Ground elder (Aegopodium podagraria), also known as bishop’s weed or goutweed, is a perennial plant belonging to the carrot family (Apiaceae). Native to Europe and Asia, it has become naturalized in various parts of the world.
While it was once cultivated for its culinary and medicinal uses, ground elder is now often considered an invasive weed due to its aggressive spreading nature.
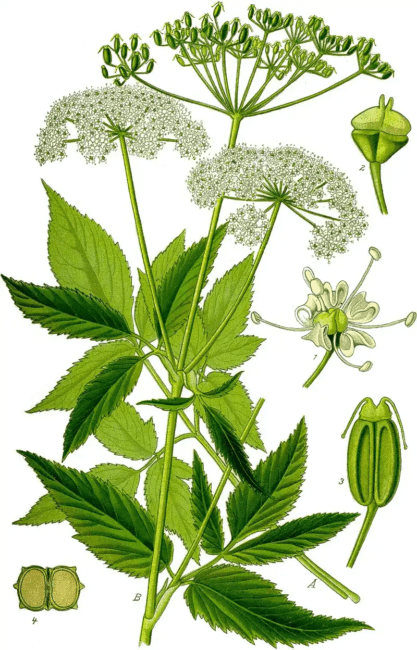
Key features of ground elder include its pinnately divided leaves that resemble those of the elder tree, hence the common name “elder.”
The leaves are bright green and toothed, and the plant produces small, white flowers arranged in umbels during late spring and early summer. Ground elder spreads through rhizomes and can form dense patches, outcompeting other plants in gardens and natural areas.
Historically, ground elder had some culinary uses, and young leaves were occasionally consumed in salads or used as a potherb. However, it’s important to note that the plant contains compounds that can be toxic in large quantities, and it is not recommended for consumption.
In herbal traditions, ground elder was also used for its potential medicinal properties. The plant was thought to have diuretic and anti-inflammatory effects and was used in traditional remedies for conditions like arthritis and gout. However, the safety and efficacy of these uses are not well-supported by modern scientific research.
Controlling ground elder can be challenging due to its rhizomatous growth and resilience. Strategies for managing ground elder include digging up the rhizomes and roots, applying mulch to suppress growth, and using herbicides selectively.
It’s important to monitor and control ground elder promptly to prevent its spread and impact on other plants.
Ground elder (Aegopodium podagraria) is a perennial plant that has become known for its invasive tendencies. While it has historical uses in traditional herbalism and, to a limited extent, in culinary practices, it is more commonly considered a challenging weed in gardens and natural landscapes.
Gardeners often need to take proactive measures to manage and control the spread of ground elder to maintain the health and diversity of their landscapes.
The Botanical Description of Ground Elder
1. Life Form: Ground Elder, scientifically known as Aegopodium podagraria, is a resilient herbaceous perennial plant with a life cycle extending over multiple years, distinguishing it from annual or biennial plants.
2. Leaves: The plant features distinctive leaves that are ternately compound, meaning they are divided into three leaflets. Each leaflet is toothed, giving the foliage a serrated appearance, and they can reach a significant size, creating a lush ground cover.
3. Flowers: Ground Elder produces small, white flowers arranged in umbrella-like clusters known as umbels. These delicate blooms appear in late spring to early summer, adding a touch of elegance to the plant’s overall appearance.
4. Stem Structure: The stems of Ground Elder are erect, hollow, and grooved, reaching heights of up to 1 meter. The grooved structure aids in distinguishing it from other similar-looking plants.
5. Root System: Below the ground, Ground Elder develops a network of rhizomes, which are underground stems. This extensive rhizomatous system contributes to the plant’s ability to spread and colonize areas rapidly.
6. Reproductive Organs: Ground Elder reproduces through both seeds and rhizomes. The seeds are produced after flowering, contributing to the plant’s ability to establish new colonies. Meanwhile, the rhizomes facilitate the vegetative spread of the plant.
7. Growth Habit: The growth habit of Ground Elder is described as invasive and aggressive, forming dense patches that outcompete other vegetation and create a challenging environment for native plants.
The Geographic Distribution of Ground Elder
1. European Origin: Ground Elder is native to Europe, with a long history of both culinary and medicinal use, dating back centuries.
2. Global Spread: Over time, Ground Elder has become naturalized in various parts of the world, including North America, Asia, and Australia, adapting well to different climates and soil conditions.
