea glandulosa (Christmas bush)
The Medicinal Health Benefits Of Cinchona officinalis (Peruvian bark)

1. Antimalarial Properties: Cinchona officinalis is renowned for its potent antimalarial properties, primarily attributed to the presence of quinine in its bark. Quinine has been a key component in the treatment of malaria, demonstrating efficacy in combating the Plasmodium parasite responsible for the disease.
2. Fever Reduction: The medicinal benefits of Cinchona officinalis extend to fever reduction. Quinine, as an antipyretic agent, helps lower fever by influencing the body’s thermoregulatory mechanisms. This property has historical significance in treating fevers associated with various illnesses.
3. Muscle Relaxant: Quinine, one of the major alkaloids in Cinchona officinalis, acts as a muscle relaxant. This property has therapeutic implications in alleviating muscle cramps and spasms, making Cinchona officinalis a potential remedy for conditions characterized by muscle tension.
4. Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Cinchona officinalis exhibits anti-inflammatory effects, attributed to its alkaloid content. These anti-inflammatory properties may contribute to the alleviation of inflammatory conditions, providing relief to individuals dealing with inflammatory disorders.
5. Digestive Aid: Traditionally, Cinchona officinalis has been used as a digestive aid. The plant’s compounds, including tannins, may contribute to improved digestion by promoting the secretion of digestive enzymes and reducing gastrointestinal discomfort.
6. Cardiovascular Health Support: Research suggests that Cinchona officinalis may offer cardiovascular health support. Compounds in the plant, such as quinine, have been studied for their potential to improve blood circulation and contribute to overall heart health.
7. Pain Relief: The analgesic properties of Cinchona officinalis can contribute to pain relief. This makes it a potential natural remedy for conditions involving pain, although specific applications may vary.
8. Antioxidant Effects: Cinchona officinalis contains antioxidants, including flavonoids, which help neutralize free radicals in the body. These antioxidant effects play a role in promoting overall health and reducing oxidative stress.
9. Immune System Modulation: Components of Cinchona officinalis may contribute to immune system modulation. While further research is needed, the plant’s potential in enhancing immune function is an area of interest.
10. Respiratory Health Benefits: Cinchona officinalis has been traditionally used to address respiratory issues. Its potential expectorant properties may aid in clearing mucus and supporting respiratory health.
The Methods of Usage to Achieve the Provided Health Benefits Of Cinchona officinalis (Peruvian bark)
1. Decoctions and Infusions: Preparing decoctions or infusions from Cinchona officinalis bark is a common method of consumption. Boiling the bark in water allows for the extraction of beneficial compounds, making it a traditional and effective approach.
2. Tinctures: Tinctures, created by soaking Cinchona officinalis bark in alcohol, offer another method of usage. Tinctures provide a concentrated form of the plant’s active constituents and are often used in herbal medicine.
3. Capsule Supplements: For convenient consumption, Cinchona officinalis is available in capsule form as a dietary supplement. Capsules provide a measured dose of the plant’s compounds, ensuring consistent intake.
4. Traditional Herbal Teas: Brewing herbal teas from Cinchona officinalis bark is a soothing and traditional method. Herbal teas offer a palatable way to experience the plant’s medicinal benefits, especially in addressing fevers and digestive concerns.
5. Topical Applications: In some cases, Cinchona officinalis extracts or preparations may be applied topically. This method is explored for localized benefits, such as muscle relaxation or addressing skin conditions.
6. Herbal Powders: Cinchona officinalis bark can be processed into herbal powders for various applications. These powders can be incorporated into recipes or consumed as part of herbal formulations.
7. Combination Formulas: Cinchona officinalis is often included in herbal formulations designed for specific health purposes. Combining it with other complementary herbs enhances its effectiveness and provides a holistic approach to health.
8. Syrups and Elixirs: Syrups and elixirs infused with Cinchona officinalis are popular methods, especially for those who prefer a sweetened form. These preparations offer a convenient and flavorful way to benefit from the plant’s properties.
9. Standardized Extracts: Standardized extracts of Cinchona officinalis ensure a consistent concentration of active compounds. These extracts, available in liquid or capsule form, are convenient for those seeking a controlled and measured dosage.
