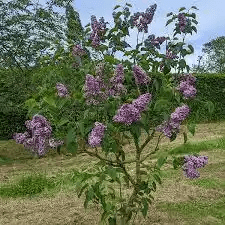
Syringa vulgaris, commonly known as Lilac, is a deciduous shrub or small tree belonging to the Oleaceae family. Celebrated for its fragrant and showy clusters of flowers, Lilac is a popular ornamental plant in gardens and landscapes, known for its aesthetic appeal and historical significance.
Lilac is characterized by its opposite, heart-shaped leaves and panicles of tubular flowers. The flowers, which come in a variety of colors, including shades of purple, pink, white, and lilac, bloom in the spring and emit a sweet and unmistakable fragrance.
The plant’s overall appearance and delightful scent contribute to its widespread use in gardens and parks.
Cultivation of Lilac is relatively straightforward, as it is adaptable to various soil types, but it thrives in well-drained, slightly alkaline soil. It prefers full sun for optimal flowering but can tolerate partial shade.
Pruning is often recommended to maintain shape and encourage vigorous growth. Lilacs are known for their longevity, and established plants can provide years of beauty and fragrance.
Beyond its ornamental value, Lilac holds cultural significance. It has been cultivated for centuries, with some varieties dating back to the 17th century. Lilacs are often associated with love and romance and are frequently used in floral arrangements and bouquets.
Lilac festivals, where communities come together to celebrate the blooming of these fragrant flowers, are popular events in various parts of the world. The plant’s charming blossoms and delightful fragrance make it a symbol of spring and renewal, evoking a sense of nostalgia and joy.
In addition to its cultural importance, Lilac has inspired poets, writers, and artists. Its timeless beauty has been captured in literature and art, further cementing its place as a beloved and iconic flowering shrub.
Syringa vulgaris, or Lilac, is a cherished and classic ornamental plant known for its fragrant blooms and cultural significance. Whether gracing gardens, parks, or bouquets, Lilac continues to captivate with its beauty and timeless charm, symbolizing the arrival of spring and evoking a sense of romance and nostalgia.
The Botanical Description of Syringa vulgaris
1. Overview: Syringa vulgaris, commonly known as the lilac, is a deciduous shrub belonging to the Oleaceae family. It is renowned for its fragrant flowers and ornamental value in gardens and landscapes.
2. Size and Shape: The lilac typically grows to a height of 8 to 15 feet, forming a dense, multi-stemmed shrub. Its growth habit is often described as upright and spreading, creating a visually appealing structure.
3. Leaves: The leaves of Syringa vulgaris are opposite, meaning they grow in pairs along the stems. They are heart-shaped, with a smooth texture and a dark green color. The leaves contribute to the shrub’s lush appearance.
4. Flowers: The most distinctive feature of Syringa vulgaris is its showy and fragrant flowers. The blossoms are arranged in large, terminal panicles, creating a stunning display in shades of purple, lavender, white, or pink, depending on the cultivar.
5. Bark: The bark of the lilac is relatively smooth and grayish-brown. As the shrub matures, the bark develops a distinctive furrowed texture, adding visual interest during the dormant season.
The Geographic Distribution of Syringa vulgaris
1. Native Range: Syringa vulgaris is native to the mountainous regions of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeastern Europe. Its natural habitat includes areas with well-drained soil and ample sunlight.
2. Global Distribution: Due to its popularity as an ornamental plant, the lilac has been widely cultivated and introduced to various regions around the world. It thrives in temperate climates and is a common sight in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia.
3. Preferred Growing Conditions: Lilacs prefer regions with cold winters and moderate summers. They are adaptable to different soil types but thrive in well-drained, slightly alkaline soil. Full sun exposure is essential for optimal flower production.
4. Cultivation in Gardens: Beyond its native range, Syringa vulgaris has found a home in gardens and landscapes globally. Gardeners appreciate its resilience, low maintenance requirements, and the ability to attract pollinators.
The Chemical Composition of Syringa vulgaris
1. Essential Oils: Syringa vulgaris flowers contain essential oils that contribute to their distinctive fragrance. These oils may include compounds such as linalool, geraniol, and eugenol, adding to the overall olfactory appeal.
2. Phenolic Compounds: Phenolic compounds, including flavonoids and tannins, are present in various parts of the lilac plant. These compounds contribute to the shrub’s antioxidant properties and potential health benefits.
3. Alkaloids: While not present in high concentrations, lilacs may contain alkaloids. These compounds have been studied for their potential pharmacological effects, although further research is needed to fully understand their significance.
4. Anthocyanins: The vibrant coloration of Syringa vulgaris flowers is attributed to anthocyanins, a group of pigments with antioxidant properties. These compounds not only contribute to the visual appeal but also play a role in plant defense mechanisms.
5. Lignans: Lignans, a class of polyphenolic compounds, are found in the bark and leaves of Syringa vulgaris. Research suggests that lignans may have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, contributing to the overall health profile of the plant.
