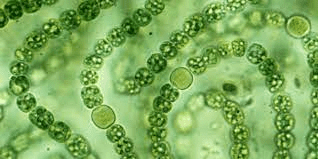
Blue-green algae, scientifically known as cyanobacteria, are a group of photosynthetic bacteria that can be found in various environments, including freshwater, marine water, and moist soil. Despite the name “blue-green algae,” they are not true algae but rather bacteria capable of photosynthesis.
These microorganisms are characterized by their blue-green pigments, primarily phycocyanin and chlorophyll, which give them their distinctive color. Cyanobacteria are among the oldest known organisms on Earth, with a history dating back billions of years.
They played a crucial role in the planet’s early atmosphere by contributing oxygen through photosynthesis.
While cyanobacteria are essential for ecological balance, certain species can produce toxins, known as cyanotoxins, under certain conditions. Blooms of cyanobacteria, often called harmful algal blooms (HABs), can occur in bodies of water, especially those rich in nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus.
These blooms may pose a threat to human and animal health as exposure to cyanotoxins can lead to various health issues, including skin irritation, gastrointestinal problems, and, in severe cases, neurological effects.
Cyanobacteria have also gained attention for their potential use in various applications, including biofuel production, wastewater treatment, and as a source of bioactive compounds with potential pharmaceutical and industrial applications.
It’s important for individuals to be cautious and avoid contact with water bodies experiencing cyanobacterial blooms. Monitoring and management strategies are implemented to mitigate the risks associated with harmful algal blooms, particularly in areas where recreational activities or water supplies may be affected.
The Botanical Description of Blue-Green Algae
1. Appearance: Blue-green algae, scientifically known as Cyanobacteria, exhibit a unique appearance, often resembling greenish-blue film or scum on the surface of bodies of water. Their microscopic size makes them challenging to identify without specialized equipment.
2. Cell Structure: Blue-green algae are prokaryotic organisms, lacking membrane-bound organelles. Their cells contain chlorophyll, allowing them to photosynthesize and contribute to the characteristic blue-green color.
3. Pigment Composition: The blue-green color results from a combination of chlorophyll (green) and phycocyanin (blue). This distinctive pigment composition sets them apart from other types of algae.
4. Habitat: Blue-green algae thrive in various aquatic environments, including freshwater lakes, ponds, and slow-moving rivers. They can also be found in marine environments, adapting to different salinity levels.
5. Colonial Formations: Some species of blue-green algae form colonies, appearing as interconnected cells. These colonies contribute to the appearance of surface scums in water bodies.
6. Filamentous Structure: Certain varieties of blue-green algae exhibit a filamentous structure, forming long chains of cells. This structure enhances their ability to float near the water’s surface.
7. Nitrogen-Fixing Ability: Blue-green algae are unique among algae in their ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen, converting it into a form usable by plants. This nitrogen-fixing capacity contributes to their ecological importance.
8. Environmental Adaptability: Blue-green algae showcase adaptability to various environmental conditions, thriving in both nutrient-rich and nutrient-poor waters. Their ability to photosynthesize allows them to create their own energy.
9. Toxicity Potential: Some species of blue-green algae can produce toxins harmful to aquatic life and humans. Understanding their botanical features is essential for identifying potential risks associated with certain varieties.
The Geographic Distribution of Blue-Green Algae
1. Worldwide Presence: Blue-green algae are found globally, adapting to a wide range of climates. They inhabit freshwater ecosystems, including lakes, ponds, rivers, and reservoirs, as well as marine environments.
2. Freshwater Environments: Many species of blue-green algae are commonly encountered in freshwater bodies, where they form blooms under suitable conditions. These blooms can have ecological impacts and affect water quality.
3. Marine Habitats: While less common in marine environments compared to freshwater, certain blue-green algae species can be found in brackish waters and coastal areas. Their distribution may vary based on salinity levels.
4. Temperature Adaptation: Blue-green algae exhibit adaptability to diverse temperature ranges. They can thrive in both warm tropical waters and cooler temperate regions, showcasing their ability to acclimate.
