Wild Carrot, scientifically known as Daucus carota, is a biennial plant that belongs to the Apiaceae family. Also commonly referred to as Queen Anne’s lace, bird’s nest, or simply wild carrot, this plant is native to Europe and southwestern Asia but has become widespread in many parts of North America.
It’s known for its distinctive white, lacy flowers and its resemblance to the cultivated carrot, wild carrot has a rich history and various uses.
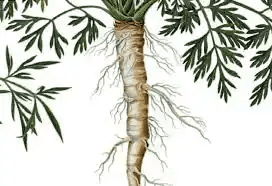
The wild carrot plant typically grows to a height of 1 to 4 feet (30 to 120 cm) and has a slender, branched stem. The leaves are finely divided and feathery, giving the plant an overall delicate and lacy appearance.
The most recognizable feature of wild carrot is its umbel of small white flowers, which form a flat-topped cluster reminiscent of lace. In the center of the umbel, there is often a single dark purple flower, creating a unique and characteristic “bird’s nest” pattern.
One of the notable aspects of wild carrot is its edible taproot, which closely resembles that of the domesticated carrot. However, the wild carrot’s root is typically smaller and more fibrous than the cultivated variety.
The taproot has a mild, carroty flavor and can be consumed when young, although caution should be exercised, as there is a risk of confusion with poisonous plants such as poison hemlock (Conium maculatum).
Historically, wild carrot has been used for various medicinal purposes. The plant was believed to have diuretic properties and was used to treat conditions such as kidney stones and urinary tract infections. Additionally, the seeds were used as a traditional contraceptive in some cultures, though their efficacy for this purpose is questionable.
In the wild, wild carrot is often found in fields, meadows, and along roadsides, thriving in well-drained soils. The plant is adaptable and can tolerate a range of soil types. It is a biennial, meaning it completes its life cycle in two years. During the first year, the plant produces a rosette of leaves, and in the second year, it bolts, producing the characteristic flower stalk.
While wild carrot is considered an invasive species in some regions due to its prolific seed production, it is also valued for its role in supporting pollinators, particularly bees and butterflies, which are attracted to its nectar-rich flowers.
The Botanical Description of Wild Carrot
1. Appearance: Wild carrot grows 1 to 3 feet tall in the first year, forming a rosette of fern-like leaves. In the second year, it produces a tall stem topped with an umbrella-like cluster of small white flowers.
2. Flowers: The flowers are small and densely packed in an umbel, with a dark red or purple central flower surrounded by white or pale flowers, resembling lace.
3. Root: The edible taproot is white, slender, and can grow up to a foot long, emitting a distinctive carroty aroma. Proper identification is crucial.
4. Foliage: Feathery and finely divided leaves, forming a basal rosette in the first year and alternating along the stem in the second year, creating a lacy appearance.
5. Stem: The stem is often hairy, green, or reddish-purple. As the plant matures, the stem elongates to support the umbrella-like inflorescence.
The Geographic Distribution of Wild Carrot
1. Native Regions: Wild carrot is native to Europe, Asia, and parts of North Africa, adapting to diverse climates and soil conditions.
2. Naturalized Regions: It has become naturalized in North America, Australia, and other regions, often found in meadows, fields, along roadsides, and disturbed areas.
3. Preferred Habitats: Thrives in well-drained soils in open areas with sunlight, including grasslands, meadows, and edges of cultivated fields.
4. Invasive Tendencies: While not highly invasive, it can spread readily in introduced areas, colonizing disturbed landscapes.
5. Altitudinal Range: Found at various altitudes, from lowlands to upland areas, showcasing ecological versatility.
The Chemical Composition of Wild Carrot
1. Carotenoids: Rich in carotenoids, including beta-carotene, giving the plant its carroty color, promoting skin health and supporting vision.
2. Essential Oils: The essential oils contribute to the distinctive aroma and may have antimicrobial properties, used in traditional practices.
3. Flavonoids: Luteolin and apigenin are flavonoids with potential anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
4. Polyacetylenes: These compounds have antibacterial and antifungal properties, contributing to the plant’s defense mechanisms.