Syringa vulgaris, or the lilac, is a botanical marvel with its captivating flowers, adaptable nature, and diverse chemical composition. Whether gracing its native landscapes in Southeastern Europe or enhancing gardens worldwide, the lilac stands as a testament to the beauty and complexity of the plant kingdom.
Read Also: How to Use Renewable Energy on your Farm
The Medicinal Health Benefits Of Syringa vulgaris (Lilac)

1. Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Syringa vulgaris exhibits anti-inflammatory effects, potentially aiding in the management of inflammatory conditions like arthritis and skin irritations.
2. Antioxidant Action: The lilac is rich in antioxidants, helping to neutralize free radicals in the body and contribute to overall cellular health.
3. Respiratory Health Support: Inhalation of lilac extracts may have respiratory benefits, potentially assisting in conditions such as asthma or respiratory infections.
4. Stress Reduction: The fragrance of Syringa vulgaris is known for its calming effect, making it a potential ally in stress reduction and relaxation.
5. Analgesic Effects: Lilac extracts may have analgesic properties, providing relief from pain associated with conditions like headaches or muscle soreness.
6. Antimicrobial Action: Compounds in Syringa vulgaris may possess antimicrobial properties, aiding in the prevention and management of infections.
7. Skin Health Promotion: Lilac extracts are believed to contribute to skin health, potentially assisting in conditions like acne or promoting overall skin radiance.
8. Immune System Support: The immune-boosting properties of Syringa vulgaris may contribute to overall immune system health, potentially reducing the risk of infections.
9. Cardiovascular Health: Some studies suggest that lilac extracts may have cardiovascular benefits, such as supporting healthy blood pressure levels.
10. Digestive Aid: Lilac may have digestive properties, potentially aiding in digestion and providing relief from digestive discomfort.
11. Anti-Cancer Potential: Preliminary research hints at the potential anti-cancer properties of Syringa vulgaris, although further studies are needed for conclusive evidence.
12. Anti-Aging Effects: The antioxidants in lilac may contribute to anti-aging effects, potentially reducing the appearance of wrinkles and promoting youthful skin.
13. Hormonal Balance: Lilac extracts may play a role in hormonal balance, potentially assisting in conditions related to hormonal fluctuations.
14. Anti-Anxiety Benefits: The calming effects of lilac fragrance may have anti-anxiety benefits, promoting mental well-being.
15. Wound Healing: External application of lilac extracts may promote wound healing, possibly due to its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties.
The Methods of Usage to Achieve the Provided Health Benefits Of Syringa vulgaris (Lilac)
1. Aromatherapy: Inhaling the fragrance through aromatherapy techniques can provide stress relief and potentially aid in respiratory health.
2. Herbal Tea: Consuming lilac herbal tea may offer internal benefits, promoting antioxidant effects and supporting overall health.
3. Topical Applications: Creams, lotions, or oils containing lilac extracts can be applied topically for skin health benefits and wound healing.
4. Steam Inhalation: Inhaling steam infused with lilac extracts may assist in respiratory health and provide a soothing effect.
5. Tinctures or Extracts: Tinctures or liquid extracts of Syringa vulgaris can be taken internally, providing a concentrated form of its medicinal properties.
6. Culinary Use: Edible lilac flowers can be incorporated into culinary creations, offering a delightful and potentially health-promoting addition to dishes.
7. Capsules or Supplements: Lilac supplements in capsule form may provide a convenient way to obtain the health benefits without the need for specific preparations.
The Side Effects Of Using Syringa vulgaris Medicinal Plant
1. Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may be allergic to lilac, leading to skin irritation or respiratory discomfort.
2. Gastrointestinal Distress: Excessive consumption may cause digestive issues such as nausea or upset stomach.
3. Photosensitivity: External application of lilac extracts may increase sensitivity to sunlight, potentially leading to sunburn.
4. Pregnancy and Lactation: Pregnant or lactating individuals should exercise caution, and consultation with a healthcare professional is advisable.
5. Interaction with Medications: Lilac supplements may interact with certain medications, necessitating consultation with a healthcare provider, especially for those on anticoagulants or blood pressure medications.
6. Not Evaluated for Long-Term Use: Long-term safety and efficacy of Syringa vulgaris for extended periods have not been extensively studied; caution is advised for prolonged use.
7. Potential Sedative Effects: The calming effects of lilac may induce drowsiness in some individuals; avoid activities requiring alertness after consuming.
8. Skin Sensitivity: Topical application may cause skin sensitivity or irritation in some individuals; perform a patch test before widespread use.
9. Not a Substitute for Professional Medical Advice: Lilac should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment; consult a healthcare professional for specific health concerns.
Syringa vulgaris, or the lilac, presents a diverse array of potential medicinal health benefits. However, it is crucial to use the plant mindfully, considering individual health conditions and seeking professional guidance when necessary.
