Animal welfare and health are essential aspects of responsible animal care. Whether dealing with pets, livestock, or wildlife, ensuring animals are treated humanely and kept in good health contributes to their well-being and impacts the environment, human health, and ethical standards.
This article explores the key concepts of animal welfare, the importance of animal health, and the various factors that influence an animal’s quality of life.
Understanding Animal Welfare: Key Concepts
Animal welfare involves treating animals humanely, meeting their needs, and avoiding unnecessary suffering. Key concepts of animal welfare include:
1. Five Freedoms: These are basic animal rights that include freedom from hunger, discomfort, pain, fear, and freedom to express normal behaviors.
2. Humane Treatment: Animal welfare emphasizes caring for animals compassionately, avoiding neglect, abuse, and cruelty.
3. Behavioral Needs: Understanding and supporting species-specific behaviors, such as social interactions and exercise, are vital for animal welfare.
4. Physical and Mental Health: Animal welfare considers both the physical and psychological well-being of animals, ensuring they live free from stress and discomfort.
5. Ethical Responsibility: Animal welfare reflects society’s ethical obligation to care for animals with respect and compassion.
Importance of Animal Health and Well-being

Animal health and well-being are crucial for animals’ quality of life and have broader implications for human health, food safety, and environmental sustainability. Key reasons animal health is important include:
1. Disease Prevention: Healthy animals are less likely to spread diseases to other animals and humans, reducing the risk of zoonotic diseases.
2. Food Safety: Healthy livestock produce safer, higher-quality meat, dairy, and eggs, benefiting consumer health.
3. Productivity: In agriculture, healthier animals are more productive, leading to increased yields and improved livelihoods for farmers.
4. Environmental Impact: Good animal health reduces environmental strain, as healthier animals use resources more efficiently.
5. Animal Welfare: Health and well-being are integral to animal welfare, as poor health often leads to suffering, reduced lifespan, and impaired quality of life.
Animal Rights vs. Animal Welfare
Animal rights and animal welfare are often confused but represent distinct philosophies. Key differences include:
1. Ethical Perspectives: Animal rights advocate for animals to have similar rights to humans, while animal welfare focuses on humane treatment.
2. Use of Animals: Animal rights oppose any use of animals for food, clothing, or research, whereas animal welfare supports ethical and humane use.
3. Legal Protection: Animal welfare often involves laws that regulate animal treatment, while animal rights may call for ending practices like factory farming or animal testing.
4. Public Perception: Animal rights are often seen as a social movement, while animal welfare is viewed as a practical approach to animal care.
5. Treatment Standards: Animal welfare promotes standards for treatment, like proper housing and nutrition, while animal rights focus on ending exploitation entirely.
Factors Affecting Animal Welfare
Various factors influence the welfare of animals, impacting their health, comfort, and overall quality of life. Key factors include:
1. Housing and Space: Adequate space and comfortable, clean housing are essential for animals to move freely and express natural behaviors.
2. Nutrition: Proper nutrition supports an animal’s physical health, preventing malnutrition and related health issues.
3. Veterinary Care: Regular veterinary check-ups, vaccinations, and treatments are crucial for preventing and managing diseases.
4. Social Interactions: Social animals, like dogs and livestock, benefit from interaction with other animals or humans, which reduces stress and promotes mental well-being.
5. Environment and Climate: Animals should be protected from extreme weather conditions and have access to shelter, which supports their comfort and health.
Here’s an article on Animal Health and Welfare Practices with headings, bolded list numbers, and straightforward explanations.
Common Animal Health Issues and Prevention
Animals face various health issues that can affect their well-being and quality of life. Understanding these common issues and how to prevent them can help improve animal welfare.
1. Parasites: Internal parasites (like worms) and external parasites (like fleas and ticks) are common. Prevention: Regular deworming and proper hygiene can prevent infestations.
2. Nutritional Deficiencies: Animals require balanced diets to avoid deficiencies. Prevention: Feeding species-appropriate diets with necessary nutrients helps maintain good health.
