Alpinia officinarum, commonly known as Lesser Galangal, is a medicinal plant with a rich history of traditional use in various herbal systems.
Alpinia officinarum, belonging to the Zingiberaceae family, is a perennial herb native to Southeast Asia and China. It has been widely recognized for its medicinal properties and culinary uses. The rhizomes of Lesser Galangal are the primary part used for their therapeutic benefits.
The use of Alpinia officinarum dates back centuries and is deeply rooted in traditional medicine systems, particularly in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and Ayurveda. Here’s a brief history of its medicinal plant use
Ancient China: In Traditional Chinese Medicine, Alpinia officinarum has been employed to treat various ailments, including digestive issues, nausea, and abdominal pain.
Ayurvedic Medicine: Ayurveda, the ancient system of medicine from India, incorporates Lesser Galangal into formulations to address digestive problems, improve appetite, and alleviate respiratory conditions.
Culinary Uses: Besides its medicinal applications, Lesser Galangal is a popular spice in Southeast Asian cuisines, known for its unique flavor.
The Botanical Description of Alpinia officinarum
Understanding the botanical characteristics of Alpinia officinarum is essential for its identification and utilization. Here are six key aspects of its botanical description:
1. Growth Habit: Alpinia officinarum is a perennial herb that typically grows to a height of 1 to 2 meters.
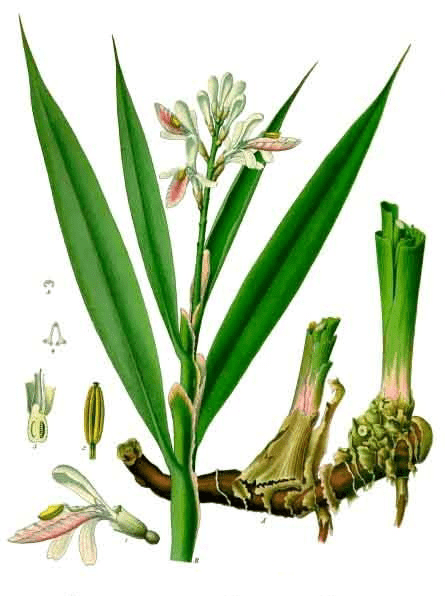
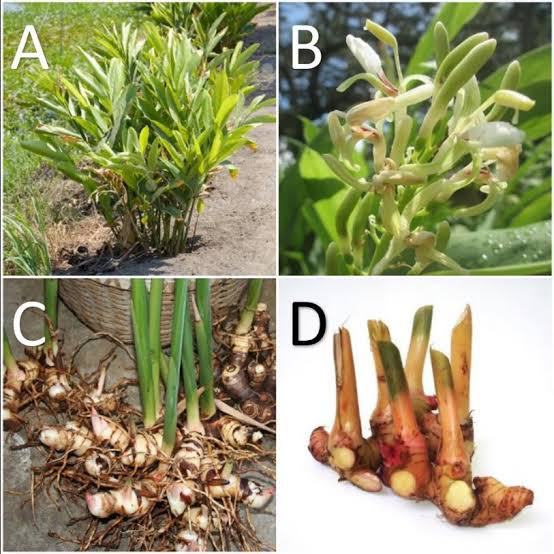
2. Leaves: The leaves are elongated, lance-shaped, and can reach lengths of up to 60 centimeters. They are green and have a glossy appearance.
3. Flowers: The plant produces clusters of showy, fragrant flowers with white petals and red streaks. These flowers are often used for ornamental purposes.
4. Rhizomes: The rhizomes of Lesser Galangal are its most valuable part. They are knobby, aromatic, and have a reddish-brown to pale brown outer layer.
5. Roots: The root system consists of fibrous roots that extend from the rhizomes, anchoring the plant in the soil.
6. Aroma: Alpinia officinarum has a distinctive, spicy, and aromatic scent, which is a hallmark of its culinary and medicinal use.
Geographic Distribution of Alpinia officinarum
Alpinia officinarum, or Lesser Galangal, is native to Southeast Asia, including countries like China, Thailand, and Indonesia. It thrives in tropical and subtropical regions with warm and humid climates. However, due to its medicinal and culinary popularity, it has been cultivated and adapted to various regions worldwide.
The Chemical Composition of Alpinia officinarum
The medicinal properties of Alpinia officinarum are attributed to its chemical composition, which includes a variety of bioactive compounds. While the exact composition can vary based on factors like growing conditions, here are some of the key constituents:
1. Essential Oils: Lesser Galangal contains essential oils rich in compounds like cineole, camphor, and terpinen-4-ol, contributing to its aromatic and therapeutic qualities.
2. Alpinin: This compound has demonstrated antioxidant properties and may contribute to the plant’s health benefits.
3. Galangin: Galangin is a flavonoid with potential anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
4. Gingerols: Although Lesser Galangal is not as well-known for gingerols as ginger, it contains some of these bioactive compounds with anti-inflammatory properties.
