Epigaea repens, commonly known as Trailing Arbutus or Mayflower, is a species of flowering evergreen plant native to eastern North America. It is primarily found in deciduous forests, woodland edges, and rocky slopes from Nova Scotia to Florida and west to Minnesota. Belonging to the Ericaceae family, this low-growing perennial herb is cherished for its delicate beauty and sweet fragrance.
Trailing Arbutus typically forms a creeping mat of trailing stems, with glossy, leathery leaves that are dark green and oval-shaped. The leaves are arranged alternately along the stems and often have a slightly serrated edge. This plant blooms in early spring, producing clusters of small, urn-shaped flowers that vary in color from white to pink. The blossoms are highly fragrant, emitting a sweet, spicy scent that attracts pollinators like bees and butterflies.
Due to its early blooming period and attractive flowers, Trailing Arbutus holds cultural significance and is celebrated as a symbol of spring and renewal. It has been the state flower of Massachusetts since 1918 and is also the provincial flower of Nova Scotia.
In addition to its ornamental value, Trailing Arbutus has been used in traditional medicine by indigenous peoples. It was historically brewed into teas or used topically to treat various ailments, including respiratory issues and skin conditions. However, it’s important to note that the plant contains compounds that can be toxic if ingested in large quantities.
While Trailing Arbutus is prized for its beauty and fragrance, it is also a vulnerable species in many regions due to habitat loss, overharvesting, and other environmental threats. Conservation efforts are underway to protect and preserve this beloved woodland plant for future generations to enjoy.
The Botanical Description of Epigaea repens
1. Leaf Structure: Epigaea repens, commonly known as Trailing Arbutus or Mayflower, features leathery, evergreen leaves arranged alternately on trailing stems. The leaves are oval-shaped with a shiny, dark green surface.
2. Flower Appearance: The plant produces delicate, urn-shaped flowers with five petals. These flowers vary in color from pink to white and emit a sweet, fragrant aroma. The blooming period typically occurs in early spring.
3. Stem Characteristics: Trailing Arbutus exhibits creeping or trailing stems that spread along the ground. The stems root at nodes, allowing the plant to form dense, low mats in its natural habitat.
4. Root System: The root system of Epigaea repens is fibrous and shallow, adapting well to the forest floor or well-drained soils. This enables the plant to efficiently extract nutrients from its surroundings.
5. Size and Height: The plant is relatively low-growing, reaching a height of 6 to 12 inches. The compact nature of Trailing Arbutus makes it well-suited for ground cover in woodland environments.
6. Fruit Formation: After flowering, Epigaea repens produces small, dry, capsule-like fruits that contain tiny seeds. These capsules contribute to the plant’s reproductive cycle.
7. Habitat Preferences: Trailing Arbutus thrives in acidic soils and is commonly found in coniferous and deciduous forests, particularly in North America. It prefers shaded areas with dappled sunlight.
8. Adaptations to Shade: The plant has developed adaptations to low-light conditions, such as its ability to grow beneath the canopy of trees. This allows Epigaea repens to flourish in the understory of forests.
9. Winter Characteristics: Trailing Arbutus retains its leaves throughout the winter, providing evergreen coverage even in colder months. This adaptation contributes to its visual appeal in seasonal landscapes.
10. Reproductive Strategy: Epigaea repens primarily reproduces through both seeds and vegetative propagation. The creeping stems root at nodes, creating new plants and contributing to the species’ expansion.
The Geographic Distribution of Epigaea repens
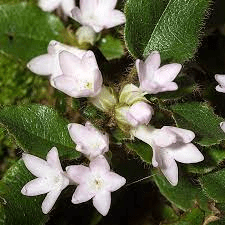
1. North American Range: Epigaea repens is native to North America, particularly widespread in the eastern United States and parts of Canada. It can be found from Nova Scotia to Florida and west to the Great Lakes region.
2. Habitat Diversity: Trailing Arbutus thrives in various habitats, including mixed woodlands, pine barrens, and sandy soils. Its adaptability contributes to its extensive distribution across diverse ecosystems.
