Cattle breeding techniques are essential practices that focus on improving the genetic quality and productivity of cattle populations. Breeding cattle is not merely about reproduction; it involves careful planning and strategic decision-making to enhance desirable traits in livestock.
These traits can include higher milk production, better growth rates, improved reproductive efficiency, disease resistance, and superior meat quality. As the demand for beef and dairy products continues to rise globally, the importance of effective breeding techniques becomes increasingly evident.
In traditional cattle breeding, farmers relied heavily on natural mating, selecting the best bulls and cows based on observable traits. However, advancements in animal genetics and reproductive technologies have introduced more sophisticated methods that allow for greater precision and efficiency.
Artificial insemination (AI) is one such technique that enables breeders to use semen from superior bulls, often from different geographic locations, to improve the genetic diversity and quality of their herds. This method not only saves time and resources but also helps reduce the risk of sexually transmitted diseases among cattle.
In addition to AI, embryo transfer is another innovative technique gaining traction in cattle breeding. This process involves fertilizing an egg outside the cow’s body and then implanting the embryo into a surrogate mother. By doing this, breeders can multiply the number of offspring from high-value cows, allowing for the rapid propagation of desirable genetic traits.
Furthermore, advancements in molecular genetics and genomic selection have transformed breeding programs. By analyzing DNA markers associated with specific traits, breeders can make informed decisions about which animals to select for breeding, thus enhancing the likelihood of producing offspring with superior characteristics.
Cattle breeding techniques also encompass considerations of health and nutrition. Ensuring that cattle are fed a balanced diet and provided with proper healthcare is crucial for maximizing their genetic potential. A well-nourished animal is more likely to exhibit the desirable traits that breeders aim for. In this regard, understanding the nutritional needs at different life stages, from weaning to maturity, plays a significant role in the success of breeding programs.
Moreover, the choice of breeding systems such as purebred, crossbreeding, or rotational grazing can significantly influence the outcomes of breeding efforts. Each system has its advantages and challenges, and the best choice depends on the goals of the cattle operation, the local environment, and market demands.
For example, crossbreeding can enhance hybrid vigor, leading to offspring that exhibit improved performance compared to their parents. This approach is often employed to create animals that are more resilient to environmental stressors and better suited for specific production systems.
Cattle breeding techniques are vital to the sustainability and productivity of livestock farming. By integrating traditional practices with modern scientific advancements, breeders can significantly improve cattle populations, ensuring a reliable supply of quality beef and dairy products.
Importance of Cattle Breeding

Cattle breeding is essential for several reasons:
1. Genetic Improvement: Through selective breeding, farmers can enhance desirable traits such as milk production, growth rates, and disease resistance. This leads to healthier and more productive herds.
2. Increased Productivity: Improved genetics contribute to higher yields in meat and milk production, which can result in increased profitability for farmers.
3. Adaptation to Environment: Cattle breeding can help develop breeds that are better adapted to specific environmental conditions, making them more resilient to climate challenges and diseases.
4. Economic Benefits: Efficient breeding programs can reduce production costs and increase the overall economic viability of cattle farming.
5. Conservation of Breeds: Breeding programs help maintain genetic diversity by preserving rare or endangered breeds, ensuring their survival for future generations.
Types of Cattle Breeding Systems
There are several types of cattle breeding systems that farmers can choose from:
1. Purebred Breeding: Involves mating animals of the same breed to produce offspring with specific traits. This system ensures the continuity of breed standards and improves overall herd quality.
2. Crossbreeding: Involves mating two different breeds to create hybrids. This system aims to combine desirable traits from both breeds, often resulting in offspring that grow faster and have better feed efficiency.
3. Composite Breeding: This system involves creating a new breed by mixing several breeds, focusing on specific traits. Composite breeds can offer the best traits from their parent breeds.
4. Artificial Insemination (AI): This advanced technique involves collecting semen from a bull and using it to breed cows. AI allows for better genetic selection and reduces the risk of disease transmission.
5. Inbreeding: This practice involves mating closely related animals to maintain desirable traits. However, it can also lead to health issues and reduced fertility if not managed properly.
Natural Breeding Methods
Natural breeding methods involve traditional techniques used to mate cattle. Some common natural breeding methods include:
1. Pasture Mating: This method involves allowing bulls to mate with cows in a pasture. It is simple and requires minimal management but can lead to uncontrolled breeding.
2. Hand Mating: In this method, the farmer controls the mating process by introducing the bull to the cow for a specific period. This allows for better management of breeding times.
3. Heat Detection: Farmers monitor cows for signs of heat or estrus and introduce the bull during this period to maximize the chances of successful breeding.
4. Timed Artificial Insemination: This method combines heat detection with AI, allowing farmers to breed cows at specific times based on hormonal treatments to synchronize estrus cycles.
5. Natural Service: This involves a bull being kept with a group of cows for a breeding season, allowing natural mating without intervention. While it can be effective, it requires careful management of bull health and breeding records.
Read Also: The Definition and 21 Amazing Importance of Forestry
Artificial Insemination Techniques
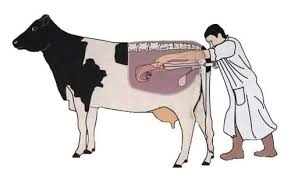
Artificial insemination (AI) is a widely used method in cattle breeding that offers numerous benefits:
1. Semen Collection: High-quality semen is collected from bulls, typically through artificial vagina or electroejaculation. This process ensures that the semen is viable for fertilization.
2. Semen Evaluation: Collected semen is evaluated for motility, morphology, and concentration. Only the best quality semen is used for insemination.