5. Diarylheptanoids: These compounds have shown potential for various health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer effects.
The Cultivation and Growth of Alpinia officinarum
The cultivation of Alpinia officinarum is essential to ensure a sustainable supply of this valuable medicinal plant. Here are key aspects of its cultivation and growth:
1. Climate: Lesser Galangal thrives in tropical and subtropical climates with high humidity and consistent rainfall.
2. Soil: Well-drained, fertile soils with organic matter are ideal for its cultivation.
3. Propagation: It can be propagated from rhizome divisions or by planting seeds, although rhizome divisions are more common.
4. Planting: Plant rhizomes horizontally in the soil at a depth of 5-7 centimeters and space them at least 30 centimeters apart.
5. Watering: Adequate moisture is crucial, and the plant should be watered regularly, especially during dry periods.
6. Sunlight: Partial shade to full sunlight is suitable for its growth.
7. Maintenance: Regular weeding and fertilization can help promote healthy growth.
The Harvesting and Processing of Alpinia officinarum
The harvesting and processing of Alpinia officinarum rhizomes are critical steps to preserve its medicinal properties. Here’s an overview of the process:
1. Harvesting: Rhizomes are typically harvested when the plant reaches maturity, which is usually after about two years of growth. Harvesting is often done by carefully digging up the rhizomes, ensuring minimal damage.
2. Cleaning: After harvesting, the rhizomes are cleaned to remove soil and debris.
3. Drying: The cleaned rhizomes are sliced thinly and dried in the sun or using a dehydrator until they become brittle.
4. Storage: Once dried, the rhizomes are stored in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight to maintain their potency.
5. Powdering: Some preparations may involve grinding the dried rhizomes into a fine powder for use in herbal formulations or culinary dishes.
Read Also: 15 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Akebia (Akebia Vine)
The Medicinal Health Benefits Of Alpinia officinarum (Lesser Galangal)
Alpinia officinarum, also known as Lesser Galangal, offers a wide range of potential health benefits, making it a valuable herb in traditional medicine systems. Here are 15 medicinal health benefits associated with Lesser Galangal:
1. Digestive Aid: Lesser Galangal has a long history of use as a digestive aid, helping to alleviate indigestion, bloating, and flatulence.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Properties: It contains compounds like galangin and gingerols, which exhibit anti-inflammatory effects and may help reduce inflammation in the body.
3. Antioxidant Activity: Lesser Galangal is rich in antioxidants, which can help neutralize harmful free radicals and protect cells from oxidative stress.
4. Nausea Relief: It has been traditionally used to alleviate nausea and motion sickness.
5. Appetite Stimulant: Lesser Galangal may help stimulate appetite and improve digestion, making it beneficial for those with reduced appetite.
6. Respiratory Health: It is used to treat respiratory conditions such as coughs, colds, and bronchitis due to its potential anti-inflammatory and expectorant properties.
7. Pain Relief: Lesser Galangal may have analgesic properties and has been used to alleviate pain and discomfort.
8. Antibacterial Effects: Some studies suggest that it may have antibacterial properties and can help combat certain bacterial infections.
9. Anti-Cancer Potential: Research has indicated that certain compounds in Lesser Galangal may have anti-cancer properties, although more studies are needed in this area.
10. Antifungal Activity: It has been used to address fungal infections, and some research suggests it may have antifungal effects.
11. Immune Support: Lesser Galangal’s antioxidant properties may help support the immune system and protect against infections.
12. Cardiovascular Health: Some studies have shown that it may have a positive impact on heart health by helping to regulate blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
13. Anti-Arthritic Effects: Lesser Galangal may have potential benefits for individuals with arthritis due to its anti-inflammatory properties.
14. Cognitive Health: It has been traditionally used to enhance cognitive function and improve memory.
15. Anti-Allergic Properties: Research indicates that certain compounds in Lesser Galangal may have anti-allergic effects, potentially helping individuals with allergies.
Methods of Usage to Achieve the Provided Health Benefits Of Alpinia officinarum (Lesser Galangal)
To harness the health benefits of Alpinia officinarum, or Lesser Galangal, various methods of usage are employed. Here are eight common methods and their explanations:
1. Herbal Tea: Lesser Galangal can be used to prepare herbal tea. To make the tea, slice or crush the rhizomes and steep them in hot water for several minutes. This method is often used to promote digestive health.
2. Tinctures: Tinctures are liquid extracts of Lesser Galangal made by soaking the rhizomes in alcohol or a glycerin-water solution. Tinctures allow for convenient and precise dosage.
3. Capsules and Tablets: Capsules and tablets containing dried and powdered Lesser Galangal rhizomes are available as dietary supplements. They offer a convenient way to incorporate Lesser Galangal into one’s daily routine.