Read Also: 18 Medicinal Health Benefits of Chenopodium album (Goosefoot)
The Scientific Research and Studies of Syringa vulgaris (Lilac)
1. Overview of Scientific Research: Scientific research on Syringa vulgaris has explored its various medicinal properties, including antioxidant effects, anti-inflammatory potential, and possible applications in skin health.
2. Antioxidant Studies: Numerous studies have investigated the antioxidant properties of lilac, highlighting its potential in combating oxidative stress and reducing cellular damage.
3. Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Research suggests that certain compounds in Syringa vulgaris may have anti-inflammatory effects, which could be beneficial in managing inflammatory conditions.
4. Respiratory Health Studies: Studies have explored the respiratory benefits of inhaling lilac extracts, indicating potential positive effects on respiratory function and health.
5. Skin Health Research: Scientific inquiries into the effects of lilac on the skin have investigated its potential in promoting skin health, addressing conditions like acne, and contributing to anti-aging effects.
6. Stress and Anxiety Studies: The calming fragrance of lilac has been the subject of studies related to stress reduction and potential anti-anxiety effects.
7. Anti-Cancer Research: Preliminary research has delved into the potential anti-cancer properties of Syringa vulgaris, identifying certain compounds that may exhibit inhibitory effects on cancer cells.
8. Immunomodulatory Effects: Some studies suggest that lilac extracts may modulate immune system function, potentially enhancing immune responses.
9. Cardiovascular Health Investigations: Research has explored the impact of lilac on cardiovascular health, with findings indicating potential benefits for maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
10. Analgesic and Pain Relief Studies: Investigations into the analgesic effects of lilac extracts have been conducted, examining their potential role in pain relief.
11. Hormonal Balance Research: Limited studies have explored the impact of lilac on hormonal balance, indicating potential effects on certain hormonal pathways.
12. Safety and Toxicity Assessments: Studies evaluating the safety and toxicity of Syringa vulgaris have been conducted to ensure its use does not pose significant risks to human health.
The Safety Precautions and Recommendations In Using Syringa vulgaris (Lilac) Medicinal Plant
1. Allergy Testing: Individuals considering the use of lilac products should conduct a patch test to assess potential allergic reactions, especially for topical applications.
2. Consultation with Healthcare Professionals: Pregnant or lactating individuals, as well as those with pre-existing health conditions or taking medications, should consult healthcare professionals before using lilac supplements or extracts.
3. Sun Protection: Due to potential photosensitivity, individuals using topical lilac products should take precautions to protect their skin from excessive sunlight.
4. Moderation in Consumption: While lilac is generally considered safe, moderation in consumption, whether in the form of herbal tea or supplements, is recommended to avoid potential adverse effects.
5. Monitoring for Side Effects: Users should monitor for any side effects, such as gastrointestinal distress or skin irritation, and discontinue use if adverse reactions occur.
6. Professional Guidance for Long-Term Use: Long-term use of lilac supplements or extracts should be done under the guidance of healthcare professionals, as the extended safety profile is not extensively studied.
7. Caution in Children: Lilac products may not be suitable for young children, and caution is advised when considering their use in this population.
8. Adherence to Recommended Dosages: Users should adhere to recommended dosages provided by healthcare professionals or product labels to prevent potential overdosing.
FAQs About Syringa vulgaris (Lilac) Medicinal Plant
1. Can Lilac Supplements Replace Medical Treatments?
Lilac supplements should not replace prescribed medical treatments. While they may complement certain health goals, professional medical advice remains essential.
2. Are Lilac Products Safe for Pregnant Women?
Pregnant women should consult healthcare professionals before using lilac products to ensure safety for both mother and baby.
3. How Soon Can Lilac’s Relaxing Effects Be Noticed?
The time to experience lilac’s relaxing effects varies among individuals, and consistent use may be needed to observe noticeable changes.
4. Can Lilac Be Used in Culinary Dishes?
Edible lilac flowers can be used in culinary dishes, adding a unique flavor. However, quantities should be moderate, considering potential health effects.
5. Are Lilac Supplements Regulated?
Lilac supplements may not be as tightly regulated as pharmaceuticals. Choosing reputable brands and consulting healthcare professionals is advisable.
6. Can Lilac Help with Acne?
Some studies suggest that lilac may contribute to skin health, potentially aiding in conditions like acne. However, individual responses may vary.
7. Is Lilac Safe for Individuals with Respiratory Conditions?
Lilac’s respiratory benefits may be beneficial for some individuals, but those with respiratory conditions should consult healthcare professionals before use.
8. Can Lilac Supplements Interact with Medications?
Lilac supplements may interact with certain medications. It’s crucial to inform healthcare providers about all supplements and medications being taken.
9. Does Lilac Have Sedative Effects?
The calming fragrance of lilac may have mild sedative effects. Individuals should avoid activities requiring alertness immediately after exposure.
10. How Should Lilac Products Be Stored?
Lilac products should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight, to preserve their quality and efficacy.
Read Also: Everything You Need to Know About Parrot Fish





