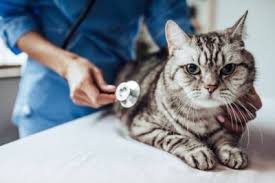
Preventive care of cats is essential for maintaining their health and well-being throughout their lives. Just like humans, cats are susceptible to various diseases that can affect their quality of life.
Regular check-ups, vaccinations, and preventive measures play a crucial role in identifying and addressing potential health issues before they become serious problems. Preventive care not only helps in avoiding common ailments but also enhances the overall longevity and happiness of our feline friends.
One of the key components of preventive care is regular veterinary visits. Annual check-ups allow veterinarians to perform a thorough examination, monitor weight and nutrition, and discuss any behavioral changes or health concerns.
During these visits, vaccinations are administered to protect against common infectious diseases such as feline viral rhinotracheitis, calicivirus, and panleukopenia. These vaccinations are vital, especially for young kittens and cats that are frequently exposed to other animals.
Another critical aspect of preventive care is proper nutrition. Feeding cats a balanced diet tailored to their specific age, weight, and health needs can prevent obesity and related diseases, such as diabetes and joint problems.
Additionally, providing fresh water and monitoring their eating habits can help detect early signs of illness. Cats are also prone to dental diseases; therefore, regular dental care, including professional cleanings and at-home oral hygiene practices, is essential for preventing periodontal disease.
Parasite control is another crucial element of preventive care for cats. Fleas, ticks, and intestinal worms can cause discomfort and transmit diseases. Regular use of veterinary-recommended parasite prevention products can help keep these pests at bay, contributing to the cat’s overall health.
Furthermore, spaying or neutering cats not only helps in controlling the pet population but also reduces the risk of certain health issues, such as mammary tumors and testicular cancer.
Common diseases in cats can vary in severity but often include conditions like upper respiratory infections, urinary tract infections, and chronic conditions such as kidney disease and hyperthyroidism.
Understanding the symptoms of these diseases is vital for early detection. For instance, signs of upper respiratory infections may include sneezing, nasal discharge, and lethargy.
In contrast, urinary tract infections can manifest as frequent urination, straining to urinate, or blood in the urine. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to timely veterinary intervention, improving the chances of a full recovery.
Another prevalent condition among cats is obesity, which can lead to several health complications, including diabetes, heart disease, and arthritis. Keeping cats active through play and providing appropriate portion sizes can help prevent obesity.
Additionally, maintaining a stimulating environment with toys and climbing structures can encourage physical activity and mental engagement.
Preventive care is crucial for the health and longevity of cats. Regular veterinary visits, vaccinations, proper nutrition, parasite control, and awareness of common diseases are essential components of a comprehensive preventive care plan.
Understanding Feline Infectious Diseases

Feline infectious diseases are caused by various pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, and parasites. Here’s an overview:
1. Viruses: These pathogens are responsible for several serious diseases in cats. Examples include feline viral rhinotracheitis (FVR) and feline leukemia virus (FeLV).
2. Bacteria: Bacterial infections can occur due to various environmental factors. Common bacterial infections include bacterial pneumonia and abscesses from fights.
3. Parasites: These organisms can cause diseases in cats, including intestinal parasites (like roundworms and tapeworms) and external parasites (like fleas and ticks).
4. Transmission: Feline infectious diseases can spread through direct contact with infected animals, contaminated environments, or through vectors like fleas and ticks.
5. Prevention: The best way to protect your cat from infectious diseases is through vaccination, good hygiene, and regular veterinary care.
Recognizing Symptoms of Common Cat Diseases
Recognizing the symptoms of common feline infectious diseases is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Here are some typical signs to look out for:
1. Coughing or Sneezing: Persistent coughing or sneezing can indicate respiratory infections like feline viral rhinotracheitis.
2. Loss of Appetite: A sudden decrease in appetite may suggest illness, including dental disease or systemic infections.
3. Vomiting or Diarrhea: These symptoms can be signs of gastrointestinal infections, parasites, or food intolerances.
4. Lethargy: If your cat seems unusually tired or less active than usual, it may indicate an underlying health issue.
5. Changes in Behavior: Any significant change in behavior, such as hiding or aggression, can signal discomfort or illness.
6. Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss can be a sign of chronic diseases like feline leukemia virus or hyperthyroidism.
7. Fever: An elevated temperature can indicate an infection. Normal cat temperature ranges from 100.5°F to 102.5°F (38°C to 39.2°C).
Read Also: Apple Maggot: Description, Damages Caused, Control and Preventive Measures
Importance of Regular Veterinary Check-ups