4. Culinary Uses: Lesser Galangal is widely used as a spice in Southeast Asian cuisines. It adds a unique flavor and aroma to dishes, enhancing their taste.
5. Topical Applications: In some traditional remedies, Lesser Galangal extracts or oils are applied topically to the skin to alleviate pain and inflammation or improve skin health.
6. Inhalation: Lesser Galangal essential oil can be used in aromatherapy or steam inhalation to address respiratory issues, such as coughs and congestion.
7. Poultices: Poultices or compresses made from crushed Lesser Galangal rhizomes may be applied to sore muscles or painful joints for pain relief.
8. Herbal Formulations: Herbal formulations and traditional remedies may combine Lesser Galangal with other herbs to address specific health concerns. These formulations are often prepared by herbalists or traditional healers.
Side Effects Of Using Alpinia officinarum Medicinal Plant
While Alpinia officinarum, or Lesser Galangal, offers numerous health benefits, it may also be associated with side effects in some individuals. Here are six potential side effects and their explanations:
1. Gastrointestinal Discomfort: Excessive consumption of Lesser Galangal may lead to gastrointestinal discomfort, including stomach upset and diarrhea. It is advisable to use it in moderation.
2. Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may be allergic to Lesser Galangal, resulting in skin rashes, itching, or swelling. Conduct an allergy test before using it extensively.
3. Skin Irritation: Topical application of Lesser Galangal extracts or essential oil can cause skin irritation in sensitive individuals. It’s recommended to dilute the oil and perform a patch test.
4. Low Blood Pressure: Lesser Galangal may lower blood pressure. Individuals with low blood pressure should use it with caution to prevent further reductions in blood pressure levels.
5. Interaction with Medications: It may interact with certain medications, including anticoagulants and blood pressure medications. Consult a healthcare provider if you are on medication.
6. Pregnancy and Nursing: Limited safety information is available regarding the use of Lesser Galangal during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Consult a healthcare provider before use if pregnant or nursing.
Read Also: 15 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Quercus durata (Leather oak)
Scientific Research and Studies of Alpinia officinarum (Lesser Galangal)
Scientific research and studies have explored the potential health benefits of Alpinia officinarum, shedding light on its therapeutic properties. Here are seven notable findings from scientific investigations:
1. Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Research suggests that Lesser Galangal may exhibit anti-inflammatory properties, attributed to compounds like galangin and gingerols. These effects may help reduce inflammation in various tissues and organs.
2. Gastroprotective Effects: Studies have indicated that Lesser Galangal may have gastroprotective effects, helping to prevent or alleviate gastrointestinal disorders such as gastritis and gastric ulcers.
3. Antioxidant Activity: The antioxidant properties of Lesser Galangal are of interest in the context of oxidative stress and cellular damage. These antioxidants can help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body.
4. Antiemetic Properties: Lesser Galangal has been investigated for its potential antiemetic (anti-nausea) effects, making it a possible remedy for nausea and motion sickness.
5. Anti-Cancer Potential: Preliminary studies have explored the anti-cancer potential of Lesser Galangal, with some findings suggesting inhibitory effects on cancer cell growth. However, more research is needed in this area.
6. Antimicrobial Activity: Lesser Galangal has demonstrated antimicrobial activity against certain bacteria and fungi, indicating its potential in addressing infections.
7. Memory Enhancement: Some studies have explored the cognitive-enhancing effects of Lesser Galangal, suggesting a possible role in improving memory and cognitive function.
Safety Precautions and Recommendations In Using Alpinia officinarum (Lesser Galangal) Medicinal Plant
When using Alpinia officinarum, or Lesser Galangal, as a medicinal plant, it’s essential to exercise caution and follow certain safety precautions to ensure safe and effective usage. Here are seven safety precautions and recommendations:
1. Allergy Testing: Before using Lesser Galangal extensively, conduct an allergy test by applying a small amount of the extract or essential oil to a patch of skin. Wait for any adverse reactions such as redness, itching, or swelling. If any occur, discontinue use.
2. Consultation with Healthcare Provider: If you have underlying health conditions, are pregnant, nursing, or taking medications, consult with a qualified healthcare provider or herbalist before using Lesser Galangal for medicinal purposes. It’s essential to ensure there are no potential interactions or contraindications.
3. Dosage Guidelines: Follow recommended dosage guidelines provided by herbalists or product labels when using Lesser Galangal supplements, tinctures, or extracts. Overconsumption can lead to gastrointestinal discomfort.
4. Topical Application Dilution: If applying Lesser Galangal extracts or essential oil topically, always dilute them with a carrier oil to prevent skin irritation. Perform a patch test on a small area of skin before widespread use.
