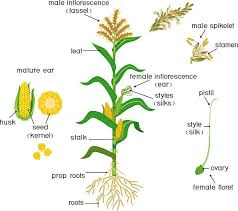
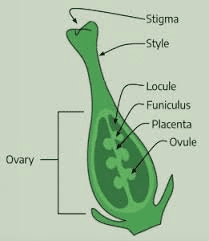
The Maize/Corn Ovary is a critical component of the female reproductive structure in maize, scientifically known as Zea mays. As part of the pistil, the ovary plays a pivotal role in the development of seeds following successful pollination and fertilization. Understanding the structure and function of the maize ovary is essential for comprehending the plant’s reproductive process and its significance in agricultural production.
The maize ovary is located at the base of the pistil and is typically situated at the center of the female inflorescence, known as the ear. It is a hollow, bulbous structure that contains ovules, which are the potential seeds of the plant. Each ovule has the potential to develop into a kernel upon successful fertilization, making the ovary crucial for seed production in maize.
Within the ovary, the ovules are arranged in rows along the inner walls. Each ovule is attached to the ovary wall by a structure called the placenta. The ovules are surrounded by protective tissues, including integuments, which enclose the developing embryo sac. The embryo sac contains the female gametophyte, which consists of the egg cell and other supportive cells necessary for fertilization and embryo development.
The ovary undergoes significant changes during the process of seed development. Following successful pollination and fertilization, the ovules within the ovary begin to develop into kernels. The fertilized ovules undergo cell division and differentiation, ultimately forming the embryo, endosperm, and seed coat of the kernel.
Environmental factors such as temperature, moisture, and nutrient availability can influence ovary development and seed production in maize. Optimal conditions, including adequate water and nutrient supply, are essential for maximizing seed yield and quality.
The structure of the maize ovary is adapted to facilitate successful seed development and dispersal. Once the seeds are fully developed, the ovary wall, known as the pericarp, matures and becomes the protective covering of the seeds. Upon maturity, the ear of maize undergoes desiccation, causing the pericarp to dry and the seeds to become dormant until the next growing season.
The maize ovary plays a crucial role not only in seed production but also in the overall reproductive success of the plant. Its structure and function are finely tuned to ensure efficient seed development and dispersal, contributing to the continuation of the maize life cycle and the propagation of the species.
In conclusion, the maize ovary is a vital component of the plant’s reproductive system, responsible for seed development and propagation. Its structure and function are intricately linked to the success of pollination and fertilization, highlighting its significance in agricultural production and food security. Understanding the biology of the maize ovary is essential for optimizing seed yield and quality in maize cultivation.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Maize/Corn Ovary
1. Seed Production: The maize ovary is crucial for seed production, as it contains the ovules that develop into kernels upon successful pollination and fertilization.
2. Crop Yield: Efficient ovary development and seed production contribute to higher crop yields, ensuring an abundant supply of maize grains for various purposes.
3. Food Industry: Maize grains derived from the ovary serve as a staple food for human consumption, with various products such as cornmeal, cornflakes, and corn oil contributing to the food industry.
4. Livestock Feed: Maize grains are used as a primary ingredient in livestock feed, providing essential nutrients for animals such as cattle, poultry, and swine.
5. Seed Industry: The maize ovary plays a critical role in the seed industry, where hybrid seeds are produced for commercial distribution, leading to improved crop performance and yield potential.
6. Genetic Research: Maize ovaries provide valuable genetic material for research purposes, aiding in genetic studies and breeding programs aimed at developing improved maize varieties.
7. Agriculture: The maize ovary supports agriculture by ensuring the continuity of maize cultivation, which is vital for food security and economic stability in many regions worldwide.
8. Biotechnology: Maize ovaries may have applications in biotechnological research, including genetic engineering for trait improvement or pharmaceutical production.
9. Ethanol Production: Maize grains derived from the ovary are utilized in ethanol production, serving as a renewable biofuel source and reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
10. Pharmaceutical Industry: Extracts derived from maize ovaries may have pharmaceutical applications, including the extraction of bioactive compounds or the production of medicinal products.
11. Textile Industry: Maize ovaries can be used in the textile industry for the production of bio-based fibers or materials.
12. Cosmetic Industry: Extracts derived from maize ovaries may find applications in the cosmetic industry for skincare or haircare products.
13. Paper Industry: Maize ovaries can be utilized in the papermaking process to produce paper products or packaging materials.
14. Environmental Remediation: Maize ovaries may play a role in environmental remediation efforts, such as phytoremediation, by assisting in the removal of pollutants from soil or water.