3. Altitudinal Range: While primarily a lowland species, Epigaea repens can be found at varying altitudes, ranging from sea level to higher elevations in mountainous regions.
4. Soil Preferences: The plant shows a preference for acidic soils, often associated with coniferous forests. It is commonly found in well-drained, sandy or loamy soils.
5. Climate Tolerance: Trailing Arbutus is well-adapted to temperate climates, with its range extending from the cold conditions of northern regions to the more temperate climates in the southern parts of its distribution.
6. Understory Habitat: The plant is frequently encountered in the understory of deciduous and coniferous forests, thriving in the dappled sunlight that filters through the canopy.
7. Eastern Coastal Plains: In the United States, Epigaea repens is notably present along the eastern coastal plains, contributing to the biodiversity of these ecosystems.
8. Biotic Associations: Trailing Arbutus interacts with various plant and animal species within its habitat, forming ecological connections and playing a role in the broader ecosystem dynamics.
9. Conservation Concerns: Despite its wide distribution, Trailing Arbutus faces conservation challenges due to habitat loss, climate change, and human activities. Conservation efforts aim to preserve its natural habitats.
10. Cultural Significance: The geographic distribution of Epigaea repens also intersects with its cultural importance, as it has been celebrated in literature and folklore, especially in regions where it is endemic.
11. Western Range: While more commonly found in the eastern United States, Epigaea repens also extends its range into parts of the western United States, including regions of California and Oregon.
12. Microhabitats: Within its broader distribution, Trailing Arbutus occupies various microhabitats, such as rocky outcrops, forest edges, and stream banks, showcasing its adaptability to different environmental conditions.
13. Global Distribution: While primarily native to North America, Trailing Arbutus has been introduced to other parts of the world, including parts of Europe and Asia, where it is cultivated for its ornamental value.
The Chemical Composition of Epigaea repens
1. Arbutin Content: Epigaea repens contains arbutin, a glycoside that has been studied for its potential anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Arbutin is also present in other plant species and is known for its skin-brightening effects.
2. Flavonoids: Trailing Arbutus contains various flavonoids, including quercetin and kaempferol. Flavonoids are antioxidants that contribute to the plant’s defense against oxidative stress.
3. Essential Oils: The plant produces essential oils with aromatic compounds. These oils contribute to the characteristic fragrance of Epigaea repens and may have antimicrobial properties.
4. Tannins: Tannins are present in the leaves of Trailing Arbutus. These polyphenolic compounds contribute to the astringent properties of the plant and have been studied for their potential health benefits.
5. Terpenes: The presence of terpenes, including monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes, contributes to the aromatic profile of the plant. Terpenes have been studied for their role in plant defense mechanisms.
6. Phenolic Compounds: Epigaea repens contains phenolic compounds, which are known for their antioxidant properties. These compounds contribute to the plant’s ability to neutralize free radicals.
7. Alkaloids: While present in trace amounts, alkaloids have been identified in Trailing Arbutus. Alkaloids are nitrogen-containing compounds that may have physiological effects.
8. Catechins: Catechins, a type of flavonoid, are found in Epigaea repens. Catechins have been studied for their potential cardiovascular and anti-inflammatory benefits.
9. Coumarins: Coumarins are present in the chemical composition of Trailing Arbutus. These compounds have diverse biological activities and are often studied for their pharmacological potential.
10. Lignans: Some studies have identified lignans in Epigaea repens. Lignans are phytochemicals with potential antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
11. Resin: The presence of resinous compounds in Trailing Arbutus contributes to its traditional uses and may have antimicrobial properties.
12. Vitamins: Trailing Arbutus contains vitamins, including vitamin C, which contributes to its overall nutritional profile.
13. Minerals: The plant may contain minerals such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium, providing additional nutritional value.