5. Monitor Blood Pressure: Individuals with low blood pressure should use Lesser Galangal with caution, as it may further reduce blood pressure levels. Regularly monitor blood pressure when using it.
6. Use in Moderation: Like many herbal remedies, moderation is key. Excessive consumption of Lesser Galangal can lead to stomach upset and diarrhea. Follow recommended serving sizes and guidelines.
7. Storage: Store Lesser Galangal products in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight to maintain their quality and potency. Keep them out of reach of children.
Legal Status and Regulations In Using Alpinia officinarum (Lesser Galangal) Medicinal Plant
The legal status and regulations regarding the use of Alpinia officinarum, or Lesser Galangal, as a medicinal plant may vary by region and country. However, there are some common principles to consider:
1. Dietary Supplement Regulations: In many countries, Lesser Galangal supplements, capsules, and extracts are regulated as dietary supplements. They should comply with the relevant regulations, including labeling requirements and safety standards. Look for products from reputable manufacturers.
2. Traditional Use: In regions where Lesser Galangal has a long history of traditional use, it may be classified as a traditional herbal remedy. This recognition may influence its legal status and availability for use in traditional medicine.
3. Novel Food Regulations: In some jurisdictions, Lesser Galangal and its extracts may fall under novel food regulations. These regulations govern the introduction of new or non-traditional foods into the market and may require safety assessments.
4. Import and Export Regulations: If you are importing or exporting Lesser Galangal products, be aware of any international regulations and restrictions that apply to herbal products. Compliance with import/export requirements is essential.
5. Local Cultivation and Harvesting Rules: If you are involved in the cultivation and harvesting of Lesser Galangal, adhere to local agricultural and environmental regulations. Sustainable and ethical harvesting practices are encouraged.
6. Registration and Certification: Some countries may require registration or certification for herbal products, especially those intended for medicinal use. Seek guidance from relevant authorities or regulatory bodies.
FAQs About Alpinia officinarum Medicinal Plant
Here are 18 frequently asked questions (FAQs) about Alpinia officinarum, or Lesser Galangal, as a medicinal plant, along with their explanations:
1. What is Alpinia officinarum?
Alpinia officinarum, commonly known as Lesser Galangal, is a medicinal plant with aromatic rhizomes. It is used in traditional medicine and culinary applications.
2. What are the health benefits of Lesser Galangal?
Lesser Galangal is believed to have various health benefits, including digestive support, anti-inflammatory effects, and antioxidant properties.
3. How is Lesser Galangal used in traditional medicine?
Lesser Galangal is used in traditional medicine for digestive ailments, nausea relief, and respiratory conditions. It is also employed as a spice in cooking.
4. Can I use Lesser Galangal during pregnancy?
Pregnant individuals should consult a healthcare provider before using Lesser Galangal, as safety during pregnancy is not well-established.
5. Is Lesser Galangal safe for breastfeeding mothers?
It is advisable for breastfeeding mothers to consult a healthcare provider before using Lesser Galangal to ensure its safety.
6. Can I use Lesser Galangal if I have low blood pressure?
Individuals with low blood pressure should use Lesser Galangal with caution, as it may further reduce blood pressure levels.
7. Are there any potential interactions with medications?
Lesser Galangal may interact with certain medications, including anticoagulants and blood pressure medications. Consult a healthcare provider if you are on medication.
8. How can I perform an allergy test for Lesser Galangal?
To perform an allergy test, apply a small amount of Lesser Galangal extract or essential oil to a patch of skin and observe for any adverse reactions, such as redness or itching.
9. What is the recommended dosage for Lesser Galangal supplements?
Follow the recommended dosage guidelines provided on the product label or consult with an herbalist or healthcare provider for guidance.
10. How should I store Lesser Galangal products?
Store Lesser Galangal products in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight to maintain their quality and potency.
11. Can Lesser Galangal be used topically for pain relief?
Yes, Lesser Galangal extracts or essential oil can be diluted and applied topically for pain relief. However, always perform a patch test first.
12. Is Lesser Galangal safe for children?
Consult with a pediatrician or healthcare provider before using Lesser Galangal in children, as dosages may need to be adjusted.
13. Are there any known side effects of using Lesser Galangal?
While generally safe, excessive consumption of Lesser Galangal can lead to stomach upset and diarrhea. Follow recommended serving sizes.
14. Can I grow Lesser Galangal at home?
Yes, Lesser Galangal can be grown at home in suitable climates. It requires well-drained soil and partial shade.
15. Is Lesser Galangal related to ginger?
Yes, Lesser Galangal belongs to the same botanical family (Zingiberaceae) as ginger and shares some similar flavor and aroma characteristics.
16. What culinary dishes can I prepare with Lesser Galangal?
Lesser Galangal is used in various Southeast Asian dishes,
Read Also: TV Wastes (Old Television) Best Money Making Methods