5. Nutrient Availability: The distribution of blue-green algae is often influenced by nutrient availability. They tend to proliferate in waters with elevated nutrient levels, leading to the formation of blooms under certain conditions.
6. Impact on Water Quality: Blue-green algae can significantly impact water quality. Their overgrowth, especially in the form of harmful algal blooms (HABs), can lead to ecological imbalances and pose risks to aquatic ecosystems.
7. Anthropogenic Factors: Human activities, such as nutrient runoff from agriculture and urban areas, can contribute to the proliferation of blue-green algae. Understanding their distribution helps in managing and mitigating potential environmental issues.
8. Monitoring and Management: Given the potential ecological and health risks associated with blue-green algae, monitoring their distribution is crucial. This aids in implementing management strategies to address issues related to water quality and ecosystem health.
The Chemical Composition of Blue-Green Algae
1. Chlorophyll: Blue-green algae contain chlorophyll, the green pigment essential for photosynthesis. Chlorophyll enables them to convert sunlight into energy, contributing to their role as primary producers in aquatic ecosystems.
2. Phycocyanin: The blue color of blue-green algae is attributed to phycocyanin, a pigment that absorbs light in the blue and red parts of the spectrum. This pigment is crucial for their adaptation to different light conditions.
3. Carotenoids: Carotenoids, including beta-carotene, are present in blue-green algae. These pigments contribute to their overall coloration and serve as antioxidants, protecting the cells from oxidative damage.
4. Proteins: Blue-green algae are rich in proteins, including essential amino acids. This makes them a potential source of protein for aquatic organisms and, in some cases, for human consumption in the form of supplements.
5. Lipids: Lipids, including fatty acids, are part of the chemical composition of blue-green algae. These compounds play a role in energy storage and may have applications in biofuel production.
6. Glycogen: Blue-green algae store excess energy in the form of glycogen. This carbohydrate serves as a reserve for periods when photosynthesis is not actively occurring.
7. Vitamins: Some species of blue-green algae produce vitamins, including B vitamins and vitamin K. These vitamins contribute to the nutritional content of the algae and may have implications for dietary supplements.
8. Minerals: Blue-green algae absorb and accumulate minerals from their aquatic environments. This includes essential minerals such as iron, magnesium, and calcium, which are vital for various physiological processes.
9. Nucleic Acids: Blue-green algae contain nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA, essential for their genetic information and cellular processes. Understanding their genetic makeup is crucial for studying their diversity and evolutionary relationships.
10. Toxins: Certain species of blue-green algae can produce toxins, such as microcystins and cyanotoxins. These toxins pose risks to aquatic life and human health when present in harmful concentrations.
11. Enzymes: Blue-green algae produce enzymes that facilitate various biochemical reactions within their cells. These enzymes are involved in processes such as photosynthesis, nitrogen fixation, and nutrient metabolism.
12 . Phenolic Compounds: Phenolic compounds with antioxidant properties are found in blue-green algae. These compounds contribute to their ability to counteract oxidative stress and play a role in potential health benefits.
Read Also: 17 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Guggul (Commiphora wightii)
The Medicinal Health Benefits Of Blue-Green Algae (Cyanobacteria)

1. Nutritional Supplementation: Blue-green algae are valued for their nutritional content, including proteins, vitamins, and minerals. As a dietary supplement, they offer a source of essential nutrients that can contribute to overall well-being.
2. Antioxidant Properties: The presence of phenolic compounds and carotenoids in blue-green algae contributes to their antioxidant properties. Antioxidants help neutralize free radicals, potentially reducing oxidative stress in the body.
3. Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Some studies suggest that blue-green algae may exhibit anti-inflammatory effects, attributed to the presence of bioactive compounds. These effects could be beneficial in managing inflammatory conditions.
4. Immune System Support: Blue-green algae, with their rich nutritional profile, may support the immune system. The presence of vitamins and minerals contributes to overall immune function and health.
5. Cognitive Health: Certain components of blue-green algae, including omega-3 fatty acids, may support cognitive health. These components are essential for brain function and may have implications for memory and concentration.