Read Also: 17 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Apocynum cannabinum (Indian Hemp)
The Medicinal Health Benefits Of Epigaea repens (Trailing Arbutus)

1. Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Epigaea repens has been traditionally used for its anti-inflammatory properties, which may help alleviate symptoms associated with inflammatory conditions such as arthritis and rheumatism.
2. Antioxidant Action: The presence of flavonoids and other antioxidants in Trailing Arbutus contributes to its potential to neutralize free radicals, protecting cells from oxidative damage and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
3. Respiratory Health: Infusions made from the leaves of Epigaea repens have been used to address respiratory ailments such as coughs, bronchitis, and congestion. The plant’s expectorant properties help loosen mucus and facilitate easier breathing.
4. Urinary Tract Health: Trailing Arbutus is known for its diuretic properties, which promote urine production and help flush out toxins from the body. This may be beneficial for supporting urinary tract health and preventing urinary tract infections.
5. Digestive Aid: Consuming Trailing Arbutus tea or extracts may aid digestion and relieve symptoms of indigestion, bloating, and gastrointestinal discomfort. The plant’s mild laxative effects can help promote regular bowel movements.
6. Antiseptic Action: The antimicrobial properties of Epigaea repens make it useful as a topical antiseptic for minor cuts, scrapes, and skin infections. Applying a poultice or wash made from the leaves may help prevent infection and promote wound healing.
7. Circulatory Support: Trailing Arbutus is believed to have tonic effects on the circulatory system, promoting healthy blood flow and cardiovascular function. Regular consumption of the plant may help maintain optimal heart health.
8. Menstrual Support: Traditional herbalists recommend Trailing Arbutus for alleviating menstrual cramps and regulating menstrual cycles. Its relaxant properties may help ease tension and discomfort associated with menstruation.
9. Immune Boost: The immune-stimulating properties of Epigaea repens may help strengthen the body’s natural defenses against infections and illnesses. Incorporating the plant into one’s diet or using it as a herbal remedy during cold and flu season may support overall immune function.
10. Stress Reduction: Trailing Arbutus is valued for its calming and relaxing effects on the nervous system. Drinking tea made from the leaves or inhaling the plant’s aroma may help reduce stress, anxiety, and tension.
11. Skin Care: The astringent properties of Epigaea repens make it beneficial for skincare purposes. It can help tighten and tone the skin, reduce excess oiliness, and improve the appearance of pores.
12. Antifungal Action: Trailing Arbutus has been traditionally used to treat fungal infections of the skin and nails. Its antifungal properties may help inhibit the growth of fungi responsible for conditions such as athlete’s foot and ringworm.
13. Anti-aging Effects: The antioxidant compounds found in Trailing Arbutus help protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals, which can contribute to premature aging. Regular use of the plant may help maintain youthful-looking skin.
14. Anti-diabetic Potential: Some studies suggest that Epigaea repens may have hypoglycemic effects, helping to lower blood sugar levels. However, more research is needed to confirm its efficacy as a treatment for diabetes.
15. Allergy Relief: Trailing Arbutus has been used in traditional medicine to alleviate symptoms of seasonal allergies, such as sneezing, nasal congestion, and itching. Its anti-inflammatory properties may help reduce allergic reactions.
16. Detoxification: The diuretic properties of Epigaea repens support the body’s natural detoxification processes by promoting the elimination of waste products and toxins through the urinary system.
17. Respiratory Health: Trailing Arbutus is known for its expectorant properties, which can help relieve coughs, congestion, and other respiratory symptoms. It may also soothe sore throats and promote overall respiratory wellness.
The Methods of Usage to Achieve the Provided Health Benefits Of Epigaea repens (Trailing Arbutus)
1. Herbal Tea: Prepare a decoction or infusion using dried Trailing Arbutus leaves to enjoy its medicinal benefits. Drink the tea regularly to support respiratory health, digestion, and overall well-being.
2. Tinctures and Extracts: Tinctures and liquid extracts made from Trailing Arbutus can be taken orally to access its therapeutic properties. Follow dosage instructions provided by a qualified herbalist or healthcare practitioner.