3. Respiratory Infections: Respiratory issues are often seen in animals kept in poor ventilation or crowded conditions. Prevention: Ensure proper housing, clean air, and regular veterinary check-ups.
4. Skin Conditions: Allergies, infections, and injuries can lead to skin issues. Prevention: Regular grooming, parasite control, and clean environments support healthy skin.
5. Zoonotic Diseases: Some diseases can transfer between animals and humans, like rabies. Prevention: Vaccination and hygiene practices help prevent the spread of zoonotic diseases.
Read Also: How to Make Tarpaulin Fish Pond
Humane Animal Handling Practices
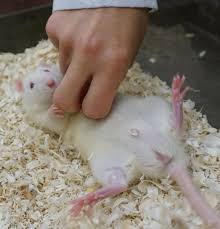
Humane handling minimizes stress and ensures animal safety, supporting overall welfare. Here are essential handling practices:
1. Gentle Approach: Avoid sudden movements or loud noises to reduce animal fear. Explanation: A calm, gentle approach helps animals feel safe, reducing stress and aggression.
2. Proper Restraint Techniques: Use appropriate restraint methods that don’t harm the animal. Explanation: Techniques vary by species but should always prioritize safety and comfort.
3. Handling Tools: Use tools (like halters or leashes) correctly and avoid overuse. Explanation: Proper tool use ensures effective handling without causing pain.
4. Training and Socialization: Animals familiar with handling respond better. Explanation: Positive reinforcement training helps animals get used to handling and reduces fear.
5. Respect Animal Space: Avoid overcrowding and respect individual boundaries. Explanation: Animals have personal spaces; overcrowding can cause stress and injuries.
Nutrition and Diet for Optimal Animal Health
A balanced diet is crucial for an animal’s health and longevity. Nutrition requirements vary by species, but the following are general guidelines:
1. Species-Appropriate Diets: Each species has unique dietary needs. Explanation: Meeting these needs ensures that animals receive necessary nutrients for their well-being.
2. Fresh Water Supply: Access to clean, fresh water is essential. Explanation: Proper hydration supports vital bodily functions and overall health.
3. Balanced Macronutrients: Animals need proteins, carbohydrates, and fats in their diet. Explanation: A balanced intake supports energy, growth, and maintenance.
4. Vitamins and Minerals: Essential nutrients like calcium and vitamins support health. Explanation: These nutrients help maintain bones, skin, immune function, and more.
5. Avoid Overfeeding: Obesity can lead to health issues. Explanation: Feed animals correct portions based on age, size, and activity level.
The Role of Housing and Shelter in Animal Welfare
Proper housing and shelter protect animals from environmental elements and provide them with a safe, comfortable living space. Important aspects include:
1. Space Requirements: Animals need adequate space for movement. Explanation: Sufficient space allows animals to express natural behaviors and reduces stress.
2. Cleanliness: Regular cleaning helps prevent disease. Explanation: Clean housing reduces pathogen buildup, supporting a healthier environment.
3. Temperature Control: Housing should protect animals from extreme weather. Explanation: Proper insulation, shade, and ventilation keep animals comfortable in different climates.
4. Bedding and Comfort: Bedding materials add warmth and comfort. Explanation: Bedding reduces pressure on joints, particularly for animals that rest frequently.
5. Access to Outdoor Areas: Animals benefit from outdoor access where possible. Explanation: Outdoor areas allow exercise, which promotes physical and mental health.
Read Also: How To Make Your Catfish Grow Bigger
Veterinary Care: Importance and Regular Check-ups
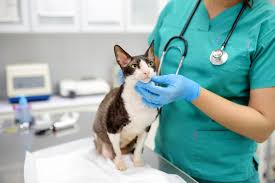
Regular veterinary care is vital for preventing and treating health issues, ensuring long-term animal welfare. Key reasons for veterinary care include:
1. Disease Prevention: Vaccinations and treatments prevent common diseases. Explanation: Preventative care reduces the risk of outbreaks and maintains herd health.
2. Early Diagnosis: Regular exams help identify health issues early. Explanation: Early treatment can prevent conditions from worsening, improving recovery outcomes.