6. Energy Boost: Blue-green algae, often considered a superfood, are known for their potential to provide a natural energy boost. The combination of proteins, vitamins, and other nutrients contributes to enhanced vitality.
7. Detoxification: Blue-green algae, particularly those known for their ability to bind to toxins, may aid in detoxification processes. This can be beneficial for individuals seeking natural methods of eliminating harmful substances from the body.
8. Weight Management: The nutritional content of blue-green algae, coupled with their potential role in boosting metabolism, may support weight management efforts. Including them in a balanced diet may contribute to overall fitness.
9. Cardiovascular Health: Omega-3 fatty acids found in certain blue-green algae varieties may have cardiovascular benefits. These fatty acids are associated with maintaining healthy cholesterol levels and supporting heart health.
10. Antiviral Properties: Preliminary research suggests that blue-green algae may possess antiviral properties. Certain compounds in these algae may inhibit the replication of viruses, contributing to immune defense.
11. Wound Healing: Some studies propose that blue-green algae extracts may have wound-healing properties. These potential effects could be attributed to their ability to promote cellular regeneration.
12. Anti-Aging Effects: The antioxidant content of blue-green algae may play a role in mitigating oxidative stress, potentially contributing to anti-aging effects. These effects may manifest in skin health and overall vitality.
13. Muscle Recovery: For individuals engaged in physical activities, blue-green algae may aid in muscle recovery. The protein content and potential anti-inflammatory effects could support the repair of muscle tissues.
14. Blood Sugar Regulation: Preliminary research indicates that certain blue-green algae may have properties that contribute to blood sugar regulation. This aspect holds promise for individuals managing blood glucose levels.
15. Adaptogenic Properties: Blue-green algae are sometimes considered adaptogens, helping the body adapt to stress. The nutritional and bioactive components may contribute to overall stress resilience.
16. Allergen Management: Some studies propose that blue-green algae supplements may have a role in managing allergic reactions. Their potential anti-inflammatory effects could contribute to alleviating allergy symptoms.
17. Joint Health: Omega-3 fatty acids and anti-inflammatory properties in blue-green algae may offer benefits for joint health. These effects could be relevant for individuals managing conditions like arthritis.
18. Hormonal Balance: The nutritional content of blue-green algae, including essential fatty acids, may contribute to hormonal balance. This aspect is relevant for overall reproductive and endocrine health.
19. Skin Health: Antioxidants and certain bioactive compounds in blue-green algae may promote skin health. Incorporating these algae into skincare routines or supplements may contribute to a radiant complexion.
The Methods of Usage to Achieve the Provided Health Benefits Of Blue-Green Algae (Cyanobacteria)
1. Dietary Supplements: Blue-green algae are commonly consumed in the form of dietary supplements. Capsules, tablets, or powders containing dried and processed algae provide a convenient way to incorporate their nutritional benefits into daily routines.
2. Smoothies and Juices: Adding blue-green algae to smoothies or juices is a popular method of consumption. Blending them with fruits, vegetables, or other superfoods enhances taste while maximizing nutritional intake.
3. Culinary Applications: Some varieties of blue-green algae, such as Spirulina, are used in culinary applications. They can be incorporated into recipes for soups, salads, or energy bars, providing a nutrient-dense boost.
4. Topical Skincare: Extracts or formulations containing blue-green algae are used in skincare products. Creams, serums, or masks with these extracts may offer benefits for skin health, contributing to a vibrant complexion.
5. Detoxification Protocols: Blue-green algae, known for their potential to bind to toxins, are included in detoxification protocols. This may involve specific formulations or regimens designed to support the body’s natural detox processes.
6. Inhalation Therapy: Some individuals explore the potential respiratory benefits of blue-green algae through inhalation therapy. Vaporizing or diffusing extracts may offer respiratory support, although research in this area is limited.
7. Dietary Integration: Including blue-green algae as part of a balanced diet is a natural way to experience their health benefits. This involves incorporating algae-containing foods into meals for sustained nutritional intake.
8. Fitness Supplements: Athletes and fitness enthusiasts may use blue-green algae supplements to support muscle recovery and overall performance. The protein content and potential anti-inflammatory effects are relevant in this context.
