Sugarcane nodes refer to the distinct sections or segments along the stem of a sugarcane plant (Saccharum officinarum). These nodes are essentially joints or points on the stem where leaves and branches emerge. They play a crucial role in the growth and propagation of the sugarcane plant.
Nodes are the swollen, slightly raised parts of the sugarcane stem, typically spaced at regular intervals along the length of the stem. They are circular or slightly oval in shape and can vary in size depending on the age and health of the plant.
The segments between two nodes are called internodes. These internodes are usually longer and contribute to the overall length of the sugarcane stem. They provide the plant with structural support and are also involved in the transport of water, nutrients, and sugars. Nodes are where buds are located. Buds are embryonic shoots that have the potential to develop into branches or new stalks. These buds can give rise to new tillers (shoots), which is how sugarcane plants propagate and form dense clumps or rows.
Leaves emerge from the nodes, usually in opposite pairs. The leaves are attached to the nodes via a sheath that partially surrounds the stem at the node. This arrangement provides stability to the leaves and facilitates the transfer of nutrients.
The nodes are critical sites for growth and development in the sugarcane plant. They are points of active cell division and elongation, allowing the plant to increase in height and produce new shoots and leaves.
Sugarcane nodes are the distinct segments along the stem of the sugarcane plant where leaves, branches, and roots emerge. They are vital for growth, development, and propagation, making them a key aspect of sugarcane cultivation and agriculture.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Strawberry Sugarcane Nodes
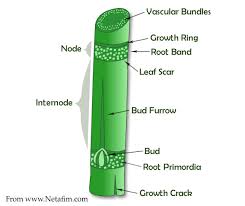
Sugarcane nodes, also known as “joints” or “segments,” are the distinct sections of the sugarcane stem that are separated by the joints where leaves emerge. These nodes have various economic importance and uses in different industries.
Here are some of the key economic benefits and uses of sugarcane nodes:
1. Propagation: Sugarcane nodes are widely used for propagating new sugarcane plants. They serve as planting material for the cultivation of sugarcane. Farmers plant these nodes horizontally in the soil, and from each node, a new sugarcane shoot emerges, giving rise to a new plant.
2. Commercial Sugarcane Cultivation: Sugarcane nodes are crucial for large-scale commercial cultivation of sugarcane. The nodes are planted in rows, and as they sprout, they grow into tall sugarcane plants that produce the sweet stalks used for sugar production.
3. Research and Breeding: Sugarcane nodes are used in research and breeding programs to develop new sugarcane varieties with improved traits such as higher sugar content, disease resistance, and yield. Researchers study the nodes to understand genetic traits and to propagate new plants with desired characteristics.
4. Tissue Culture: Sugarcane nodes are used as starting materials in tissue culture techniques to produce disease-free and genetically uniform sugarcane plants. This method helps in rapid multiplication of superior sugarcane varieties.
5. Livestock Feed: Sugarcane nodes have been used as livestock feed, especially for cattle. While the main stalks are more commonly used, nodes also contain some nutrients and fiber that can be beneficial for animal nutrition.
Read Also: Sugarcane Internodes: Economic Importance, Uses and By-Products
6. Art and Craft: In some regions, sugarcane nodes have been utilized in traditional arts and crafts. They can be carved or shaped into decorative items, baskets, and other handicrafts.
7. Biodegradable Packaging: Sugarcane nodes have been explored for their potential use in biodegradable packaging materials. Their fibrous nature and availability make them a candidate for sustainable packaging alternatives.
8. Energy Production: While not as common as other uses, sugarcane nodes, like other plant biomass, could potentially be used for energy production through processes like biomass gasification or biofuel production.
9. Composting: Sugarcane nodes can be used in composting processes to contribute organic matter to soil and improve soil structure and nutrient content.
10. Medicinal and Herbal Uses: In some traditional medicine systems, certain compounds found in sugarcane nodes have been used for their potential medicinal properties. They are believed to have anti-inflammatory and diuretic effects, although more research is needed to fully understand and validate these claims.
11. Mulching: Sugarcane nodes, due to their fibrous and organic nature, can be used as a mulching material in agriculture. Mulching helps retain soil moisture, suppress weed growth, and improve soil structure.