10. Consultation with Healthcare Professionals: Before using Cinchona officinalis for medicinal purposes, it is advisable to consult with healthcare professionals. They can provide personalized guidance based on individual health conditions, ensuring safe and effective usage.
The Side Effects Of Using Cinchona officinalis Medicinal Plant
1. Allergic Reactions: Individuals with allergies to Cinchona officinalis or related plants may experience allergic reactions. This includes symptoms such as skin rashes, itching, or respiratory discomfort. It is crucial to discontinue use if allergic reactions occur.
2. Gastrointestinal Upset: Excessive consumption of Cinchona officinalis may lead to gastrointestinal upset, including nausea, vomiting, or stomach cramps. Moderation
is key to avoiding these side effects.
3. Cinchonism: Cinchonism is a set of symptoms associated with the excessive intake of quinine, a prominent compound in Cinchona officinalis. Symptoms may include ringing in the ears (tinnitus), headaches, dizziness, and visual disturbances.
4. Interactions with Medications: Cinchona officinalis may interact with certain medications, particularly those metabolized by the liver. Individuals taking medications should consult healthcare professionals to avoid potential interactions.
5. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Concerns: Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should exercise caution with Cinchona officinalis due to limited safety data. Consulting healthcare professionals before use is advisable in these situations.
6. Blood Sugar Impact: Cinchona officinalis may influence blood sugar levels. Individuals with diabetes or those on medications to control blood sugar should monitor their levels closely when using this plant.
7. Central Nervous System Effects: In some cases, Cinchona officinalis may impact the central nervous system, leading to symptoms such as dizziness or headaches. Individuals experiencing such effects should seek medical advice.
8. Hematological Effects: Excessive use of Cinchona officinalis may have hematological effects, including potential changes in blood cell counts. Regular monitoring is advisable for individuals using this plant over an extended period.
9. Sensitivity to Quinine: Some individuals may be sensitive to quinine, experiencing adverse reactions even at lower doses. Recognizing individual sensitivity is essential for safe usage.
10. Environmental Considerations: Harvesting Cinchona officinalis raises environmental considerations. Sustainable cultivation practices and conservation efforts are vital to ensure the long-term viability of this valuable medicinal plant.
Read Also: 18 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Handroanthus impetiginosus (Pink trumpet)
The Scientific Research and Studies of Cinchona officinalis
1. Antimalarial Efficacy: Numerous scientific studies have investigated the antimalarial properties of Cinchona officinalis, specifically focusing on the efficacy of its key component, quinine. Research has demonstrated the ability of quinine to inhibit the growth of the malaria parasite, showcasing the plant’s potential in antimalarial treatments.
2. Pharmacological Investigations: Pharmacological studies have delved into the various alkaloids present in Cinchona officinalis, exploring their mechanisms of action and potential therapeutic applications. These investigations provide insights into the plant’s diverse pharmacological effects, including antipyretic, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory properties.
3. Muscle Relaxant Properties: The muscle relaxant properties of Cinchona officinalis, particularly attributed to quinine, have been a subject of scientific interest. Studies aim to elucidate the specific pathways through which quinine exerts its muscle-relaxing effects, contributing to the understanding of its potential applications in muscle-related conditions.
4. Immunomodulatory Effects: Scientific research has explored the immunomodulatory effects of Cinchona officinalis, investigating its impact on the immune system. Preliminary findings suggest that certain compounds within the plant may modulate immune responses, presenting avenues for further research in immune-related disorders.
5. Cardiovascular Health Studies: Studies examining the cardiovascular effects of Cinchona officinalis have explored its influence on blood circulation and heart health. The potential cardiovascular benefits, attributed to specific alkaloids, contribute to ongoing research into the plant’s role in supporting cardiovascular well-being.
6. Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms: Scientific investigations have sought to unravel the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of Cinchona officinalis. Understanding how the plant’s compounds mitigate inflammation can inform the development of novel therapies for inflammatory conditions.
7. Gastrointestinal Effects: Researchers have examined the impact of Cinchona officinalis on the gastrointestinal system, particularly its traditional use as a digestive aid. Studies aim to elucidate the interactions between the plant’s components and digestive processes, shedding light on its potential therapeutic applications.