3. Timing of Insemination: Successful AI relies on precise timing. Farmers monitor cows for signs of estrus (heat) and inseminate them at the optimal time to maximize conception rates.
4. Insemination Technique: The inseminator uses a catheter to deposit the semen directly into the cow’s reproductive tract, either in the cervix or uterus. Proper technique is crucial for successful fertilization.
5. Record Keeping: Maintaining accurate records of breeding dates, cow identification, and the bull used helps track breeding performance and improve management practices.
Embryo Transfer in Cattle Breeding
Embryo transfer (ET) is a valuable technique that allows for the rapid multiplication of desirable genetics:
1. Donor Cow Selection: High-quality cows with desirable traits are selected as donors. They undergo superovulation to produce multiple eggs in a single estrous cycle.
2. Embryo Collection: After ovulation, embryos are collected from the donor cow’s uterus using a non-surgical procedure. This process requires skilled technicians to minimize stress on the donor.
3. Embryo Evaluation: Collected embryos are evaluated for quality before being frozen or transferred to recipient cows.
4. Recipient Cow Selection: Healthy recipient cows are chosen based on reproductive status, age, and overall health to receive the embryos.
5. Embryo Transfer: The embryos are transferred into the uterus of the recipient cow, where they can implant and develop into calves. This method allows farmers to produce multiple offspring from a single donor.
Genetic Selection and Its Impact
Genetic selection is a powerful tool in cattle breeding that influences herd performance:
1. Traits to Consider: Farmers should focus on traits that enhance productivity, such as growth rate, milk production, fertility, and disease resistance.
2. Selection Methods: Common methods include pedigree selection, performance testing, and genomic selection. Genomic selection utilizes DNA testing to identify desirable traits at a young age.
3. Long-Term Benefits: Genetic selection leads to cumulative improvements in herd quality over generations. This results in healthier animals, better productivity, and increased profitability.
4. Economic Impact: By focusing on traits that enhance production efficiency, farmers can reduce costs and increase market competitiveness.
5. Genetic Diversity: Maintaining genetic diversity within a herd is essential to prevent inbreeding depression and ensure the long-term sustainability of breeding programs.
Health and Nutrition for Breeding Cattle
Proper health management and nutrition are critical for successful cattle breeding:
1. Nutritional Needs: Breeding cattle require a balanced diet that includes essential nutrients such as protein, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. Proper nutrition supports reproductive health and overall well-being.
2. Pre-Breeding Health Checks: Conducting health checks before breeding helps identify and address any health issues that could affect fertility.
3. Vaccination Programs: Implementing a comprehensive vaccination program protects cattle from common diseases that could impact reproduction and calf survival.
4. Body Condition Scoring: Regularly assessing body condition helps ensure that cattle are at optimal weight for breeding. Under- or overweight cattle may experience reproductive challenges.
5. Stress Management: Minimizing stress through proper handling, comfortable housing, and adequate space contributes to better reproductive performance and overall health.
Read Also: Why Eggs Are Good For You – The Exceptional Super Food for Your Health
Record Keeping and Data Management

Effective record keeping and data management are essential for successful cattle breeding:
1. Breeding Records: Keeping detailed records of each animal’s breeding history, including dates of breeding, bull used, and outcomes, allows for better management of breeding programs.
2. Performance Data: Collecting data on growth rates, milk production, and reproductive performance helps farmers identify trends and make informed decisions.
3. Health Records: Maintaining health records for vaccinations, illnesses, and treatments ensures that cattle receive appropriate care and helps identify patterns that may affect breeding outcomes.
4. Software Tools: Utilizing software programs designed for livestock management can simplify data collection and analysis, allowing farmers to make data-driven decisions more efficiently.
5. Data Analysis: Regularly analyzing collected data enables farmers to assess the effectiveness of their breeding strategies and make adjustments as needed for improved performance.
Breeding for Specific Traits
Targeting specific traits in cattle breeding can lead to significant improvements in herd quality:
1. Desired Traits: Common traits to focus on include high milk production, rapid growth rates, disease resistance, and improved fertility.
2. Genetic Testing: Employing genetic testing can help identify animals that possess desirable traits, allowing farmers to make informed breeding decisions.
3. Crossbreeding: Crossbreeding different cattle breeds can produce offspring with specific traits that are advantageous for particular production systems or environmental conditions.
4. Selecting Breeding Stock: Carefully selecting breeding stock based on desired traits helps ensure that these characteristics are passed on to future generations.
5. Long-Term Goals: Establishing long-term breeding goals focused on specific traits can lead to more efficient and sustainable cattle production systems.
Common Challenges in Cattle Breeding
Cattle breeding can present several challenges that farmers need to be aware of:
1. Reproductive Issues: Problems such as low fertility rates, irregular estrus cycles, and issues with conception can significantly impact breeding success.
2. Genetic Disorders: Some breeds may be prone to genetic disorders that can affect animal health and productivity, making genetic selection crucial.
3. Environmental Factors: Changes in climate, feed availability, and pasture quality can impact cattle health and breeding performance, requiring adaptive management strategies.
4. Labor and Management Costs: The labor and resources needed for effective breeding programs can be substantial, and managing these costs is essential for profitability.
5. Market Variability: Fluctuations in market demand for cattle products can affect breeding decisions and financial stability for farmers.
Do you have any questions, suggestions, or contributions? If so, please feel free to use the comment box below to share your thoughts. We also encourage you to kindly share this information with others who might benefit from it. Since we can’t reach everyone at once, we truly appreciate your help in spreading the word. Thank you so much for your support and for sharing!
Read Also: The Power of Free Education: How It Can Transform Lives
Frequently Asked Questions
We will update this section soon.

