Aneuploidy is a numerical variation that affects a particular chromosome and not the whole set as is the case with euploidy. Aneuploidy is the second major category of chromosome mutations in which chromosome number is abnormal.
An aneuploidy is an individual organism whose chromosome number differs from the wild type by part of a chromosome set. Generally, the aneuploid chromosome set differs from wild type by only one or a small number of chromosomes.
Aneuploids can have a chromosome number either greater or smaller than that of the wild type. Aneuploid nomenclature is based on the number of copies of the specific chromosome in the aneuploid state.
For example, the aneuploid condition 2n-1 is called monosomic (meaning “one chromosome”) because only one copy of some specific chromosome is present instead of the usual two found in its diploid progenitor. The aneuploid 2n +1 is called trisomic, 2n-2 is nullisomic, and n +1 is disomic.
Aneuploid Series
Aneuploid series refers to all possible aneuploids. Thus, it is equal to the number of haploid chromosome number.
Therefore, if an organisms has chromosome number 2n = 5, then there will be 5 kinds of aneuploids given a particular type of aneuoploidy. This is because each chromosome type can be affected by aneuploidy.
Causes of Aneuploidy
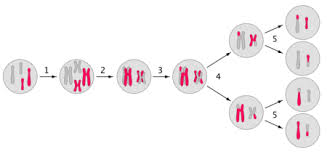
Nindisjunction: Members of a pair of chromosomes or chromatids fail to disjoin (separate) properly so that some gametes are formed containing more or less of a particular chromosome. This may lead to hypoploidy and hyperploidy.
Lagging Chromosomes: Lagging chromosomes or laggards are characterized by retarded movement during anaphase resulting in non- incorporation into gametes. This always leads to hypoploidy.
Read Also : How to Plant Fruit Trees for Optimum Performance

Irregular Chromosome Distribution: Random chromosome distribution into gametes may cause more or less of particular chromosomes in the resulting individual.
Multipolar Mitosis: Abnormal chromosome distribution.
Concept of Genic Balance
Genic balance refers to the proper amount of gene products resulting from appropriate rate of transcription and consequently the number of copies of that gene in a cell.
Genic Balance and Development
Normal development depends on gene balance i.e. genes in appropriate amount. In euploidy multiples of the whole set does not affect this balance significantly because there is no change in the relative proportions of genes.
However, in aneuploidy, numerical changes not involving the whole set alters the proportions of genes. Therefore, polyploidy does not usually cause a wide change in development as aneuploidy.
Note: Aneuploidy disturbs genic balance more significantly than euploidy.
In summary, aneuploidy is a numerical variation that affects a particular chromosome and not the whole set.
Aneuploids are produced by nondisjunction or some other types of chromosome misdivision at either meiosis or mitosis. Aneuploidy causes alteration of delicate genetic balance that enables normal development.
Aneuploids usually results in an unbalanced genome with an abnormal phenotype. Examples of aneuploids include nullisomic (2n-3), monosomic (2n- 1), trisomics (2n+1). There are also double, triple etc. aneuploids. Aneuploid series refers to all possible aneuploids of a particular type.
Read Also : Waste Management, Types and Classification of Wastes
Frequently Asked Questions
We will update this section soon.