8. Antioxidant Capacity: Scientific studies have assessed the antioxidant capacity of Cinchona officinalis, exploring its ability to neutralize free radicals. These findings contribute to understanding the plant’s role in oxidative stress management and overall cellular health.
9. Respiratory Health Investigations: The traditional use of Cinchona officinalis in addressing respiratory issues has prompted scientific investigations into its respiratory health benefits. Studies aim to identify specific compounds that may contribute to expectorant effects, supporting respiratory function.
10. Safety and Toxicology Assessments: To ensure the safe use of Cinchona officinalis, researchers conduct safety and toxicology assessments. These studies evaluate potential adverse effects, dosage considerations, and interactions to provide comprehensive guidelines for the plant’s medicinal use.
The Safety Precautions and Recommendations In Using Cinchona officinalis Medicinal Plant
1. Allergic Reactions: Individuals with known allergies to Cinchona officinalis or related plants should exercise caution. Allergic reactions, although rare, may include skin rashes, itching, or respiratory discomfort. Discontinuation of use is recommended if such reactions occur.
2. Moderation in Consumption: To prevent gastrointestinal upset, users are advised to consume Cinchona officinalis in moderation. Excessive intake may lead to nausea, vomiting, or stomach cramps. Following recommended dosage guidelines is crucial.
3. Monitoring for Cinchonism: Cinchonism, characterized by symptoms such as tinnitus, headaches, dizziness, and visual disturbances, may occur with excessive quinine intake. Users should be vigilant for these symptoms and reduce dosage if cinchonism is suspected.
4. Caution with Medication Interactions: Individuals taking medications, especially those metabolized by the liver, should consult healthcare professionals before using Cinchona officinalis. Potential interactions may impact medication effectiveness or lead to adverse effects.
5. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Considerations: Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should exercise caution, as limited safety data are available. Consulting healthcare professionals before using Cinchona officinalis during these periods is advisable.
6. Blood Sugar Monitoring: Individuals with diabetes or those on medications to control blood sugar should monitor levels closely when using Cinchona officinalis. The plant may influence blood sugar, requiring adjustments in diabetes management.
7. Central Nervous System Effects: Some users may experience central nervous system effects, such as dizziness or headaches. If these effects persist or worsen, seeking medical advice is recommended.
8. Regular Hematological Monitoring: For individuals using Cinchona officinalis over an extended period, regular hematological monitoring is advisable to detect potential changes in blood cell counts.
9. Sensitivity to Quinine: Recognition of individual sensitivity to quinine is crucial. Even at lower doses, some individuals may experience adverse reactions. Immediate discontinuation is advised if sensitivity is suspected.
10. Sustainable Harvesting Practices: To address environmental concerns, users and cultivators of Cinchona officinalis should prioritize sustainable harvesting practices. Conservation efforts and ethical cultivation contribute to the plant’s long-term viability.
FAQs About Cinchona officinalis Medicinal Plant
Q1. Is Cinchona officinalis safe for long-term use?
While Cinchona officinalis has been traditionally used over extended periods, it is advisable to consult healthcare professionals for personalized guidance. Regular monitoring can help ensure the plant’s safe and effective long-term usage.
Q2. Can Cinchona officinalis be used during pregnancy?
Pregnant individuals should exercise caution due to limited safety data. Consulting healthcare professionals before use is recommended to assess potential risks and benefits.
Q3. What precautions should be taken when using Cinchona officinalis alongside medications?
Individuals taking medications, especially those metabolized by the liver, should consult healthcare professionals to prevent potential interactions. Monitoring for adverse effects is crucial.
Q4. Are there specific recommendations for individuals with allergies to related plants?
Individuals with known allergies to Cinchona officinalis or related plants should be vigilant for allergic reactions. Discontinuation of use is advised if symptoms occur.
Q5. How does Cinchona officinalis contribute to cardiovascular health?
Research suggests that certain compounds in Cinchona officinalis may support cardiovascular health by improving blood circulation. However, further studies are needed to fully understand its cardiovascular benefits.
Read Also: Hydroponics Guide 101: All You Need to Know About it