5. Vitamins and Minerals: The root is a source of vitamin A, vitamin K, and potassium, essential for various physiological functions.
Read Also: How to Grow and Care for Mungbean
The Medicinal Health Benefits Of Wild Carrot (Daucus carota)
1. Digestive Health: Wild carrot aids digestion and alleviates gastrointestinal discomfort, promoting overall digestive health.
2. Diuretic Properties: It supports kidney function by promoting urine production, aiding in toxin elimination, and maintaining fluid balance.
3. Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Wild carrot exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, potentially relieving conditions like arthritis and inflammatory bowel diseases.
4. Respiratory Support: It provides respiratory benefits, easing symptoms of coughs, bronchitis, and asthma.
5. Menstrual Health: For women, it supports menstrual health by regulating menstrual cycles and easing discomfort.
6. Skin Conditions: Antioxidant properties contribute to skin health, managing conditions like eczema or dermatitis.
7. Vision Support: Rich in beta-carotene, it promotes eye health and supports vision by converting to vitamin A.
8. Immune System Modulation: Wild carrot modulates the immune system, maintaining a balanced immune response.
9. Antimicrobial Effects: Preliminary studies suggest antimicrobial properties, inhibiting the growth of certain bacteria and fungi.
10. Cardiovascular Support: Compounds in wild carrot contribute to heart health and maintain healthy blood pressure levels.
11. Anxiety and Stress Reduction: Traditionally used for calming effects, it reduces anxiety and stress, promoting relaxation.
12. Joint Health: Anti-inflammatory properties support joint health, providing relief for conditions like arthritis.
13. Antispasmodic Action: Wild carrot’s antispasmodic effects alleviate muscle spasms, beneficial for muscular tension.
14. Liver Detoxification: It supports liver health by aiding in detoxification processes and eliminating toxins.
15. Urinary Tract Health: Due to diuretic properties, it contributes to urinary tract health, promoting regular urine flow.
16. Weight Management: Some herbal practices suggest a role in weight management, though more research is needed.
17. Anti-Cancer Potential: Early studies suggest potential anti-cancer properties, warranting further investigation.
18. Blood Sugar Regulation: Initial studies indicate a role in regulating blood sugar levels, beneficial for diabetes management.
The Methods of Usage to Achieve the Provided Health Benefits Of Wild Carrot (Daucus carota)
1. Herbal Infusions and Teas: Prepare teas by steeping dried leaves or flowers for digestive and respiratory benefits.
2. Tinctures: Create tinctures for a concentrated form, monitoring dosage carefully.
3. Poultices: Apply crushed leaves or flowers directly to the skin for skin conditions or joint health.
4. Culinary Use: Add fresh leaves to salads or use the root in cooking, ensuring proper identification.
5. Essential Oils: Extract oils for aromatherapy, contributing to stress reduction and relaxation.
6. Capsules and Supplements: Take supplements for a convenient daily incorporation, following recommended dosage.
7. Topical Creams: Use creams with wild carrot extract for skin-related benefits, promoting overall skin health.
8. Culinary Preparations: Include wild carrot in soups, stews, or dishes, maintaining moderation.
9. Steam Inhalation: Inhale steam for respiratory benefits, particularly helpful for respiratory conditions.
10. Herbal Baths: Add wild carrot-infused water to baths for a relaxing experience, promoting skin health.
The Side Effects Of Using Wild Carrot Medicinal Plant
1. Allergic Reactions: Monitor for itching or swelling in individuals allergic to Apiaceae family plants.
2. Photosensitivity: Avoid sun exposure after topical application to prevent skin reactions.
3. Pregnancy and Lactation: Exercise caution due to potential effects on uterine contractions; limited safety data available.