3. Parasite Control: Vets provide treatments for parasite control. Explanation: Regular parasite treatments help keep animals free from worms, fleas, and ticks.
4. Nutritional Advice: Vets can provide dietary guidance. Explanation: A vet’s recommendations can help ensure an animal receives the necessary nutrients.
5. Emergency Care: Veterinary services provide care during emergencies. Explanation: Access to emergency care ensures animals receive treatment for injuries or sudden illnesses.
Here’s an article on Animal Welfare in Farming and Agriculture with headings, bolded list numbers, and concise explanations.
Animal Welfare in Farming and Agriculture
Animal welfare in farming and agriculture is essential for both ethical and economic reasons. By prioritizing welfare, farmers can improve the quality of animal products while ensuring that animals live in humane conditions. Key welfare practices include proper feeding, housing, health monitoring, and humane handling.
The Impact of Environment on Animal Health
The environment plays a major role in animal health and well-being. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and cleanliness directly affect animals’ physical and mental states.
1. Temperature Control: Animals require temperature regulation to prevent heat stress or hypothermia. Explanation: Proper ventilation, shading, and heating systems help maintain a suitable climate for animal comfort and health.
2. Air Quality: Poor air quality can lead to respiratory issues. Explanation: Adequate ventilation removes dust and ammonia buildup, protecting animal health.
3. Shelter: Animals need protection from weather elements. Explanation: Housing protects animals from rain, wind, and extreme sunlight, which can prevent diseases and discomfort.
4. Bedding and Cleanliness: Clean bedding reduces pathogen exposure. Explanation: Regular cleaning helps maintain sanitary conditions, minimizing the risk of infections.
5. Space Requirements: Adequate space prevents overcrowding and stress. Explanation: Enough space allows animals to move freely and engage in natural behaviors, reducing stress and aggression.
Mental Health and Enrichment for Animals
Mental health is essential to overall animal welfare. Enrichment activities help stimulate animals, reducing boredom and stress.
1. Physical Enrichment: Toys, exercise equipment, and open spaces keep animals active. Explanation: Physical stimulation supports mental health and reduces destructive behaviors.
2. Social Interaction: Many animals are social and benefit from companionship. Explanation: Group housing or interaction periods help animals fulfill their social needs.
3. Sensory Enrichment: New sights, sounds, and smells keep animals engaged. Explanation: Sensory stimulation prevents boredom and improves animals’ quality of life.
4. Behavioral Training: Training encourages animals to engage in positive behaviors. Explanation: Positive reinforcement training not only enriches animals but also improves handling safety.
5. Varied Diet: Offering a variety of foods adds stimulation. Explanation: Different textures and flavors provide sensory enjoyment and mimic natural foraging.
Laws and Regulations on Animal Welfare
Animal welfare laws and regulations ensure that animals are treated humanely. These laws vary by country but typically cover housing, transport, handling, and slaughter practices.
1. Housing Standards: Regulations set minimum space and comfort requirements. Explanation: Standards ensure animals have adequate living conditions, reducing health risks.
2. Transport Regulations: Guidelines govern how animals are transported. Explanation: These regulations protect animals from stress and injury during transportation.
3. Slaughter Practices: Humane slaughter methods are legally required. Explanation: Laws mandate practices that minimize pain and stress during slaughter, supporting ethical treatment.
4. Health Monitoring Requirements: Regular health checks are often mandated by law. Explanation: Health regulations ensure early detection of diseases, promoting public health and animal welfare.
5. Animal Cruelty Laws: Legal penalties for mistreatment discourage abuse. Explanation: These laws protect animals from neglect and cruelty, ensuring they are treated with respect and care.
Do you have any questions, suggestions, or contributions? If so, please feel free to use the comment box below to share your thoughts. We also encourage you to kindly share this information with others who might benefit from it. Since we can’t reach everyone at once, we truly appreciate your help in spreading the word. Thank you so much for your support and for sharing!
Read Also: How to Start an Urban Farm

