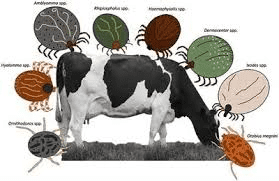
Pests and diseases are major concerns for livestock farmers. They can lead to significant losses in production, affect animal health, and reduce the overall profitability of a farm. Understanding how pests and diseases impact livestock is crucial for implementing effective management strategies to protect and maintain a healthy herd.
How Pests and Diseases Affect Livestock Production: Key Challenges and Solutions
Pests and diseases can severely disrupt livestock production in several ways. Here’s a look at the key challenges they present and the solutions to address them:
1. Decreased Productivity: Pests like ticks and flies can cause discomfort and stress in livestock, leading to reduced milk production, slower growth rates, and lower fertility. Diseases can lead to poor weight gain, low milk yield, and high mortality rates.
Solution: Implement regular pest control measures, such as using insecticides or setting up traps. Ensure vaccinations and health checks are up-to-date to prevent disease outbreaks.
2. Increased Veterinary Costs: Treating pests and diseases can be expensive. Costs include medication, veterinary visits, and loss of production during treatment.
Solution: Invest in preventive health measures to reduce the need for treatment. Regular health checks and vaccinations can minimize the risk of costly outbreaks.
3. Economic Losses: Both direct losses (e.g., reduced production) and indirect losses (e.g., increased labor and management costs) can impact a farm’s profitability.
Solution: Develop a comprehensive pest and disease management plan. This includes monitoring, early detection, and prompt treatment to minimize losses.
Understanding the Impact of Pests and Diseases on Livestock Health and Productivity

1. Health Effects: Pests like lice, mites, and flies can cause skin irritation, anemia, and secondary infections. Diseases such as foot-and-mouth disease or bluetongue can lead to severe illness, fever, and even death.
Solution: Regularly inspect livestock for signs of pests and diseases. Use appropriate treatments as needed and consult with a veterinarian for advice.
2. Productivity Losses: Infected or infested animals often produce less milk, grow more slowly, and have reduced reproductive performance. For instance, an outbreak of mastitis in dairy cattle can lead to a significant drop in milk yield.
Solution: Implement good hygiene practices, such as regular cleaning of animal housing and equipment. Ensure proper nutrition and stress management to support animal health.
3. Spread of Diseases: Some diseases can spread rapidly among livestock, especially in crowded or unsanitary conditions. This can lead to widespread outbreaks and higher mortality rates.
Solution: Practice biosecurity measures, such as isolating new or sick animals and controlling access to your farm. Maintain clean and sanitary conditions to reduce the risk of disease spread.
Read Also: 16 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Sophora flavescens (Kushen)
Pests and Diseases: Critical Threats to Livestock Production and How to Manage Them

Managing pests and diseases effectively is crucial to protecting livestock production. Here’s a guide to understanding and managing these critical threats:
1. Identify Common Pests and Diseases: Know which pests and diseases are common in your area. For example, ticks are a major problem in cattle, while respiratory diseases affect poultry.
Solution: Stay informed about local pest and disease issues through agricultural extension services or veterinary advice.
2. Monitor and Inspect Regularly: Regular monitoring helps detect problems early before they escalate. Check for signs of pests (e.g., scratching, poor coat condition) and symptoms of disease (e.g., coughing, diarrhea).
Solution: Develop a routine inspection schedule and train farm staff to recognize early signs of issues.
3. Implement Control Measures: Use integrated pest management (IPM) strategies that combine physical, biological, and chemical controls. For diseases, vaccination and treatment protocols should be followed.
Solution: Apply pest control measures like insecticides or biological agents and ensure that vaccination schedules are strictly followed.
4. Maintain Good Farm Hygiene: Cleanliness reduces the risk of pest infestations and disease outbreaks. Regularly clean animal pens, feed troughs, and water sources.
Solution: Establish a cleaning and disinfection routine. Use appropriate cleaning agents and ensure all areas are thoroughly sanitized.
Read Also: 18 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Psilopeganum
The Impact of Pests and Diseases on Livestock: What Every Farmer Needs to Know

Farmers need to be aware of the following key points to effectively manage the impact of pests and diseases on livestock:
1. Understand the Lifecycle of Pests: Knowing how pests breed and spread helps in targeting control measures. For example, knowing that flies lay eggs in manure can guide manure management practices.
Solution: Implement strategies such as regular manure removal and using fly traps to break the pest lifecycle.
2. Recognize Early Symptoms: Early detection is crucial for effective treatment. Symptoms like weight loss, abnormal behavior, or changes in milk or egg production can indicate problems.
Solution: Educate yourself and your staff on the signs of common pests and diseases and act promptly when symptoms are noticed.
3. Use Proven Treatments: Not all treatments are equally effective. Choose treatments that are proven to work for the specific pest or disease and follow recommended dosages and application methods.
Solution: Consult with veterinarians or agricultural experts to select appropriate treatments and ensure they are used correctly.
4. Keep Records: Maintain detailed records of pest and disease incidents, treatments used, and their outcomes. This information helps in assessing the effectiveness of control measures and adjusting strategies as needed.
Solution: Use farm management software or manual logs to track and review pest and disease management efforts.
Protecting Livestock from Pests and Diseases: Essential Strategies for Farmers
Farmers can protect their livestock by implementing these essential strategies:
1. Develop a Management Plan: Create a comprehensive plan that includes pest and disease prevention, monitoring, and treatment strategies. Ensure it is tailored to the specific needs of your farm.
Solution: Work with veterinarians or agricultural advisors to develop a plan that covers all aspects of pest and disease management.
2. Enhance Biosecurity Measures: Prevent the introduction of pests and diseases by controlling access to your farm, disinfecting equipment, and quarantining new or sick animals.
Solution: Implement strict biosecurity protocols, including footbaths, vehicle disinfection, and restricted access to animal areas.
3. Educate and Train Staff: Ensure that all farm staff are trained in recognizing and managing pests and diseases. Regular training helps maintain awareness and adherence to management practices.
Solution: Organize training sessions and provide resources on pest and disease management for your team.
4. Invest in Quality Feed and Nutrition: Proper nutrition supports overall health and helps livestock withstand pest and disease challenges. Ensure feed is of high quality and free from contaminants.
Solution: Source feed from reputable suppliers and consider supplementing with vitamins and minerals to boost immunity.
5. Regular Veterinary Care: Schedule regular health check-ups and vaccinations for your livestock. Routine veterinary care helps in early detection and prevention of diseases.
Solution: Establish a relationship with a trusted veterinarian and adhere to recommended health care schedules.
Conclusion
Managing the impact of pests and diseases on livestock production is vital for maintaining animal health, productivity, and farm profitability. By understanding the challenges, implementing effective management strategies, and staying informed, farmers can protect their livestock and ensure a successful and sustainable operation. Regular monitoring, proper hygiene, and preventive measures are key components of an effective pest and disease management plan.
Read Also: How to Make Your Own Organic Pesticides