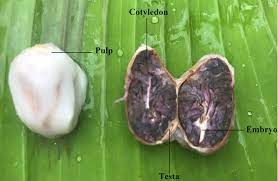
Cocoa/Cacao Cotyledons are terms often used interchangeably, but they typically refer to the same plant species. Cocoa or cacao is the tree that produces the seeds used to make chocolate. The cotyledons are a crucial part of the cocoa seed structure and play an essential role in the early growth and development of the plant.
Cocoa seeds, commonly known as cocoa beans, are contained within large pods that grow on the trunk and main branches of the cocoa tree. When the pods are harvested, they are cracked open to reveal the cocoa beans inside. Each cocoa bean is surrounded by a sweet-tasting pulp that varies in color from white to light purple.
The cocoa seed itself consists of two cotyledons. Cotyledons are the first embryonic leaves of the seedling and serve as a source of energy and nutrients during the early stages of germination. They are an integral part of the seed and contain stored reserves of fats and proteins that provide the necessary nourishment for the young cocoa plant as it begins to grow.
When cocoa beans are processed, the cotyledons are removed from the seed and undergo several steps to produce cocoa products such as cocoa powder, cocoa butter, and chocolate. These products are widely used in the food and confectionery industries to make a variety of delicious treats enjoyed by people around the world.
Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products of Cocoa/Cacao Cotyledons
Cocoa, also known as cacao, is the primary ingredient used to produce chocolate and other cocoa-based products. The cotyledons, which are the seed leaves of the cocoa bean, are of significant economic importance and have various uses. Below are some of the key economic importance and uses of cocoa/cacao cotyledons:
1. Chocolate production: The primary economic importance of cocoa cotyledons lies in chocolate production. Cocoa beans are fermented, dried, roasted, and ground to produce cocoa liquor, which is the base for all chocolate products. Cocoa cotyledons contain cocoa butter and cocoa solids, which are crucial components of chocolate. The cocoa butter provides the smooth texture and richness, while the cocoa solids give the characteristic chocolate flavor.
2. Confectionery industry: Apart from chocolate, cocoa cotyledons are also used in the confectionery industry to produce a wide range of cocoa-based products. These include chocolate bars, truffles, pralines, chocolate-covered nuts and fruits, and many more.
3. Cocoa powder production: After the cocoa beans are ground into cocoa liquor, they undergo a hydraulic press process to separate the cocoa butter from the cocoa solids. The remaining dry mass is further processed into cocoa powder, which is used in baking, beverages, desserts, and other food products.
4. Beverage production: Cocoa cotyledons are used to produce cocoa drinks and hot chocolate mixes. Cocoa powder is often mixed with sugar and milk powder to create instant hot chocolate beverages.
Read Also : Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products of Cocoa/Cacao Pods
5. Cosmetics and skincare products: Cocoa butter, extracted from cocoa cotyledons, is widely used in cosmetics and skincare products due to its moisturizing and emollient properties. It is used in body lotions, lip balms, creams, and other skincare formulations.
6. Pharmaceutical applications: Cocoa cotyledons contain various bioactive compounds, including polyphenols and flavonoids, which have antioxidant properties. These compounds may have potential health benefits and are being studied for their use in pharmaceutical applications.
7. Nutritional value: Cocoa cotyledons are a rich source of various nutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, fats (cocoa butter), and dietary fiber. They also contain essential minerals like magnesium, iron, potassium, and zinc.
8. Economic impact on cocoa-producing countries: Cocoa cultivation and trade have a significant economic impact on many countries, especially in West Africa, Latin America, and Southeast Asia. Cocoa is a major export commodity for these regions, providing employment and income to millions of farmers and laborers.
9. Culinary uses: Cocoa cotyledons have culinary applications beyond chocolate and cocoa powder. They are used in various recipes to enhance flavor and texture. Cocoa nibs, which are small pieces of roasted cocoa beans, can be added to baked goods, granola, and desserts for a crunchy texture and intense chocolate flavor.
10. Artisanal and gourmet products: The unique flavors of cocoa cotyledons, influenced by factors like terroir and post-harvest processing, have given rise to the production of artisanal and gourmet cocoa products. These include single-origin chocolates, specialty cocoa powders, and fine cocoa-based delicacies sought after by discerning consumers.
11. Export revenue and trade: Cocoa cotyledons represent a valuable commodity in international trade. Many cocoa-producing countries heavily depend on cocoa exports to generate foreign exchange and boost their economies. The global demand for chocolate and cocoa-based products continues to drive the trade in cocoa cotyledons.
12. Livelihoods and employment: Cocoa cultivation provides a source of livelihood for millions of smallholder farmers and laborers in cocoa-producing regions. It supports rural economies and provides employment opportunities throughout the value chain, from farming and harvesting to processing and exporting.
13. Sustainability and environmental impact: The economic importance of cocoa cotyledons has also raised concerns about sustainability and environmental impacts. Sustainable cocoa farming practices, such as agroforestry and certification programs (e.g., Fair Trade and Rainforest Alliance), aim to promote responsible cocoa production that protects the environment and supports farmers’ welfare.
