Agric4Profits.com – Your Comprehensive Practical Agricultural Knowledge and Farmer’s Guide Website…
It’s All About Agriculture – The Way Forward!
Browse Our Categories
Free Consultancy for African Women (Let’s Feed Africa!)
Free Agricultural Consultation Form
Testimonials
Agric4Profits TV
Check out the latest videos from Agric4Profits TV here....

Regenerative Agriculture Explained: Profit with Soil Health
Farmers are transforming their land and boosting profits through regenerative agriculture! In this video, titled Regenerative Agriculture Explained: Profit with Soil Health, discover how soil restoration, crop rotation, and natural… Read More

5 Climate-Smart Practices to Slash Farm Costs
Climate-smart farming isn’t just eco-friendly — it’s profit-smart! In this video, discover 5 essential practices that help African farmers slash costs while boosting sustainability. Learn how mulching conserves soil moisture,… Read More

Top 5 Precision Farming Tools Every Farmer Needs
Discover the future of farming with our latest video, “Top 5 Precision Farming Tools Every Farmer Needs!” 🌾✨ These 5 smart tools will revolutionize your agricultural practices forever! From high-tech… Read More

How to Use Drones for Field Mapping and Pest Control
Discover how drones are helping farmers reduce losses and boost yields! How drones are used in agriculture for mapping, pest detection, and crop health. Include drone footage and animation to… Read More

What is Precision Agriculture? Simple Guide for African Smallholders
Welcome to Agric4Profits TV, where we turn small farms into big profits. Let’s explore how precision agriculture is transforming African farming. Discover how precision agriculture is revolutionizing farming for smallholder… Read More

The Secret Life of Tortoise Reproduction!
Discover the fascinating world of tortoise reproduction in “The Secret Life of Tortoise Reproduction!” 🐢 In this video, we explore their unique mating rituals, nest-building behaviors, and the incredible journey… Read More

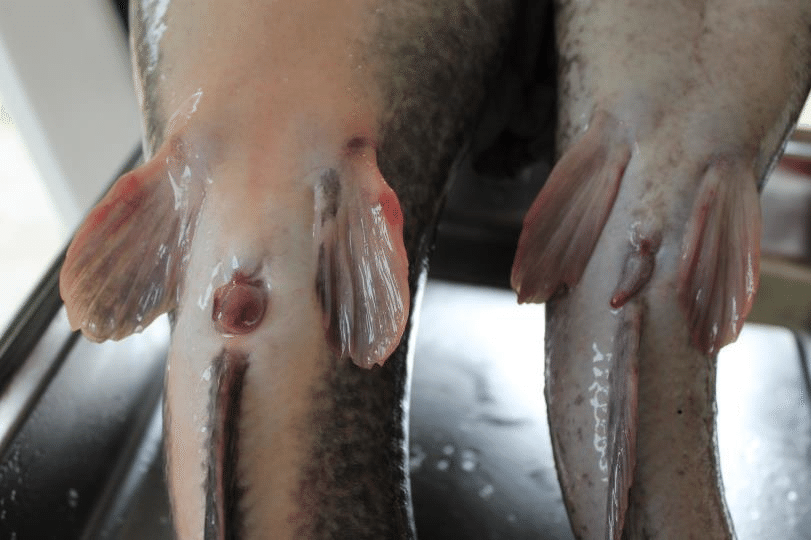
Unveiling Catfish Secrets: Anatomy and Reproduction!
Featured Image Description: Female (Left), Male (Right) Let’s dive into the fascinating world of catfish as we unveil their secrets in this in-depth exploration of catfish anatomy and reproduction! Discover… Read More

Mastering Vertical Farming: A Step-by-Step Ultimate Guide
Unlock the future of agriculture with our comprehensive tutorial, “Mastering Vertical Farming: A Step-by-Step Guide.” In just 10 minutes, we’ll walk you through the essentials of vertical farming, showcasing its… Read More
Latest Posts
Amazing Benefits of Drinking Okra Water First thing in the Morning
When it comes to okra water, a lot of people are not even aware that okra can be soaked and that the water is drinkable not just as a water… Read More

Types and Uses of Cereals, Nuts, Fats and Oils
This article examines the types, nutritional value, storage requirements, and culinary applications of cereals, nuts, fats, and oils. Cereals are cultivated grasses, but the term extends to include sago, rice,… Read More
Health Benefits and Uses of Pork Meat
Pork meat refers to the flesh of domestic pigs or pig meat that is consumed as food. It is a popular meat in many cultures around the world and is… Read More

A Comprehensive Guide to Selecting, Storing, and Preserving Vegetables and Fruits
In this article, the focus is on exploring different types of vegetables and fruits, their uses, storage methods, and preservation techniques. Fresh vegetables and fruits are vital foods from both… Read More

Eggs and Dairy Products: Production, Nutritional Value, Storage, and Uses
This article focuses on eggs and dairy products, exploring their production, nutritional value, storage requirements, and culinary applications. Eggs The term “egg” applies not only to those of hens but… Read More

Understanding the Menu: Meaning, History, Types, and Organization
A menu is a document that controls and directs an outlet’s operations and is considered the primary selling instrument of a restaurant. It is a statement of food and beverage… Read More

A Comprehensive Guide to Selecting, Storing, and Preserving Fish in Food Commodities
In this article, the focus is on selecting, storing, and preserving various types of fish. Fish constitute a significant portion of the diet due to their abundance and relative ease… Read More

Food Hygiene Regulations: Ensuring Compliance in Food Businesses
Food hygiene laws affect all food businesses, including caterers, primary producers (such as farmers), manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. How the legislation affects an establishment will depend on the size and… Read More