3. Habitat Preference: Ground Elder displays a preference for shaded or partially shaded areas, often found in woodlands, hedgerows, and along riverbanks. It can also tolerate more open and sunny environments.
4. Soil Adaptability: Adaptable to a range of soil types, Ground Elder thrives in moist, well-drained soils, contributing to its ability to establish itself in diverse ecosystems.
5. Invasive Nature: Considered an invasive species in many regions, Ground Elder’s rapid spread and ability to form dense colonies can have ecological impacts, particularly in areas where it outcompetes native vegetation.
The Chemical Composition of Ground Elder
1. Alkaloids: Ground Elder contains various alkaloids, including podophyllotoxin, contributing to the plant’s bioactivity and potential medicinal uses.
2. Essential Oils: The plant produces essential oils, adding to its characteristic fragrance, and these oils may have ecological roles and potential applications.
3. Flavonoids: Flavonoids, known for their antioxidant properties, are present in Ground Elder, contributing to the plant’s resilience to environmental stressors.
4. Coumarins: Coumarins, aromatic compounds found in Ground Elder, may contribute to its distinct odor and have potential pharmacological activities.
5. Phenolic Compounds: Ground Elder contains phenolic compounds, including various phenolic acids, contributing to its antioxidant capacity and potential implications for human health.
6. Vitamins and Minerals: The plant is a source of certain vitamins and minerals, providing nutritional value and adding to its historical use in traditional cuisines.
7. Polyacetylenes: Polyacetylenes, a group of bioactive compounds, are found in Ground Elder, potentially possessing anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties.
8. Polysaccharides: Polysaccharides, complex carbohydrates, are present in Ground Elder, contributing to its structural integrity and potential health benefits.
9. Tannins: Tannins, known for their astringent properties, are part of Ground Elder’s chemical composition, playing a role in its interactions with other organisms.
10. Resins: Resins, with protective functions, are found in Ground Elder, contributing to the plant’s defense mechanisms against pests and environmental challenges.
11. Saponins: Ground Elder contains saponins, compounds with soap-like properties, potentially influencing its interactions with herbivores and microbial communities.
12. Lignans: Lignans are present in Ground Elder, contributing to its overall chemical complexity, and these compounds may have potential health benefits and ecological significance.
Read Also: 18 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Konjac (Amorphophallus konjac)
The Medicinal Health Benefits Of Ground Elder (Aegopodium podagraria)
1. Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Ground Elder exhibits anti-inflammatory effects, making it beneficial for conditions such as arthritis and inflammatory disorders.
2. Diuretic Action: The diuretic properties of Ground Elder promote the elimination of excess fluids, aiding in the management of edema and supporting kidney function.
3. Digestive Health: It supports digestive health by promoting proper digestion, alleviating indigestion, and soothing gastrointestinal discomfort.
4. Antispasmodic Effects: Ground Elder’s antispasmodic properties make it useful for relieving muscle spasms and cramps, contributing to overall muscular well-being.
5. Respiratory Support: It may aid respiratory health, helping to alleviate symptoms of respiratory conditions such as asthma and bronchitis.
6. Analgesic Properties: Ground Elder exhibits analgesic effects, providing relief from various types of pain, including headaches and muscle aches.
7. Cardiovascular Support: Traditionally used to support cardiovascular health by regulating blood pressure and promoting heart function.
8. Immune System Modulation: It may have immunomodulatory effects, supporting the overall function of the immune system.
9. Stress Reduction: Ground Elder has been traditionally used for its sedative properties, helping to reduce stress and anxiety.
10. Antimicrobial Activity: It exhibits antimicrobial properties, suggesting potential effectiveness against certain infections.
11. Wound Healing: Topical application of Ground Elder may aid in wound healing due to its potential antiseptic properties.
12. Anti-Rheumatic Effects: It may have benefits for individuals with rheumatic conditions, providing relief from associated symptoms.
13. Menstrual Health: Ground Elder may help regulate menstrual cycles and alleviate menstrual cramps, promoting women’s reproductive health.
14. Antioxidant Properties: The plant contains antioxidants that help neutralize free radicals, contributing to overall cellular health.
15. Anti-Anxiety Effects: Ground Elder’s sedative properties may extend to anti-anxiety effects, providing a calming influence on the nervous system.
16. Anti-Allergic Effects: Some studies suggest that Ground Elder may have anti-allergic properties, potentially beneficial for individuals with allergies.