14. Research and development: The economic significance of cocoa cotyledons drives continuous research and development in the cocoa industry. Efforts are made to improve cocoa cultivation techniques, enhance disease resistance, increase yield, and develop new cocoa-based products to cater to evolving consumer preferences.
15. Cultural and social significance: Cocoa has a rich cultural history and holds significant social importance in various regions. It is often associated with special occasions, celebrations, and traditional practices in many cocoa-consuming countries.
16. Biotechnology and genetic improvement: The economic importance of cocoa cotyledons has spurred interest in biotechnological approaches for genetic improvement, disease resistance, and higher yield potential. These efforts aim to ensure the long-term sustainability of cocoa production.
17. Value addition and processing industries: Cocoa cotyledons provide the raw material for various value-added processing industries. Apart from chocolate production, they are utilized in making cocoa-based spreads, cocoa liqueurs, and cocoa-flavored snacks, adding diversity to the product offerings in the market.
18. By-products utilization: Cocoa cotyledons generate several by-products during processing, such as cocoa husks and cocoa shells. These by-products are not wasted; instead, they are used for various purposes. For example, cocoa husks are used as organic fertilizers, and cocoa shells can be used as mulch for gardens or as a renewable energy source.
19. International trade and market dynamics: The cocoa market is influenced by global demand, weather conditions, and geopolitical factors. Fluctuations in cocoa prices can have significant impacts on cocoa-producing countries’ economies and the overall global trade dynamics.
20. Cocoa tourism: Cocoa-producing regions often attract tourists interested in learning about cocoa cultivation, processing, and chocolate production. Cocoa farms and plantations offer educational tours and experiences, contributing to local tourism and providing an additional income stream for farmers.
21. Research and innovation opportunities: The study of cocoa cotyledons opens up opportunities for scientific research and innovation in various fields, including agriculture, food technology, biotechnology, and health sciences. This research can lead to improvements in cocoa quality, disease resistance, and new product development.
22. Employment in cocoa processing industries: Beyond farming, cocoa cotyledons create employment opportunities in cocoa processing facilities, where beans are transformed into various products. This contributes to job creation and economic development in both cocoa-producing and consuming regions.
23. Cocoa in the beauty industry: Cocoa cotyledons have found applications in the beauty and personal care industry. Cocoa-based skincare products, such as cocoa butter lotions and body creams, capitalize on the moisturizing and nourishing properties of cocoa butter.
24. Social and cultural traditions: Cocoa has cultural significance in many cocoa-producing regions. It is often linked to cultural traditions, rituals, and festivities, contributing to social cohesion and preserving cultural heritage.
25. Supporting smallholder farmers: Cocoa cultivation often involves smallholder farmers who grow cocoa alongside other crops in agroforestry systems. The economic importance of cocoa cotyledons extends to these farmers, helping to improve their livelihoods and socioeconomic conditions.
26. Niche markets and premium products: The distinct flavors and qualities of cocoa cotyledons from different regions create opportunities for niche markets and premium products. Artisanal chocolate makers and specialty chocolatiers capitalize on these unique characteristics to cater to discerning consumers.
27. Economic diversification: For some cocoa-producing countries, cocoa cotyledons represent an essential agricultural product that supports economic diversification, reducing dependence on a narrow range of commodities.
28. Corporate social responsibility (CSR): Cocoa processing companies and chocolate manufacturers often engage in CSR initiatives that support cocoa farmers and their communities. These initiatives may include farmer training, access to education, healthcare, and infrastructure development.
Overall, the economic importance and uses of cocoa cotyledons extend far beyond the production of chocolate. They influence various industries, trade dynamics, livelihoods, and cultural practices. As the cocoa industry continues to evolve, efforts are being made to address sustainability challenges, improve farmers’ livelihoods, and meet consumers’ changing preferences. Balancing economic development with environmental and social responsibility remains crucial for the long-term sustainability of the cocoa sector.
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Cocoa/Cacao Cotyledons
Cocoa (also known as cacao) cotyledons, the seed of the Theobroma cacao tree, serve as the primary raw material for various products in the chocolate industry. The cotyledons are the edible part of the cocoa bean and undergo several processing steps to yield different products and by-products. Let’s explore the main ones:
1. Cocoa Liquor/Paste: Cocoa liquor, also known as cocoa paste or cocoa mass, is produced by grinding roasted cocoa cotyledons into a smooth, liquid-like substance. It contains cocoa solids and cocoa butter in roughly equal proportions. Cocoa liquor is an essential ingredient in chocolate-making and is used in various confectionery products. It can be further processed to separate cocoa solids and cocoa butter.
2. Cocoa Powder: Cocoa powder is obtained by pressing the cocoa liquor to remove cocoa butter. The remaining solid mass is then ground into a fine powder. There are two main types of cocoa powder: natural cocoa powder (acidity is not neutralized) and Dutch-processed cocoa powder (treated with an alkali to neutralize acidity). Cocoa powder is commonly used in baking, desserts, hot chocolate, and beverages.
