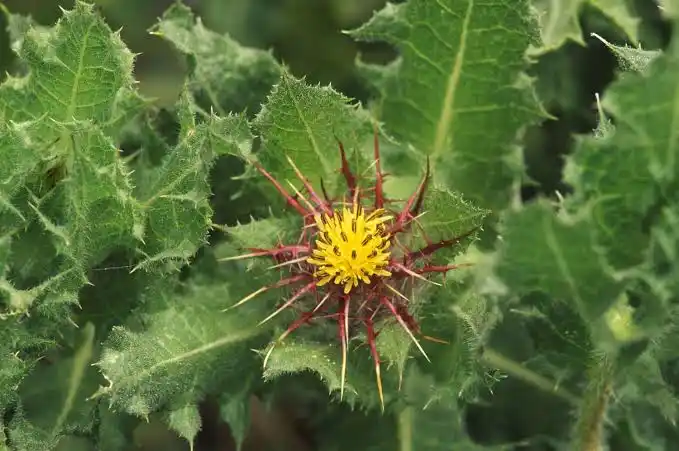
Holy Thistle, scientifically known as Cnicus benedictus, is a herbaceous plant that has a long history of medicinal use, particularly in traditional and herbal medicine.
Also commonly referred to as Blessed Thistle, this plant belongs to the Asteraceae family and is native to the Mediterranean region. Its botanical name, “Cnicus benedictus,” reflects its historical association with religious and medicinal practices.
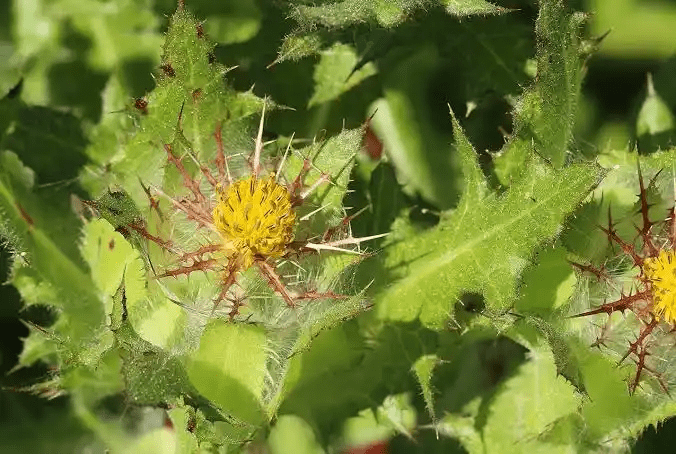
The plant is characterized by its spiny leaves, yellow flowers, and a distinctive, slightly bitter aroma. Holy Thistle has been utilized for centuries for its purported health benefits and healing properties.
In medieval Europe, it gained a reputation as a “blessed” herb due to its perceived ability to address a range of ailments. The plant’s historical significance is tied to various religious traditions, where it was believed to have divine qualities.
One of the primary traditional uses of Holy Thistle is its association with digestive health. It has been employed as a tonic to stimulate appetite and aid in digestion.
The bitter compounds found in the plant are thought to contribute to its digestive benefits by triggering the production of digestive juices and enzymes.
In herbal medicine, Holy Thistle has also been used for its potential diuretic properties, helping to increase urine production and promote the elimination of waste from the body.
Additionally, it has been explored for its supposed anti-inflammatory effects, and some traditional practices suggest its use for conditions associated with inflammation.
The active compounds in Holy Thistle include bitter substances, tannins, and essential oils. The bitter components are believed to be responsible for the herb’s digestive and stimulant properties.
As with many herbal remedies, it’s essential to note that scientific research on Holy Thistle is limited, and its efficacy for various health claims may vary.
Holy Thistle is often prepared and consumed as an herbal tea or included as an ingredient in herbal formulations. The dried aerial parts of the plant, including leaves and flowers, are typically used for medicinal purposes.
It’s crucial for individuals considering the use of Holy Thistle for health reasons to consult with a healthcare professional, especially if they have pre-existing medical conditions or are taking other medications.
While Holy Thistle has a history deeply rooted in traditional medicine, it’s essential to approach its usage with caution and with an awareness of the limited scientific evidence supporting its efficacy.