17. Anti-Cancer Potential: Preliminary research indicates that certain compounds in Ground Elder may have anti-cancer properties, though further studies are needed.
18. Detoxification Support: The diuretic and antioxidant properties of Ground Elder contribute to its potential role in supporting the body’s natural detoxification processes.
The Methods of Usage to Achieve the Provided Health Benefits Of Ground Elder (Aegopodium podagraria)
1. Herbal Tea: Prepare a herbal tea by steeping Ground Elder leaves in hot water, providing a convenient way to enjoy its health benefits.
2. Tinctures: Tinctures offer a concentrated form of Ground Elder extract, allowing for controlled and measured usage.
3. Poultices: Create poultices by crushing Ground Elder leaves and applying them topically to wounds or areas of pain for localized relief.
4. Culinary Use: Incorporate Ground Elder into culinary dishes, such as salads or soups, to enjoy its medicinal benefits while adding flavor to meals.
5. Infusions: Infuse Ground Elder in oil to create infusions that can be used topically for skin conditions or massage.
6. Capsules: For those seeking a standardized dosage, Ground Elder is available in capsule form, making it convenient for daily use.
7. Bath Additive: Add Ground Elder to baths to benefit from its potential stress-relieving and muscle-relaxing properties.
8. Steam Inhalation: Inhale steam infused with Ground Elder to support respiratory health and relieve congestion.
9. Compresses: Apply compresses soaked in a Ground Elder infusion to areas of pain or inflammation for targeted relief.
10. Dietary Supplement: Include Ground Elder as a dietary supplement in various forms, promoting overall health and well-being.
The Side Effects Of Using Ground Elder Medicinal Plant
1. Gastrointestinal Distress: Excessive consumption may lead to gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
2. Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may experience allergic reactions, especially if sensitive to plants in the Apiaceae family.
3. Skin Irritation: Topical application may cause skin irritation or allergic dermatitis in some individuals.
4. Photosensitivity: Ground Elder may increase sensitivity to sunlight, leading to skin reactions with prolonged sun exposure.
5. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Pregnant and breastfeeding individuals should avoid Ground Elder due to potential effects on fetal development and nursing infants.
6. Kidney Issues: Excessive use of the diuretic properties may impact individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions.
7. Blood Pressure Effects: Ground Elder may influence blood pressure; caution is advised for individuals with cardiovascular conditions.
8. Sedative Effects: Excessive sedative effects may lead to drowsiness or fatigue, impacting cognitive function.
9. Drug Interactions: Ground Elder may interact with certain medications; consultation with a healthcare professional is recommended.
10. Reproductive Effects: Due to its historical use in traditional medicine, caution is advised for individuals planning to conceive.
11. Liver Toxicity: High doses may lead to liver toxicity, emphasizing the importance of moderation in usage.
12. Respiratory Distress: Inhalation therapies may lead to respiratory distress in sensitive individuals.
13. Central Nervous System Effects: Excessive intake may lead to central nervous system depression, affecting coordination and alertness.
14. Hypotension: Individuals with low blood pressure should use Ground Elder cautiously, as it may exacerbate hypotensive effects.
15. Neurological Symptoms: In some cases, usage may lead to dizziness, confusion, and other neurological symptoms.
Read Also: A Guide to Growing and Caring for Switchgrass (Panicum Virgatum)
The Scientific Research and Studies of Ground Elder

1. Antimicrobial Properties: Scientific research has explored the antimicrobial properties of Ground Elder, revealing its potential effectiveness against various pathogens. Studies have identified compounds within the plant that exhibit antimicrobial activity, laying the groundwork for further investigations into its applications in medicine and healthcare.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Several scientific studies have delved into the anti-inflammatory effects of Ground Elder. These studies focus on understanding the molecular mechanisms behind its anti-inflammatory properties, shedding light on its potential use in treating inflammatory conditions.
3. Phytochemical Composition: The phytochemical composition of Ground Elder has been a subject of scientific interest. Researchers have conducted comprehensive analyses to identify and quantify the various compounds present in the plant, providing valuable insights into its chemical makeup and potential health benefits.
4. Pharmacological Potential: Scientific investigations into the pharmacological potential of Ground Elder have explored its impact on different physiological systems. This includes studies on its effects on the cardiovascular system, nervous system, and other vital functions, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of its medicinal properties.