12. Soil Erosion Control: In areas prone to soil erosion, sugarcane nodes can be used as a natural means of stabilizing soil. They can be placed on slopes or areas vulnerable to erosion to help prevent the loss of topsoil.
13. Ethnobotanical and Cultural Uses: In some cultures, sugarcane nodes have historical and cultural significance. They might be used in rituals, ceremonies, or as offerings.
14. Bioactive Compounds: Sugarcane nodes contain various bioactive compounds, including antioxidants and phenolic compounds. These compounds have potential applications in the food and pharmaceutical industries for their health-promoting properties.
15. Environmental Remediation: Sugarcane nodes could potentially be used in phytoremediation, a process in which plants are used to remove contaminants from soil or water. Certain plants, including sugarcane, have been investigated for their ability to absorb heavy metals and other pollutants.
16. Construction Material: In some rural areas, sugarcane nodes have been used to construct fences, small structures, and temporary shelters. Their flexibility and availability make them suitable for such applications.
16. Agricultural Training and Education: Sugarcane nodes can be used as educational tools in agriculture and biology classes to demonstrate concepts like vegetative propagation, growth stages, and plant anatomy.
17. Traditional Crafts and Textiles: In some cultures, sugarcane nodes have been incorporated into traditional crafts, textiles, and weaving to create decorative patterns and textures.
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Sugarcane Nodes
Sugarcane is a versatile plant that can be processed to yield a variety of products and by-products. The primary product obtained from sugarcane is sugar, which is derived from the sugarcane stalk’s juice. However, there are several other valuable products and by-products that can be derived from different parts of the sugarcane plant.
Here’s a list along with explanations:
1. Sugar: The most well-known product from sugarcane is sucrose, which is processed from the juice extracted from the stalks. This sugar can be further refined to produce various types such as granulated sugar, brown sugar, and powdered sugar.
Molasses: This by-product is a thick, dark syrup that remains after sugar extraction from the sugarcane nodes. It’s often used in food production, as a sweetener, and in the production of alcoholic beverages. Molasses has a distinct flavor and is rich in minerals.
3. Ethanol/Biofuel: Sugarcane nodes can be used to produce bioethanol, a renewable fuel source. The juice extracted from sugarcane can be fermented to produce ethanol, which is used as a fuel additive or even as a substitute for gasoline in some cases.
4. Bagasse: This is the fibrous residue left after sugarcane nodes are crushed to extract juice. Bagasse can be used as a biofuel to produce heat and electricity for sugarcane mills and nearby communities. It’s also used in the production of paper and certain types of building materials.
5. Sugarcane Wax: A by-product obtained from the sugarcane refining process, sugarcane wax has applications in the production of candles, polishes, and even cosmetics.
Read Also: Sugarcane Internodes: Economic Importance, Uses and By-Products
6. Sugarcane Juice: Apart from its role in sugar production, sugarcane node can be consumed directly or processed into various beverages like sugarcane juice drinks and sugarcane-based energy drinks.
7. Sugarcane Syrup: This is a sweet syrup made from sugarcane node. It’s often used as a topping for pancakes, waffles, and desserts.
8. Sugarcane Fiber: The fibrous residue from sugarcane processing can be used to create biodegradable plates, bowls, and packaging materials. These products are eco-friendly alternatives to plastic.
9. Sugarcane-based Plastics: Researchers are exploring ways to convert sugarcane-derived ethanol into bioplastics, which are more environmentally friendly than traditional plastics made from fossil fuels.
10. Animal Feed: The fibrous remains of sugarcane after juice extraction, known as bagasse, can be utilized as a source of fiber and energy in livestock feed.
11. Fertilizers: Ash obtained from burning bagasse can be used as a source of potash and other minerals in fertilizers.
12. Medicinal Products: Some compounds found in sugarcane are being investigated for their potential medicinal properties, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
In conclusion, it is important to recognize that while sugarcane nodes have a range of potential uses beyond their primary role in sugarcane cultivation, the economic viability and sustainability of these applications may vary.
Read Also: Collective Farming: The Key to Sustainable Food Systems