9. Nutrient-Rich Snacks: Blue-green algae can be incorporated into nutrient-rich snacks, such as energy bars or trail mix. These snacks offer a convenient way to enjoy the benefits of these algae on the go.
10. Herbal Blends: Blue-green algae can be combined with other herbs or superfoods to create customized herbal blends. This allows individuals to tailor their supplementation to specific health goals.
The Side Effects Of Using Blue-Green Algae Medicinal Plant
1. Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to blue-green algae supplements or extracts. It’s advisable to perform a patch test before widespread use, especially for those with known allergies.
2. Contamination Risks: Blue-green algae, when harvested from natural water bodies, may carry contaminants such as microcystins
3. Gastrointestinal Issues: In some cases, the consumption of blue-green algae supplements or high doses may lead to gastrointestinal issues, including nausea, stomach cramps, or diarrhea. Adhering to recommended dosage guidelines helps minimize these effects.
4. Interactions with Medications: Blue-green algae may interact with certain medications, including immunosuppressants or medications affecting the immune system. Individuals on medication should consult healthcare professionals before incorporating these supplements into their routines.
5. Heavy Metal Accumulation: Blue-green algae have the potential to accumulate heavy metals from their environment. Continuous consumption, especially from unregulated sources, may lead to increased exposure to heavy metals, posing health risks.
6. Risk of Overconsumption: Excessive intake of blue-green algae supplements may lead to an overabundance of specific nutrients, potentially causing imbalances. Following recommended dosage guidelines is crucial to avoid adverse effects.
7. Toxin Production: While not all blue-green algae produce toxins, certain species can generate harmful substances like microcystins and cyanotoxins. Consuming contaminated blue-green algae can have detrimental effects on liver health.
8. Photosensitivity: Some individuals may experience increased sensitivity to sunlight after using blue-green algae supplements. This photosensitivity could result in skin irritation or other adverse reactions when exposed to sunlight.
9. Lack of Regulation: The lack of stringent regulation in the production of blue-green algae supplements raises concerns about quality control. Choosing reputable and well-established brands ensures a higher likelihood of safety and efficacy.
10. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Limited research exists on the safety of blue-green algae during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should exercise caution and consult healthcare professionals before using these supplements.
11. Potential Bacterial Contamination: Blue-green algae harvested from natural water bodies may carry bacterial contaminants. Ensuring that the source is free from harmful bacteria is crucial for preventing infections.
12. Risk of Misidentification: Harvesting wild blue-green algae for personal use carries the risk of misidentification. Confusing toxic species with non-toxic ones can have severe consequences. Reliable sources and expert guidance are essential.
13. Environmental Impact: Intensive harvesting of blue-green algae from natural environments may have ecological consequences. Responsible and sustainable harvesting practices are necessary to preserve aquatic ecosystems.
14. Impact on Liver Function: In cases of exposure to blue-green algae toxins, particularly microcystins, there is a risk of hepatotoxicity. These toxins can adversely affect liver function and pose serious health threats.
15. Lack of Standardization: The lack of standardized guidelines for blue-green algae supplements contributes to variability in product quality. Standardization ensures consistent potency and reduces the risk of unintended side effects.
16. Respiratory Irritation: Inhaling blue-green algae extracts, especially during certain therapeutic practices, may lead to respiratory irritation. Adequate ventilation and cautious inhalation practices are essential.
17. Individual Sensitivity: Responses to blue-green algae can vary among individuals. Factors such as overall health, existing medical conditions, and medications being taken may influence how the supplements affect different people.
Read Also: 17 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Sweet Melilot (Melilotus officinalis)
The Scientific Research and Studies of Blue-Green Algae (Cyanobacteria)

1. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Scientific research has explored the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of blue-green algae. Compounds such as phycocyanin and phenolic compounds contribute to their potential as natural anti-inflammatory agents.
2. Nutritional Composition: Numerous studies have investigated the nutritional composition of blue-green algae. These organisms are recognized for their rich content of proteins, essential amino acids, vitamins, and minerals.