As with any herbal remedy, individual responses can vary, and it’s advisable to seek guidance from healthcare professionals to ensure safe and informed use.
The Botanical Description of Holy Thistle
1. Plant Structure: Holy thistle, scientifically known as Cnicus benedictus, is an herbaceous plant that belongs to the Asteraceae family. It typically grows to a height of 30 to 60 centimeters and features a branched and upright stem.
2. Leaves: The leaves of Holy thistle are deeply lobed, spiky, and can grow up to 15 centimeters in length. They are arranged alternately along the stem and have a distinct silver-green color, giving the plant its characteristic appearance.
3. Flowers: Holy thistle produces striking yellow flowers with spiky bracts, creating a visually appealing and distinct appearance. The flowers are clustered at the ends of the branches, adding to the overall charm of the plant.
4. Habitat: Native to the Mediterranean region, Holy thistle thrives in well-drained soils and is often found in dry, sunny locations. It has adapted to various climates and is known for its resilience in the face of different environmental conditions.
5. Growing Season: Holy thistle is an annual plant, completing its life cycle within a year. It typically germinates in the spring, flowers in the summer, and produces seeds before the onset of winter.
6. Medicinal Properties: Beyond its botanical characteristics, Holy thistle has been historically revered for its medicinal properties. The plant has been used in traditional herbal medicine for various health benefits.
7. Cultural Significance: Holy thistle has cultural significance in herbalism, with historical references highlighting its association with monks and healing practices. The plant’s botanical features contribute to its identification and utilization in traditional remedies.
8. Adaptive Features: Holy thistle exhibits adaptive features such as a taproot, which enables it to access water from deeper soil layers. This adaptation enhances its resilience in arid or drought-prone environments.
9. Seed Characteristics: The seeds of Holy thistle are small and achenelike, possessing a pappus that aids in wind dispersal. This reproductive strategy contributes to the plant’s ability to colonize new areas.
10. Seasonal Changes: Throughout its growing season, Holy thistle undergoes notable changes, from the emergence of spiky leaves to the vibrant display of yellow flowers, showcasing its botanical life cycle.
The Geographic Distribution of Holy Thistle
1. Origin: Holy thistle is believed to have originated in the Mediterranean region, including parts of Southern Europe and North Africa. Its historical use traces back to ancient cultures that recognized its medicinal value.
2. Spread Across Continents: Over time, Holy thistle has spread to various continents and is now found in regions beyond its native habitat. It has adapted to diverse climates, showcasing its versatility as a plant species.
3. European Presence: Holy thistle is well-established in European countries, including Spain, Italy, and Greece. Its presence in these regions is both historical and integral to traditional herbal practices.
4. Introduction to the Americas: European colonization played a role in introducing Holy thistle to the Americas. The plant adapted to new environments, and it is now found in parts of North and South America.
5. Asian Distribution: Holy thistle has also found its way to certain Asian regions, where it may be cultivated or grow as a wild plant. The plant’s adaptability allows it to thrive in various soil and climate conditions.
6. Human-Mediated Distribution: Human activities, such as trade and exploration, have contributed to the dispersal of Holy thistle across different continents. The plant’s utility in traditional medicine has likely influenced its intentional cultivation and spread.
7. Naturalization: Holy thistle has naturalized in some areas outside its native range, establishing self-sustaining populations. This adaptability underscores its ability to thrive in diverse ecosystems.
8. Ecological Impact: While not considered invasive in many regions, Holy thistle may have ecological impacts in specific environments. Understanding its geographic distribution helps assess its role in local ecosystems.
9. Current Cultivation Practices: In addition to its natural distribution, Holy thistle is cultivated in various regions for medicinal and ornamental purposes. Cultivation practices contribute to the availability of Holy thistle for traditional herbal remedies.
10. Conservation Status: The geographic distribution of Holy thistle has implications for its conservation status. Monitoring its presence in both native and introduced regions informs conservation efforts and sustainable use practices.
The Chemical Composition of Holy Thistle
1. Active Compounds: Holy thistle is rich in active compounds, including flavonoids, lignans, and polyacetylenes. These bioactive substances contribute to the plant’s medicinal properties.
2. Flavonoids: Holy thistle contains flavonoids with antioxidant properties. These compounds play a role in scavenging free radicals, contributing to the plant’s potential health benefits.