3. Topical Applications: Apply a poultice, compress, or infused oil made from Trailing Arbutus leaves directly to the skin to treat wounds, infections, and skin conditions. Ensure the affected area is clean before application.
4. Inhalation Therapy: Inhale the steam from a pot of boiling water infused with Trailing Arbutus leaves to relieve respiratory congestion, sinusitis, and bronchial discomfort. Cover your head with a towel to trap the steam and inhale deeply.
5. Bath Additives: Add dried Trailing Arbutus leaves or extracts to your bathwater to promote relaxation, soothe sore muscles, and improve circulation. Allow the botanicals to infuse the water before soaking in the bath.
6. Dietary Supplement: Incorporate Trailing Arbutus leaves or extracts into your diet as a nutritional supplement. Add dried leaves to soups, stews, or salads for added flavor and health benefits.
7. Aromatherapy: Use Trailing Arbutus essential oil in aromatherapy diffusers or oil burners to create a calming and uplifting atmosphere. The aromatic properties of the plant can help reduce stress and promote relaxation.
8. Capsules and Tablets: Trailing Arbutus supplements are available in capsule or tablet form for convenient consumption. Follow the recommended dosage instructions provided by the manufacturer or healthcare professional.
9. Herbal Combinations: Combine Trailing Arbutus with other complementary herbs to enhance its therapeutic effects. Consult with a qualified herbalist or naturopathic doctor for personalized herbal formulations.
10. Traditional Poultices: Prepare a poultice using fresh or dried Trailing Arbutus leaves and apply it directly to the skin to alleviate inflammation, pain, and swelling. Secure the poultice with a bandage and leave it in place for several hours.
11. Infused Oils: Create infused oils by steeping Trailing Arbutus leaves in carrier oils such as olive oil or coconut oil. Use the infused oil topically for massage, moisturizing, and healing purposes.
12. Herbal Baths: Make a strong infusion of Trailing Arbutus leaves and add it to your bath for a therapeutic soak. The aromatic steam and herbal properties of the plant can help relax muscles and calm the mind.
The Side Effects Of Using Epigaea repens Medicinal Plant
1. Digestive Discomfort: In some individuals, consuming large amounts of Trailing Arbutus tea or extracts may cause gastrointestinal upset, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Start with small doses to assess tolerance.
2. Allergic Reactions: People with known allergies to plants in the Ericaceae family, such as blueberries and cranberries, may experience allergic reactions to Trailing Arbutus. Discontinue use if any adverse symptoms occur.
3. Skin Sensitivity: Applying Trailing Arbutus poultices or infused oils to the skin may cause irritation or allergic dermatitis in sensitive individuals. Conduct a patch test before widespread use and dilute essential oils as needed.
4. Drug Interactions: Trailing Arbutus may interact with certain medications, including blood thinners, diuretics, and diabetes medications. Consult with a healthcare professional before using the plant alongside prescription drugs.
5. Pregnancy and Lactation: Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid using Trailing Arbutus due to a lack of safety data. The plant’s potential effects on hormonal balance and fetal development are not well understood.
6. Liver Toxicity: Some herbalists caution against long-term or excessive use of Trailing Arbutus due to the potential risk of liver toxicity. Monitor liver function regularly if using the plant for an extended period.
7. Central Nervous System Effects: Large doses of Trailing Arbutus may have sedative effects on the central nervous system, causing drowsiness, dizziness, or impaired cognitive function. Use caution when operating heavy machinery or driving.
8. Hypoglycemia Risk: Individuals with diabetes or hypoglycemia should use Trailing Arbutus with caution, as the plant may lower blood sugar levels. Monitor blood glucose levels closely and adjust medication doses as needed.
9. Renal Impairment: Excessive use of Trailing Arbutus may put strain on the kidneys, especially in individuals with pre-existing renal impairment. Stay hydrated and avoid prolonged or high-dose use of the plant.
10. Photosensitivity: Some individuals may experience increased sensitivity to sunlight (photosensitivity) after topical application of Trailing Arbutus preparations. Use sunscreen and protective clothing when exposed to the sun.