4. Interaction with Medications: Consult a healthcare professional before use, especially with other medications.
5. Digestive Discomfort: Adhere to recommended dosage to prevent bloating or diarrhea.
6. Neurological Effects: High doses may cause dizziness and confusion; exercise caution with concentrated extracts.
7. Blood Pressure Impact: Monitor blood pressure, especially in individuals with cardiovascular conditions.
8. Liver Conditions: Use cautiously in individuals with existing liver conditions, monitoring liver function.
9. Kidney Function: Maintain hydration to support kidney function due to diuretic properties.
10. Avoidance in Elderly Individuals: Consider lower dosages for elderly individuals, monitoring for adverse reactions.
11. Discontinuation Prior to Surgery: Discontinue use a few weeks before surgery to prevent potential blood clotting effects.
12. Gastrointestinal Irritation: Prolonged or excessive use may lead to gastrointestinal irritation; monitor for discomfort.
13. Central Nervous System Depression: High doses may cause mild central nervous system depression; avoid activities requiring alertness.
14. Potential for Misidentification: Proper identification is crucial due to poisonous look-alikes.
15. Caution in Children: Exercise caution, adjusting dosages based on age and weight, and consult with a healthcare professional.
Read Also: 8 Medicinal Health Benefits Of German Chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla)
The Scientific Research and Studies of Wild Carrot (Daucus carota)

1. Antioxidant Properties: Scientific research has delved into the antioxidant properties of wild carrot, exploring compounds like beta-carotene. Studies suggest its potential in neutralizing free radicals, reducing oxidative stress.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Researchers have investigated the anti-inflammatory effects of wild carrot. Findings indicate its impact on inflammatory markers, suggesting potential benefits for conditions with chronic inflammation.
3. Antimicrobial Activity: Scientific studies have explored the antimicrobial activity of wild carrot against various pathogens. Preliminary findings suggest effectiveness against certain bacteria and fungi, highlighting its potential as a natural antimicrobial agent.
4. Phytochemical Composition: Research has focused on the phytochemical composition of wild carrot, identifying bioactive compounds like polyacetylenes, flavonoids, and essential oils. These contribute to the plant’s diverse medicinal properties.
5. Cytotoxic Potential: Some studies have explored the cytotoxic potential of wild carrot against certain cancer cells. While in the early stages, these findings suggest a potential avenue for further research on its anticancer properties.
6. Hypoglycemic Effects: Investigations have examined the hypoglycemic effects of wild carrot, indicating potential in regulating blood sugar levels. This area of research holds promise for individuals managing diabetes.
7. Hepatoprotective Properties: Studies on animals have suggested hepatoprotective properties of wild carrot, indicating potential in protecting the liver from damage. Further research is needed to understand its implications for human liver health.
8. Immunomodulatory Activity: Scientific studies have explored the immunomodulatory activity of wild carrot, indicating its potential to modulate immune responses. This research contributes to understanding its impact on the immune system.
9. Wound Healing: Research has investigated the wound healing properties of wild carrot. Studies suggest its potential role in promoting the healing process, possibly attributed to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
10. Effects on Cardiovascular Health: Some scientific studies have explored the effects of wild carrot on cardiovascular health. While preliminary, these findings indicate potential benefits in supporting heart function and maintaining healthy blood pressure.
11. Neuroprotective Potential: Initial research has hinted at the neuroprotective potential of wild carrot. Studies on animals suggest a role in protecting nerve cells, paving the way for further investigations in neurology.
12. Respiratory Benefits: Scientific studies have examined the respiratory benefits of wild carrot, especially in conditions like asthma and bronchitis. This research sheds light on its potential as a natural remedy for respiratory ailments.
The Safety Precautions and Recommendations In Using Wild Carrot (Daucus carota) Medicinal Plant
1. Proper Identification: Accurate identification of wild carrot is crucial to avoid confusion with toxic look-alikes. Users should familiarize themselves with distinguishing features and consult field guides if needed.
2. Allergic Reactions: Individuals allergic to plants in the Apiaceae family, including carrots and celery, should exercise caution. Monitor for allergic reactions such as itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
3. Photosensitivity: Due to potential photosensitivity, individuals using wild carrot externally should avoid prolonged sun exposure. Apply creams or ointments in the evening to reduce the risk of skin reactions.
4. Pregnancy and Lactation: Pregnant and breastfeeding individuals should consult healthcare professionals before using wild carrot, as limited safety data is available.