Regular veterinary check-ups are vital for maintaining your cat’s health and well-being. Here are key reasons why these check-ups are important:
1. Early Detection of Diseases: Routine check-ups can help identify health issues before they become severe, allowing for timely treatment.
2. Vaccination Updates: Regular visits ensure that your cat receives necessary vaccinations on schedule, providing protection against infectious diseases.
3. Monitoring Overall Health: A veterinarian can assess your cat’s weight, dental health, and overall condition during check-ups.
4. Preventive Care: Your vet can recommend preventive measures, such as parasite control, proper nutrition, and dental care.
5. Owner Education: Regular visits provide an opportunity for you to ask questions and learn more about caring for your cat’s health.
Vaccination Schedule for Cats
Vaccinations are crucial for protecting your cat from infectious diseases. Here’s a general vaccination schedule for cats:
1. Kittens (6-8 weeks old): Start vaccinations with the first round of core vaccines, which usually include:
i. Feline Viral Rhinotracheitis (FVR)
ii. Feline Calicivirus (FCV)
iii. Feline Panleukopenia (FPV)
2. Booster Shots (10-12 weeks old): Administer the second round of core vaccinations and consider adding Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV) for at-risk cats
3. Final Booster (14-16 weeks old): Give the final booster for core vaccines.
4. Annual Boosters: After the initial series, cats typically receive booster shots for core vaccines every 1-3 years, depending on the vaccine type and veterinarian recommendations.
5. Additional Vaccinations: Discuss with your vet about additional vaccinations based on your cat’s lifestyle, health status, and local disease prevalence.
Preventive Measures Against Parasites
Taking preventive measures against parasites is crucial for your cat’s overall health. Here are some effective strategies:
1. Regular Veterinary Check-ups: Schedule routine visits to the veterinarian to ensure your cat is parasite-free and to receive necessary vaccinations and treatments.
2. Parasite Control Products: Use veterinarian-recommended flea and tick preventatives. These can include topical treatments, collars, or oral medications.
3. Deworming: Regular deworming treatments are essential, especially for kittens and outdoor cats. Follow your vet’s recommendations for the appropriate schedule.
4. Indoor and Outdoor Safety: For indoor cats, keeping windows and doors secure helps prevent exposure to outdoor parasites. If your cat goes outside, limit their time outdoors and supervise them.
5. Clean Litter Boxes: Maintain a clean litter box to prevent the spread of intestinal parasites. Clean it daily and use a scoopable litter to make cleaning easier.
6. Proper Grooming: Regular grooming helps detect and remove fleas, ticks, and other parasites. Brush your cat’s fur regularly and check their skin for signs of infestation.
7. Hygiene Practices: Wash your hands after handling your cat, especially after cleaning their litter box or grooming them. This helps prevent the spread of parasites.
Read Also: Proper Layers Management Practices for Better Performance
Nutritional Considerations for Cat Health

Proper nutrition plays a vital role in maintaining your cat’s overall health and immune system, making it essential in parasite prevention. Here’s what you should consider:
1. Balanced Diet: Provide a balanced diet that includes high-quality proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. This strengthens your cat’s immune system, making them less susceptible to parasites.
2. High-Quality Commercial Food: Choose reputable brands of commercial cat food that meet the nutritional standards set by organizations like the Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO).
3. Hydration: Ensure your cat has access to fresh, clean water at all times. Proper hydration supports overall health and can help flush out toxins.
4. Regular Feeding Schedule: Establish a consistent feeding schedule to maintain a healthy weight and digestion. Overweight cats may have compromised immune systems.
5. Avoid Table Scraps: Refrain from feeding your cat table scraps, as they may be unhealthy or lead to obesity. Stick to cat-specific treats and food.
6. Nutritional Supplements: Consult your veterinarian about nutritional supplements that can boost your cat’s immune system, especially if they have specific health concerns.
Maintaining a Clean and Safe Environment
A clean environment is essential for preventing parasite infestations and ensuring your cat’s well-being. Here’s how to maintain a safe space for your feline friend:
1. Regular Cleaning: Clean your home frequently, focusing on areas where your cat spends most of their time. Vacuum carpets and furniture to remove fur and dander.
2. Wash Bedding and Toys: Regularly wash your cat’s bedding, toys, and any fabric they frequently come into contact with to remove potential parasites.
3. Outdoor Care: If your cat spends time outside, ensure your yard is free of debris where parasites can thrive. Trim bushes and grass to limit hiding places for pests.
4. Pest Control: If you notice a pest problem in your home, such as fleas or rodents, address it promptly using safe and effective pest control methods.
5. Safe Spaces: Create a designated safe area for your cat that is free from potential hazards, including toxic plants or chemicals.
6. Monitor for Signs of Parasites: Regularly check your cat for signs of parasites, such as excessive scratching or grooming, and consult your vet if you notice anything unusual.
Signs of Illness: When to Seek Veterinary Care
Recognizing the signs of illness in your cat is crucial for timely intervention. Here are common symptoms that indicate it’s time to seek veterinary care:
1. Changes in Appetite: A sudden increase or decrease in appetite can be a sign of underlying health issues, including parasitic infections.
2. Lethargy: If your cat becomes unusually tired or less active, it may indicate an illness or infection.
3. Vomiting or Diarrhea: Persistent vomiting or diarrhea can suggest gastrointestinal parasites or other health problems.
4. Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss can be a sign of several health issues, including parasitic infections and metabolic disorders.
5. Changes in Behavior: Significant changes in behavior, such as increased aggression or withdrawal, can indicate illness or discomfort.
6. Excessive Scratching or Grooming: If your cat is scratching or grooming excessively, it may be due to fleas, ticks, or other skin irritations.
7. Signs of Pain: If your cat shows signs of pain, such as vocalizing, reluctance to move, or sensitivity to touch, seek veterinary attention.
Do you have any questions, suggestions, or contributions? If so, please feel free to use the comment box below to share your thoughts. We also encourage you to kindly share this information with others who might benefit from it. Since we can’t reach everyone at once, we truly appreciate your help in spreading the word. Thank you so much for your support and for sharing!
Read Also: How To Raise Chickens – The Simple Secrets To A Great Backyard Flock
Frequently Asked Questions
We will update this section soon.