11. Potassium Imbalance: Trailing Arbutus has diuretic properties that can lead to potassium loss in the body. Monitor potassium levels, especially in individuals with cardiovascular or renal conditions.
12. Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Long-term use of Trailing Arbutus may increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding, particularly in individuals with a history of ulcers or other digestive disorders. Use with caution and discontinue use if bleeding occurs.
13. Respiratory Effects: Inhalation of Trailing Arbutus steam or dust may irritate the respiratory tract and exacerbate existing respiratory conditions such as asthma or bronchitis. Use in well-ventilated areas and discontinue use if respiratory symptoms worsen.
14. Drug Sensitization: Prolonged use of Trailing Arbutus may lead to sensitization to certain medications or environmental allergens, increasing the risk of allergic reactions. Use the plant cautiously and discontinue use if sensitivity develops.
The Scientific Research and Studies of Epigaea repens
Read Also: 17 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Adiantum capillus-veneris (Maidenhair Fern)

1. Anti-Inflammatory Activity: Research suggests that Epigaea repens exhibits anti-inflammatory properties due to its ability to inhibit pro-inflammatory enzymes and cytokines, potentially offering therapeutic benefits for inflammatory conditions.
2. Antioxidant Effects: Studies have shown that Trailing Arbutus extracts possess significant antioxidant activity, scavenging free radicals and reducing oxidative stress in cells. These antioxidant properties may contribute to the plant’s health benefits.
3. Antimicrobial Action: Epigaea repens has demonstrated antimicrobial activity against various pathogens, including bacteria and fungi. Its constituents may help inhibit the growth of harmful microorganisms and prevent infections.
4. Diuretic Properties: Research indicates that Trailing Arbutus has diuretic effects, increasing urine production and promoting the elimination of excess fluids and toxins from the body. This diuretic action may support kidney health and urinary tract function.
5. Wound Healing Potential: Some studies suggest that Trailing Arbutus extracts may promote wound healing by accelerating the closure of skin wounds, reducing inflammation, and enhancing tissue regeneration. Further research is needed to explore its potential applications in wound care.
6. Anti-diabetic Effects: Preliminary evidence suggests that Epigaea repens may have hypoglycemic effects, lowering blood sugar levels in animal models of diabetes. However, more research is needed to elucidate the mechanisms and potential clinical applications of this effect.
The Safety Precautions and Recommendations In Using Epigaea repens Medicinal Plant
1. Consultation with Healthcare Provider: Before using Epigaea repens or any herbal remedy, consult with a qualified healthcare provider, especially if you have pre-existing medical conditions, are pregnant or breastfeeding, or are taking medications.
2. Dosage Guidance: Follow recommended dosage guidelines provided by herbalists, naturopaths, or product labels when using Trailing Arbutus preparations. Avoid exceeding recommended doses to minimize the risk of adverse effects.
3. Allergy Testing: Conduct a patch test before using Trailing Arbutus topically to check for skin sensitivity or allergic reactions. Apply a small amount of the product to a small area of skin and monitor for any adverse reactions.
4. Quality and Purity: Purchase Trailing Arbutus products from reputable sources to ensure quality, purity, and safety. Look for products that have undergone third-party testing and adhere to good manufacturing practices (GMP).
5. Monitoring for Side Effects: Pay attention to any side effects or adverse reactions that may occur while using Trailing Arbutus. Discontinue use and seek medical attention if you experience any concerning symptoms.
6. Avoiding Long-Term Use: Limit the duration of Trailing Arbutus use, especially in high doses or for prolonged periods. Extended use may increase the risk of side effects and complications.
7. Drug Interactions: Be aware of potential interactions between Trailing Arbutus and medications you are taking. Consult with a healthcare provider to determine if there are any contraindications or precautions to consider.