3. Lignans: The presence of lignans in Holy thistle adds to its chemical complexity. Lignans are compounds with potential antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, which may contribute to the plant’s traditional uses in herbal medicine.
4. Polyacetylenes: Holy thistle is known to contain polyacetylenes, compounds with reported anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. The presence of polyacetylenes adds to the plant’s therapeutic potential.
5. Essential Oils: The essential oils found in Holy thistle contribute to its aromatic characteristics. These oils may also possess certain medicinal properties and are part of the overall chemical profile of the plant.
6. Terpenes: Terpenes, including sesquiterpenes and diterpenes, are constituents found in Holy thistle. These compounds can have various biological activities, adding to the diverse chemical composition of the plant.
7. Alkaloids: Some species of thistles, including Holy thistle, may contain alkaloids. Alkaloids are nitrogen-containing compounds with potential pharmacological effects, contributing to the plant’s overall chemical diversity.
8. Phenolic Compounds: Holy thistle is rich in phenolic compounds, which are known for their antioxidant properties. Phenolic compounds contribute to the plant’s potential in promoting overall health.
9. Saponins: Saponins, another group of compounds found in Holy thistle, have reported anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating properties. These compounds play a role in the plant’s traditional uses for various health benefits.
10. Variation in Chemical Composition: The chemical composition of Holy thistle can vary among different plant parts, environmental conditions, and geographic locations. Understanding this variation is crucial for optimizing its medicinal use.
Read Also: 5 Health Benefits of St. John’s Wort (Hypericum perforatum)
The Medicinal Health Benefits Of Holy Thistle (Cnicus benedictus)

1. Liver Support: Holy thistle is renowned for its hepatoprotective properties. It may aid in liver detoxification processes, promoting overall liver health and functionality.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects: The presence of compounds like flavonoids and polyacetylenes contributes to the plant’s anti-inflammatory properties, potentially assisting in managing inflammatory conditions.
3. Digestive Aid: Holy thistle has been traditionally used to support digestion. It may help alleviate digestive discomfort and promote a healthy gastrointestinal tract.
4. Antioxidant Boost: The rich content of antioxidants, including flavonoids and phenolic compounds, can help neutralize free radicals, supporting the body’s defense against oxidative stress.
5. Immune System Modulation: Certain compounds in Holy thistle may have immune-modulating effects, potentially enhancing the body’s ability to defend against infections and illnesses.
6. Respiratory Support: Holy thistle, when used appropriately, may offer respiratory benefits, contributing to overall respiratory health and well-being.
7. Anti-Diabetic Potential: Some studies suggest that Holy thistle may have potential benefits for individuals with diabetes, including helping regulate blood sugar levels.
8. Cardiovascular Health: The plant’s bioactive compounds, particularly flavonoids, may contribute to cardiovascular health by supporting blood vessel function and reducing inflammation.
9. Menstrual Health: Holy thistle has been traditionally used to address certain menstrual issues, potentially providing relief from symptoms associated with the menstrual cycle.
10. Wound Healing: External applications of Holy thistle, such as poultices, may aid in wound healing due to its reported anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties.
The Methods of Usage to Achieve the Provided Health Benefits Of Holy Thistle (Cnicus benedictus)
1. Herbal Infusions: Prepare herbal infusions by steeping Holy thistle leaves in hot water. This method allows for the extraction of medicinal compounds, promoting digestive and liver health.
2. Tinctures: Tinctures are alcohol-based extracts that provide a concentrated form of Holy thistle. They can be taken orally and are known for their ease of use and potency.
3. Capsule Supplements: Holy thistle supplements, available in capsule form, offer a convenient way to incorporate the herb into a daily routine. This method ensures standardized dosages for consistent benefits.
4. External Compresses: Create external compresses using Holy thistle extracts for wound healing. The anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties may aid in promoting the healing process.
5. Culinary Use: Incorporate Holy thistle into culinary preparations, such as salads or soups. While the flavor may be bitter, culinary use allows for a creative and palatable integration into meals.
6. Traditional Herbal Formulas: Holy thistle is often part of traditional herbal formulas designed for liver support and detoxification. These formulas may include a combination of herbs for synergistic effects.