5. Interaction with Medications: Individuals taking medications should seek medical advice before using wild carrot, as it may interact with certain drugs. This precaution ensures the safety of concurrent use.
6. Digestive Discomfort: While generally well-tolerated, excessive consumption of wild carrot may lead to digestive discomfort. Users should adhere to recommended dosage guidelines.
7. Neurological Effects: High doses of wild carrot may cause mild neurological effects, such as dizziness. Caution is advised, especially when using concentrated extracts.
8. Blood Pressure Monitoring: Individuals with cardiovascular conditions should monitor blood pressure, as wild carrot may have an impact. Regular checks ensure timely adjustments if needed.
9. Liver Conditions: Individuals with existing liver conditions should use wild carrot cautiously, with regular monitoring of liver function. Healthcare supervision is advisable.
10. Kidney Function: Due to diuretic properties, users should maintain proper hydration when using wild carrot to support kidney function and prevent dehydration.
11. Avoidance in Elderly Individuals: Elderly individuals may be more susceptible to the effects of wild carrot. Consideration should be given to lower initial dosages, with close monitoring for any adverse reactions.
12. Caution in Children: Exercise caution when using wild carrot in children, adjusting dosages based on age and weight. Consultation with a healthcare professional is advisable.
FAQs About Wild Carrot (Daucus carota) Medicinal Plant
1. Is wild carrot safe for culinary use?
Yes, wild carrot is safe for culinary use when consumed in moderate amounts. The root can be added to soups, stews, or salads, providing a unique flavor.
2. Can wild carrot be used during pregnancy?
Pregnant individuals should exercise caution and consult healthcare professionals before using wild carrot due to potential effects on uterine contractions.
3. Are there specific precautions for topical use?
Yes, individuals using wild carrot externally should be aware of potential photosensitivity. It is advisable to avoid prolonged sun exposure after topical application to prevent skin reactions.
4. Can wild carrot interact with medications?
Yes, individuals taking medications should seek medical advice before using wild carrot, as it may interact with certain drugs. Healthcare professionals can provide guidance on safe use.
5. Is wild carrot safe for children?
While wild carrot is generally safe, caution should be exercised when using it in children. Dosages should be adjusted based on age and weight, and consultation with a healthcare professional is recommended.
6. Can wild carrot be used for respiratory conditions?
Yes, scientific studies suggest that wild carrot may have respiratory benefits, making it a potential natural remedy for conditions like asthma and bronchitis.
7. Is wild carrot safe for individuals with liver conditions?
Individuals with existing liver conditions should use wild carrot cautiously and monitor liver function regularly. Consulting with a healthcare professional is advisable.
8. Can wild carrot be used during breastfeeding?
Breastfeeding individuals should exercise caution and consult healthcare professionals before using wild carrot, as limited safety data is available for this period.
9. What are the potential side effects of wild carrot?
Potential side effects may include allergic reactions, neurological effects, and digestive discomfort. Users should adhere to recommended dosages and monitor for any adverse reactions.
10. Is wild carrot suitable for individuals with cardiovascular conditions?
Individuals with cardiovascular conditions should monitor blood pressure when using wild carrot, as it may have an impact on blood pressure levels. Regular checks ensure safety.
11. Are there any age-related considerations for using wild carrot?
Elderly individuals may be more susceptible to the effects of wild carrot, and lower initial dosages with close monitoring are advisable.
12. Can wild carrot be used in conjunction with other herbs or supplements?
Individuals using other herbs or supplements should exercise caution and consult healthcare professionals before combining them with wild carrot. Interaction risks can be assessed for safe use.
Do you have any questions, suggestions, or contributions? If so, please feel free to use the comment box below to share your thoughts. We also encourage you to kindly share this information with others who might benefit from it. Since we can’t reach everyone at once, we truly appreciate your help in spreading the word. Thank you very much for your support and for sharing!
Disclaimer: This article is for educational and informational purposes only. The health benefits described are based on scientific research and traditional knowledge. They ayre not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a healthcare professional before using any herb or natural remedy for medical purposes.
Read Also: Complete Steps in Aluminum Recycling Guide