3. Immune-Modulating Effects: Some studies suggest that blue-green algae may have immune-modulating effects. Components like beta-glucans and phycocyanin are believed to contribute to immune system support.
4. Cognitive Benefits: Research has explored the cognitive benefits of blue-green algae, particularly in relation to memory and concentration. Omega-3 fatty acids and other neurologically relevant compounds may play a role.
5. Cardiovascular Health: Scientific investigations have delved into the cardiovascular health benefits of blue-green algae. Studies suggest potential effects on lipid profiles and blood pressure regulation.
6. Detoxification Potential: Certain compounds in blue-green algae have been studied for their potential detoxification effects. This includes their ability to bind to and eliminate toxins from the body.
7. Antiviral Properties: Preliminary research indicates that blue-green algae may exhibit antiviral properties. Compounds within these algae may interfere with viral replication, contributing to antiviral effects.
8. Anti-Cancer Potential: Scientific studies have explored the anti-cancer potential of blue-green algae. Compounds like phycocyanin and beta-carotene are investigated for their role in inhibiting cancer cell growth.
9. Wound Healing Effects: Some research suggests that extracts from certain blue-green algae may have wound-healing effects. These effects could be attributed to their ability to promote cell regeneration.
10. Impact on Metabolic Health: Studies have investigated the impact of blue-green algae on metabolic health. Components like chlorophyll and omega-3 fatty acids may play a role in metabolic regulation.
11. Effects on Respiratory Health: Scientific research has explored the effects of blue-green algae on respiratory health. Inhalation therapy and potential benefits for individuals with respiratory conditions have been subjects of investigation.
The Safety Precautions and Recommendations In Using Blue-Green Algae (Cyanobacteria) Medicinal Plant
1. Quality and Source: Choose blue-green algae supplements from reputable and well-established brands. Ensuring the quality and purity of the product minimizes the risk of contamination and maximizes safety.
2. Dosage Guidelines: Adhere to recommended dosage guidelines provided by healthcare professionals or product labels. Avoid exceeding recommended doses to prevent potential adverse effects.
3. Consultation with Healthcare Professionals: Before incorporating blue-green algae supplements into health routines, especially for individuals with existing health conditions or taking medications, consult healthcare professionals for personalized guidance.
4. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Pregnant and breastfeeding individuals should exercise caution with blue-green algae supplements. Consultation with healthcare providers is essential to assess safety during these periods.
5. Allergy Testing: Perform a patch test before widespread use of blue-green algae supplements, especially for individuals with known allergies. This precaution helps identify potential allergic reactions.
6. Monitoring for Side Effects: Be vigilant for any side effects or adverse reactions while using blue-green algae supplements. If unusual symptoms occur, discontinue use and seek medical advice.
7. Periodic Assessments: Periodically reassess the use of blue-green algae supplements, especially if health conditions change or new symptoms arise. Adjust usage based on individual needs and professional recommendations.
8. Children’s Usage: Blue-green algae supplements are not recommended for children without the guidance of healthcare professionals. Parents or caregivers should seek professional advice for safe and appropriate use.
9. Interactions with Medications: Individuals taking medications, especially immunosuppressants or drugs affecting the immune system, should inform healthcare providers about blue-green algae use to assess potential interactions.
10. Responsible Harvesting Practices: If harvesting blue-green algae from natural environments, practice responsible and sustainable harvesting to minimize ecological impact and reduce the risk of contamination.
11. Sun Sensitivity: Be aware of potential photosensitivity associated with blue-green algae supplements. Take precautions, such as using sunscreen and protective clothing, to avoid adverse reactions when exposed to sunlight.
12. Environmental Awareness: Individuals practicing inhalation therapy with blue-green algae extracts should ensure proper ventilation and be mindful of potential respiratory irritation. Environmental awareness is crucial during such practices.
FAQs About Blue-Green Algae (Cyanobacteria) Medicinal Plant
1. Is Blue-Green Algae Safe for Regular Consumption?
Blue-green algae can be safe for regular consumption when obtained from reputable sources and used in adherence to recommended dosage guidelines. However, individual responses may vary, and consultation with healthcare professionals is advisable.