7. Tea Blends: Combine Holy thistle with other complementary herbs to create tea blends. This approach enhances flavor while providing a holistic mix of health-promoting compounds.
8. Poultices: For localized benefits, prepare poultices using Holy thistle leaves. Apply these poultices to wounds or inflamed areas for potential anti-inflammatory and healing effects.
9. Herbal Salves: Craft herbal salves using Holy thistle extracts, suitable for topical application. Salves offer a convenient way to utilize the plant’s medicinal properties externally.
10. Syrups: Prepare syrups by combining Holy thistle with sweetening agents. This method provides a palatable option for those who prefer a sweeter delivery of the herb’s benefits.
The Side Effects Of Using Holy Thistle Medicinal Plant
1. Allergic Reactions: Individuals with known allergies to plants in the Asteraceae family, which includes Holy thistle, may experience allergic reactions. Symptoms may include skin rashes or respiratory issues.
2. Gastrointestinal Discomfort: In some cases, excessive consumption of Holy thistle may lead to gastrointestinal discomfort, including nausea, bloating, or stomach cramps.
3. Interactions with Medications: Holy thistle may interact with certain medications, including blood thinners or drugs metabolized by the liver. Consultation with a healthcare professional is advisable.
4. Photosensitivity: Some individuals may experience heightened sensitivity to sunlight after using Holy thistle. It is recommended to take precautions, such as using sunscreen, to avoid potential skin reactions.
5. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Pregnant and breastfeeding individuals should exercise caution with Holy thistle, as its safety during these periods is not well-established. Consultation with a healthcare provider is crucial.
6. Not Suitable for Every Condition: While Holy thistle has numerous health benefits, it may not be suitable for every health condition. Individuals with specific medical conditions should seek professional advice before using the herb.
7. Potential Blood Sugar Effects: Individuals with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar levels when using Holy thistle, as the herb may have effects on blood sugar regulation.
8. Bitter Taste: The bitter taste of Holy thistle may be unappealing to some individuals. While this characteristic is inherent to its medicinal properties, it is essential to consider personal preferences.
9. Not a Substitute for Professional Medical Advice: Holy thistle, like any herbal remedy, should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. Individuals with existing health conditions should consult healthcare providers before using the herb.
10. Quality of Herbal Products: The quality of Holy thistle products, including supplements and extracts, can vary. Choosing reputable sources ensures the purity and efficacy of the product, minimizing the risk of contaminants.
Read Also: Health Benefits of Cashew Nuts
The Scientific Research and Studies of Holy Thistle (Cnicus benedictus)
1. Hepatoprotective Properties: Scientific research has delved into the hepatoprotective properties of Holy thistle, highlighting its potential to protect and support the liver. Compounds found in the plant may contribute to liver health and detoxification processes.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Studies explore the anti-inflammatory effects of Holy thistle, shedding light on its role in managing inflammatory conditions. The presence of flavonoids and polyacetylenes contributes to its potential anti-inflammatory properties.
3. Antimicrobial Activity: Scientific investigations have examined the antimicrobial activity of Holy thistle, showcasing its potential in addressing microbial infections. This research adds to the understanding of the plant’s traditional uses for immune support.
4. Antioxidant Capacity: Research studies delve into the antioxidant capacity of Holy thistle, elucidating its ability to combat oxidative stress. The plant’s rich content of antioxidants, including flavonoids and phenolic compounds, contributes to this aspect.
5. Impact on Blood Sugar Levels: Scientific inquiries explore the impact of Holy thistle on blood sugar levels, especially relevant for individuals with diabetes. The plant’s potential in regulating blood sugar levels is a subject of interest in diabetes management research.
6. Cardiovascular Health Benefits: Studies investigate the cardiovascular health benefits of Holy thistle, with a focus on its potential to support blood vessel function and reduce inflammation. Flavonoids present in the plant contribute to these cardiovascular effects.
7. Immunomodulatory Effects: Scientific research examines the immunomodulatory effects of Holy thistle, exploring how certain compounds may modulate the immune system. This research contributes to understanding the plant’s role in immune health.
8. Wound Healing Properties: Research studies explore the wound healing properties of Holy thistle, particularly when used externally. The plant’s reported anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects may contribute to the acceleration of the healing process.