15. Soil Health: Maize ovaries contribute to soil health through organic matter decomposition and nutrient cycling, supporting sustainable agricultural practices.
16. Cultural and Traditional Uses: Maize ovaries hold cultural significance in many societies and may be used in traditional ceremonies or rituals.
17. Economic Stability: The cultivation and utilization of maize ovaries contribute to economic stability by providing employment opportunities and supporting rural livelihoods in maize-growing regions.
18. Bio-based Materials: Maize ovaries can be utilized in the production of bio-based materials such as biodegradable plastics or packaging materials, contributing to sustainable manufacturing practices.
Read Also General Features of Ruminant Animals
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Maize/Corn Ovary
1. Maize Grains: Maize ovaries produce grains that serve as a staple food for human consumption, with various culinary uses such as cornmeal, cornflakes, and corn oil.
2. Livestock Feed: Maize grains are a primary ingredient in livestock feed, providing essential nutrients for animals such as cattle, poultry, and swine.
3. Hybrid Seeds: Maize ovaries are crucial for hybrid seed production, leading to the development of seeds with desirable traits for improved crop performance and yield potential.
4. Genetic Material: Maize ovaries provide valuable genetic material for research purposes, aiding in genetic studies and breeding programs aimed at developing improved maize varieties.
5. Ethanol Production: Maize grains derived from the ovary are utilized in ethanol production, serving as a renewable biofuel source and reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
6. Pharmaceutical Extracts: Extracts derived from maize ovaries may have pharmaceutical applications, including the extraction of bioactive compounds for medicinal purposes.
7. Textile Fibers: Maize ovaries can be used in the textile industry for the production of bio-based fibers or materials.
8. Cosmetic Ingredients: Extracts derived from maize ovaries may find applications in the cosmetic industry for skincare or haircare products.
9. Paper Products: Maize ovaries can be utilized in the papermaking process to produce paper products or packaging materials.
10. Environmental Remediation: Maize ovaries may play a role in environmental remediation efforts, such as phytoremediation, by assisting in the removal of pollutants from soil or water.
11. Soil Amendments: Maize ovaries, when composted, can serve as organic soil amendments, contributing to soil fertility and structure.
12. Fertilizers: Composted maize ovaries can serve as organic fertilizers, providing essential nutrients for plant growth.
13. Animal Bedding: Maize ovaries can be used as animal bedding material for livestock such as poultry or small mammals.
14. Bio-based Chemicals: Maize ovaries can be utilized in the production of bio-based chemicals such as ethanol or organic acids.
15. Green Energy: Maize ovaries contribute to the production of green energy through biofuel production and biogas generation.
16. Cultural and Traditional Crafts: Maize ovaries may be used in cultural or traditional crafts, such as decorative items or artwork.
17. Economic Stability: The cultivation and utilization of maize ovaries contribute to economic stability by providing employment opportunities and supporting rural livelihoods in maize-growing regions.
Read Also Feeding Materials for Ruminant Animals
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Maize/Corn Ovary
1. What is the role of the maize ovary in seed production?
The maize ovary contains ovules that develop into kernels upon successful pollination and fertilization, contributing to seed production.
2. How does the development of the maize ovary influence crop yield?
Efficient ovary development and seed production contribute to higher crop yields, ensuring an abundant supply of maize grains for various purposes.
3. Can maize ovaries be utilized in genetic research?
Yes, maize ovaries provide valuable genetic material for research purposes, aiding in genetic studies and breeding programs aimed at developing improved maize varieties.
4. What industrial applications do maize ovaries have?
Maize ovaries have various industrial applications, including biofuel production, pharmaceuticals, textile manufacturing, and environmental remediation.
5. How do maize ovaries contribute to environmental sustainability?
Maize ovaries support environmental sustainability through organic matter decomposition, nutrient cycling, and phytoremediation efforts.
6. Are there any cultural or traditional uses of maize ovaries?
Maize ovaries hold cultural significance in many societies and may be used in traditional ceremonies or rituals.
7. Can maize ovaries be used to produce bio-based materials?
Yes, maize ovaries can be utilized in the production of bio-based materials such as biodegradable plastics or packaging materials.
8. How do maize ovaries contribute to economic stability?
The cultivation and utilization of maize ovaries provide employment opportunities and support rural livelihoods in maize-growing regions, contributing to economic stability.
9. Are there any emerging technologies utilizing maize ovaries?
Emerging technologies may utilize maize ovaries in biotechnological applications, such as genetic engineering or pharmaceutical production.
Read Also Low-Maintenance Plants for Beginners