2. Can Blue-Green Algae Be Used During Pregnancy?
Pregnant individuals should exercise caution when using blue-green algae supplements. Consultation with healthcare providers is essential to assess safety during pregnancy. It’s advisable to avoid use unless under professional guidance.
3. What Precautions Should Be Taken for Individuals with Allergies?
Individuals with known allergies should perform a patch test before widespread use of blue-green algae supplements. This precaution helps identify potential allergic reactions and informs safe usage.
4. How Can Blue-Green Algae Be Used for Detoxification?
Blue-green algae, known for potential detoxification effects, can be incorporated into detox protocols. This may involve specific formulations or regimens designed to support the body’s natural detox processes.
5. Can Blue-Green Algae Interact with Medications?
Blue-green algae may interact with certain medications, particularly those affecting the immune system. Individuals on medication should inform healthcare providers about blue-green algae use to assess potential interactions.
6. Is Blue-Green Algae Safe for Children?
Blue-green algae supplements are not recommended for children without the guidance of healthcare professionals. Parents or caregivers should consult with experts to determine safe and appropriate use for children.
7. Can Blue-Green Algae Cause Photosensitivity?
Yes, blue-green algae supplements may cause photosensitivity in some individuals. Precautions, such as using sunscreen and protective clothing, should be taken to avoid adverse reactions when exposed to sunlight.
8. Are Blue-Green Algae Supplements Regulated?
Answer: The regulation of blue-green algae supplements varies, and quality control may be a concern. Choosing supplements from reputable and well-established brands enhances the likelihood of safety and efficacy.
9. How Can Blue-Green Algae Be Used for Respiratory Support?
Blue-green algae’s potential respiratory benefits may be explored through methods like inhalation therapy. Vaporizing or diffusing extracts may offer respiratory support, but cautious inhalation practices are essential.
10. Can Blue-Green Algae Be Used for Weight Management?
The nutritional content of blue-green algae, coupled with potential effects on metabolism, may support weight management efforts. Including them in a balanced diet may contribute to overall fitness.
11. Is Blue-Green Algae Suitable for Individuals with Joint Issues?
Blue-green algae, with potential anti-inflammatory properties, may offer benefits for joint health. These effects could be relevant for individuals managing conditions like arthritis.
12. Can Blue-Green Algae Be Used in Skincare?
Yes, extracts or formulations containing blue-green algae are used in skincare products. Creams, serums, or masks with these extracts may offer benefits for skin health, contributing to a vibrant complexion.
13. Is Blue-Green Algae Safe for Long-Term Use?
Long-term use of blue-green algae supplements should be approached with caution. Regular monitoring for side effects and periodic reassessment of usage are advisable for responsible and informed consumption.
14. Can Blue-Green Algae Be Used During Breastfeeding?
Breastfeeding individuals should exercise caution when using blue-green algae supplements. Consultation with healthcare providers is essential to assess safety during breastfeeding, and use should be avoided without professional guidance.
15. Are There Specific Recommendations for Inhalation Therapy with Blue-Green Algae?
Individuals exploring inhalation therapy with blue-green algae extracts should ensure proper ventilation and be aware of potential respiratory irritation. Environmental awareness and cautious inhalation practices are crucial.
16. Can Blue-Green Algae Be Used as a Replacement for Professional Medical Advice?
Blue-green algae should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Individuals with health concerns should seek guidance from healthcare providers for personalized recommendations.
17. How Can Blue-Green Algae Be Incorporated into Culinary Practices?
Some varieties of blue-green algae, such as Spirulina, can be incorporated into culinary practices. They can be
Do you have any questions, suggestions, or contributions? If so, please feel free to use the comment box below to share your thoughts. We also encourage you to kindly share this information with others who might benefit from it. Since we can’t reach everyone at once, we truly appreciate your help in spreading the word. Thank you very much for your support and for sharing!
Disclaimer: This article is for educational and informational purposes only. The health benefits described are based on scientific research and traditional knowledge. They ayre not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a healthcare professional before using any herb or natural remedy for medical purposes.
Read Also: Operation and Maintenance for Comminutor and Grinder