9. Effects on Menstrual Health: Scientific investigations delve into the effects of Holy thistle on menstrual health, exploring its potential benefits for addressing menstrual symptoms. Traditional uses of Holy thistle in this context find validation in contemporary research.
10. Gastrointestinal Support: Studies highlight the gastrointestinal support offered by Holy thistle. The plant’s traditional use for digestive health aligns with research findings on its potential to alleviate digestive discomfort and promote a healthy gastrointestinal tract.
The Safety Precautions and Recommendations In Using Holy Thistle (Cnicus benedictus) Medicinal Plant
1. Allergic Reactions: Individuals with known allergies to plants in the Asteraceae family, which includes Holy thistle, may experience allergic reactions. Skin rashes or respiratory issues could manifest, necessitating caution and, if applicable, an allergy test.
2. Gastrointestinal Sensitivity: Excessive consumption of Holy thistle may lead to gastrointestinal discomfort, including symptoms like nausea or stomach cramps. It is advisable to use the plant in moderation to prevent such discomfort.
3. Interactions with Medications: Holy thistle may interact with certain medications, including blood thinners or drugs metabolized by the liver. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial, especially for those on medication regimens.
4. Photosensitivity: Some individuals may experience heightened sensitivity to sunlight after using Holy thistle. Precautions, such as using sunscreen, are recommended to avoid potential skin reactions.
5. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Pregnant and breastfeeding individuals should exercise caution with Holy thistle, as its safety during these periods is not well-established. Consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial for personalized advice.
6. Not Suitable for Every Condition: While Holy thistle has numerous health benefits, it may not be suitable for every health condition. Individuals with specific medical conditions should seek professional advice before using the herb.
7. Potential Blood Sugar Effects: Individuals with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar levels when using Holy thistle, as the herb may have effects on blood sugar regulation. Regular monitoring ensures safe usage.
8. Bitter Taste: Holy thistle has a bitter taste that may be unappealing to some individuals. Considering personal preferences is important, and alternative forms of consumption can be explored.
9. Not a Substitute for Professional Medical Advice: Holy thistle, like any herbal remedy, should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. Individuals with existing health conditions should consult healthcare providers before using the herb.
10. Quality of Herbal Products: The quality of Holy thistle products, including supplements and extracts, can vary. Choosing reputable sources ensures the purity and efficacy of the product, minimizing the risk of contaminants.
FAQs About Holy Thistle (Cnicus benedictus) Medicinal Plant
1. Is Holy thistle safe for individuals with allergies?
Yes, Holy thistle is generally safe for consumption, but individuals with known allergies to plants in the Asteraceae family should exercise caution and perform an allergy test.
2. How does Holy thistle support liver health?
Holy thistle has hepatoprotective properties, potentially supporting liver health and detoxification processes. Compounds in the plant contribute to these benefits.
3. Can Holy thistle be used during pregnancy?
Pregnant individuals should exercise caution with Holy thistle, and consultation with a healthcare provider is crucial, as its safety during pregnancy is not well-established.
4. What precautions should be taken for photosensitivity?
Some individuals may experience heightened sensitivity to sunlight after using Holy thistle. Using sunscreen and taking protective measures can help avoid potential skin reactions.
5. How does Holy thistle impact blood sugar levels?
Research suggests that Holy thistle may have effects on blood sugar levels, making it important for individuals with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly.
6. What are the potential gastrointestinal side effects of Holy thistle?
Excessive consumption of Holy thistle may lead to gastrointestinal discomfort, including symptoms like nausea or stomach cramps. Using the plant in moderation can help prevent such discomfort.
7. Can Holy thistle be used in culinary preparations?
While Holy thistle has a bitter taste, it can be incorporated into culinary preparations like salads or soups to make it more palatable.
8. Is Holy thistle suitable for every health condition?
While Holy thistle has numerous health benefits, it may not be suitable for every health condition. Individuals with specific medical conditions should seek professional advice before using the herb.
9. How does Holy thistle contribute to wound healing?
Holy thistle’s reported anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects may contribute to wound healing when used externally. The plant’s properties may accelerate the healing process.
10. How can one ensure the quality of Holy thistle products?
Choosing reputable sources for Holy thistle products, including supplements and extracts, ensures the purity and efficacy of the product, minimizing the risk of contaminants.