3. Cocoa Butter: After pressing cocoa liquor, the extracted fat is known as cocoa butter. It has a smooth texture, a pleasant aroma, and is solid at room temperature but melts easily. Cocoa butter is a vital ingredient in chocolate production and is also used in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and personal care products.
4. Chocolate: The combination of cocoa liquor, cocoa butter, sugar, and other ingredients results in the creation of chocolate. There are various types of chocolate based on the proportion of cocoa solids and cocoa butter, including dark chocolate, milk chocolate, and white chocolate. Chocolate is one of the most popular and widely consumed confectioneries globally.
5. Cocoa Nibs: Cocoa nibs are small pieces of crushed cocoa beans or cotyledons. They are the “raw” form of chocolate and are commonly used in baking, smoothies, and as toppings for various desserts.
6. Cocoa Husks: After the cotyledons are removed from the cocoa beans during processing, the outer shells or husks remain. These husks are often considered waste products, but they can be utilized in various ways. For example, they can be used as mulch or fertilizer, and in some cases, they are used to make cocoa tea or infusions.
7. Cocoa Shell Mulch: Cocoa shells can be further processed into mulch, which is used as a garden cover to retain moisture, suppress weed growth, and add nutrients to the soil. However, caution should be exercised with cocoa shell mulch, as it can be toxic to pets if ingested.
8. Cocoa Tea/Infusion: Cocoa husks can be used to make a cocoa-flavored tea or infusion. The husks are steeped in hot water to create a beverage with a subtle chocolate flavor. It’s a popular drink in some regions.
9. Cocoa Soap: Cocoa butter is an excellent moisturizer, and cocoa-based soaps are popular for their skin-nourishing properties. These soaps often have a pleasant chocolate aroma.
10. Cocoa Extracts and Flavors: Cocoa extracts and flavors are concentrated forms of cocoa used to add chocolate taste to various products, including beverages, desserts, and baked goods.
11. Cocoa Liqueur: Cocoa liqueur is a beverage made by combining cocoa liquor with alcohol, typically rum or brandy. It results in a chocolate-flavored liqueur that can be enjoyed as a standalone drink or used as an ingredient in cocktails and desserts.
12. Cocoa Spread/Paste: Cocoa spread, also known as chocolate spread, is a sweet and creamy spread made by blending cocoa powder, sugar, cocoa butter, and sometimes milk solids or vegetable oils. It is a popular topping for bread, pancakes, waffles, and as a filling for pastries.
13. Cocoa Energy Bars: Cocoa cotyledons can be used in the production of energy bars, combining them with various nuts, seeds, and sweeteners to create nutritious and chocolate-flavored snacks.
Read Also : Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products of Cocoa/Cacao Seeds
14. Cocoa Snack Coatings: Cocoa cotyledons can be ground and processed to create coatings for snacks like nuts, dried fruits, or pretzels, adding a chocolatey touch to these items.
15. Cocoa Fertilizer: The cocoa husks, which are considered a by-product of the cocoa bean processing, can be composted and used as organic fertilizer, enriching the soil with essential nutrients.
16. Cocoa Dietary Supplements: Cocoa cotyledons contain various beneficial compounds like polyphenols and flavonoids, which have antioxidant properties. As a result, cocoa extracts are used in the production of dietary supplements and nutraceuticals.
17. Cocoa Skincare Products: Cocoa butter’s emollient properties make it a popular ingredient in skincare products such as lotions, creams, lip balms, and body butters. It helps to moisturize and soften the skin.
18. Cocoa Lip Balms: Cocoa butter is often the main ingredient in lip balms due to its hydrating and nourishing effects on the lips.
19. Cocoa Cosmetics: Cocoa extracts and cocoa powder are used in cosmetic products, such as eyeshadows, lipsticks, and face powders, to add color and a hint of chocolate scent.
20. Cocoa Scented Candles: Cocoa-scented candles are created using cocoa extracts or synthetic fragrances to infuse a space with the pleasant aroma of chocolate.
21. Cocoa Flavoring for Beverages: Cocoa extracts and cocoa powder are used to flavor a wide range of beverages, including coffee, hot chocolate mixes, smoothies, and milkshakes.
22. Cocoa Extract for Aromatherapy: Cocoa extracts are sometimes used in aromatherapy to evoke feelings of relaxation and comfort.
It’s important to note that while cocoa cotyledons have diverse applications, sustainable and ethical practices in the cocoa industry are essential to ensure the long-term viability of cocoa production. Many cocoa-producing regions face challenges related to fair trade, child labor, and environmental sustainability. Consumers can support ethical cocoa production by choosing products that are certified with labels like Fair Trade or Rainforest Alliance. These certifications help promote responsible and sustainable practices in the cocoa supply chain.
The process of obtaining these products and by-products from cocoa cotyledons involves several steps, such as harvesting, fermenting, drying, roasting, winnowing (removing the outer husks), grinding, and pressing. Each step plays a crucial role in obtaining the desired products while preserving the unique flavors and characteristics of cocoa. The end products have a wide range of applications, from culinary delights to cosmetics and beyond.
Read Also : How Supporting Farmers Can Benefit Our Communities