5. Toxicological Studies: To ensure the safe use of Ground Elder, toxicological studies have been conducted to assess any potential adverse effects. These studies aim to establish a clear understanding of the plant’s safety profile, helping to inform guidelines for its responsible use in traditional medicine.
6. Wound Healing Properties: Research has been conducted on the wound healing properties of Ground Elder. Studies have investigated its ability to promote tissue regeneration and accelerate the healing process, offering potential applications in topical formulations for wounds and skin injuries.
7. Antioxidant Capacity: Scientific research has explored the antioxidant capacity of Ground Elder. Investigations into its ability to neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress contribute to our understanding of its potential role in promoting overall health and preventing chronic diseases.
The Safety Precautions and Recommendations In Using Ground Elder Medicinal Plant
1. Dosage Guidelines: When using Ground Elder for medicinal purposes, it is crucial to adhere to recommended dosage guidelines. Excessive consumption may lead to adverse effects, emphasizing the importance of moderation.
2. Allergy Testing: Individuals with known allergies to plants in the Apiaceae family should exercise caution and consider allergy testing before using Ground Elder. Allergic reactions, though rare, can occur.
3. Consultation with Healthcare Professionals: Before incorporating Ground Elder into a medicinal regimen, individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or those taking medications should consult with healthcare professionals. This ensures compatibility and minimizes potential interactions.
4. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Pregnant and breastfeeding individuals should avoid using Ground Elder without consulting a healthcare provider. Limited information is available on its safety during these periods.
5. Kidney Conditions: Individuals with kidney conditions should exercise caution due to Ground Elder’s diuretic properties. Consulting a healthcare professional is advisable to determine suitability.
6. Sun Sensitivity: Ground Elder may increase sensitivity to sunlight. Individuals using topical preparations should take precautions to protect their skin from excessive sun exposure.
7. Adverse Reactions: Users should monitor for any adverse reactions, including gastrointestinal distress or skin irritation. Discontinuation and seeking medical advice are recommended if adverse effects occur.
8. Moderation in Culinary Use: While Ground Elder has culinary uses, moderation is key. Excessive consumption, especially in concentrated forms, may lead to unwanted effects.
9. Children and Elderly: Special consideration should be given to children and the elderly, and usage should be guided by healthcare advice to ensure safety and appropriateness.
10. Quality of Plant Material: Ensure the use of high-quality, uncontaminated Ground Elder plant material. Sourcing from reputable suppliers and proper harvesting practices are essential.
FAQs About Ground Elder Medicinal Plant
Q1: Can Ground Elder be consumed as a daily supplement?
While Ground Elder has potential health benefits, daily consumption as a supplement should be done cautiously. It’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to determine suitability and appropriate dosage.
Q2: Is Ground Elder safe for pregnant women?
Pregnant women should avoid using Ground Elder without consulting their healthcare provider due to limited safety data during pregnancy.
Q3: Are there any known drug interactions with Ground Elder?
Ground Elder may interact with certain medications. Individuals taking medications should seek guidance from a healthcare professional to avoid potential interactions.
Q4: Can Ground Elder be used topically for skin conditions?
Yes, Ground Elder has been traditionally used topically. However, a patch test is recommended to check for potential skin reactions before widespread use.
Q5: How long does it take to observe the effects of Ground Elder for specific health benefits?
The timeframe for observing effects may vary. Consistent use over several weeks may be necessary to experience the full range of health benefits.
Q6: Can Ground Elder be used in combination with other herbal remedies?
Combining herbal remedies should be approached with caution. Consultation with a healthcare professional is advisable to ensure compatibility and safety.
Q7: What should be done in case of an allergic reaction to Ground Elder?
In case of an allergic reaction, discontinue use immediately and seek medical attention. Individuals with known allergies should exercise caution.
Q8: Can Ground Elder be used in cooking without adverse effects?
Yes, Ground Elder can be used in culinary dishes. However, moderation is recommended to avoid excessive intake.
Q9: Is Ground Elder suitable for individuals with liver conditions?
Individuals with liver conditions should exercise caution, and usage should be guided by healthcare advice to prevent potential liver toxicity.
Q10: Can Ground Elder be cultivated at home for personal use?
Yes, Ground Elder can be cultivated at home. However, proper cultivation practices should be followed, and sourcing from reliable seed or plant suppliers is recommended.
Read Also: Characteristics and Flow Rates of Waste-Water