8. Pregnancy and Lactation: Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid using Trailing Arbutus due to a lack of safety data. Consult with a healthcare provider before using herbal remedies during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
9. Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels: If you have diabetes or hypoglycemia, monitor your blood sugar levels closely when using Trailing Arbutus, as it may affect blood glucose levels. Adjust medication doses as needed under medical supervision.
10. Kidney Function Monitoring: Individuals with kidney conditions should use Trailing Arbutus with caution, as it has diuretic effects that may affect kidney function. Stay hydrated and monitor renal function regularly.
11. Sun Protection: If using Trailing Arbutus topically, protect your skin from sunlight exposure, as it may increase photosensitivity and the risk of sunburn. Apply sunscreen and wear protective clothing when outdoors.
12. Discontinuation of Use: Discontinue use of Trailing Arbutus if you experience any adverse reactions, such as allergic symptoms, digestive upset, or skin irritation. Seek medical advice if symptoms persist or worsen.
FAQs About Epigaea repens Medicinal Plant
1. Is Trailing Arbutus Safe for Children?
While Trailing Arbutus is generally considered safe for adults when used appropriately, it is not recommended for use in children without consulting a healthcare provider. Dosage and safety considerations may differ for pediatric populations.
2. Can Trailing Arbutus Be Used During Pregnancy?
Pregnant women should avoid using Trailing Arbutus due to a lack of safety data. The potential risks to maternal and fetal health are not well understood, so it is best to err on the side of caution and avoid use during pregnancy.
3. How Should Trailing Arbutus Products Be Stored?
Store Trailing Arbutus products, such as dried leaves, teas, tinctures, and extracts, in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture. Proper storage helps maintain potency and shelf life.
4. Are There Any Contraindications for Trailing Arbutus Use?
Individuals with known allergies to plants in the Ericaceae family, as well as those with certain medical conditions such as kidney disease, diabetes, or liver disorders, should use Trailing Arbutus with caution. Consult with a healthcare provider before use.
5. Can Trailing Arbutus Interact with Medications?
Trailing Arbutus may interact with certain medications, including blood thinners, diuretics, and diabetes medications. Consult with a healthcare provider before using Trailing Arbutus alongside prescription drugs to avoid potential interactions.
6. How Long Does It Take to Experience the Health Benefits of Trailing Arbutus?
The time it takes to experience the health benefits of Trailing Arbutus may vary depending on factors such as dosage, frequency of use, individual health status, and the specific health condition being addressed. Consistent use over time may yield gradual improvements.
7. Can Trailing Arbutus Be Used to Treat Acne?
Some people use Trailing Arbutus topically to help alleviate acne symptoms due to its astringent and antimicrobial properties. However, individual responses may vary, and it is essential to patch test and use caution to avoid skin irritation.
8. Is Trailing Arbutus Legal to Harvest and Use?
In regions where Trailing Arbutus grows abundantly, it may be legal to harvest for personal use. However, it is important to check local regulations and obtain permission if harvesting on public or protected lands. Sustainable harvesting practices are encouraged to preserve wild populations.
9. Can Trailing Arbutus Be Used as a Food Ingredient?
While Trailing Arbutus has a history of traditional use as a food source among certain Indigenous communities, it is not commonly consumed as a food ingredient today. Some herbalists may incorporate dried leaves or extracts into culinary recipes for flavor or added health benefits.
10. What Should I Do If I Experience Adverse Reactions to Trailing Arbutus?
If you experience adverse reactions such as allergic symptoms, gastrointestinal upset, or skin irritation after using Trailing Arbutus, discontinue use immediately and seek medical advice. Be prepared to provide information about the product used and the symptoms experienced for proper evaluation.
Do you have any questions, suggestions, or contributions? If so, please feel free to use the comment box below to share your thoughts. We also encourage you to kindly share this information with others who might benefit from it. Since we can’t reach everyone at once, we truly appreciate your help in spreading the word. Thank you very much for your support and for sharing!
Disclaimer: This article is for educational and informational purposes only. The health benefits described are based on scientific research and traditional knowledge. They ayre not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a healthcare professional before using any herb or natural remedy for medical purposes.

