Benefits, Uses and the Economic Impact of Cotton
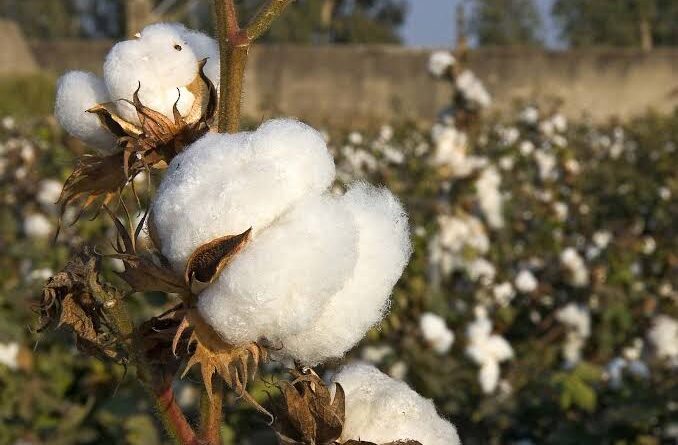
Cotton is a versatile and essential natural fiber that has played a significant role in human history and daily life for centuries. It is derived from the fluffy fibers surrounding the seeds of the cotton plant, scientifically known as Gossypium. These soft fibers have been woven into fabric to create textiles that are used in a myriad of products, ranging from clothing to household items.
The journey of cotton begins in the fields where cotton plants flourish. The cultivation of cotton involves careful attention to soil quality, climate conditions, and proper irrigation. Farmers harvest the cotton bolls when they ripen, carefully collecting the white, downy fibers that will later undergo processing to become the cotton we know.
Once harvested, cotton fibers go through a series of processes to transform them into usable materials. These processes include ginning, where the seeds are separated from the fibers, and spinning, which turns the fibers into yarn. Weaving or knitting follows, creating the fabric that will eventually be fashioned into various products.
One of the remarkable characteristics of cotton is its breathability and comfort. Cotton fabric allows air circulation, making it an ideal choice for clothing in various climates. Its natural absorbency also makes cotton suitable for towels and other household items. The softness and durability of cotton contribute to its popularity, ensuring that it remains a staple in the textile industry.
Moreover, cotton serves as a crucial economic commodity for many countries. Its cultivation supports livelihoods and provides income for countless farmers and workers across the globe. The cotton industry has a significant impact on the economies of nations that produce and export this valuable crop.
In addition to its economic importance, cotton has witnessed technological advancements. Innovations in agricultural practices and genetic modifications have led to the development of more resilient cotton varieties, enhancing yields and sustainability. These advancements contribute to the ongoing evolution of the cotton industry.
Furthermore, cotton has historical significance, playing a pivotal role in the economies of civilizations such as ancient India and Egypt. Its cultivation and trade have influenced cultural and social practices, shaping the course of human history. The cotton gin, invented by Eli Whitney in the 18th century, revolutionized cotton processing and significantly impacted the textile industry.
In contemporary society, concerns about sustainability and environmental impact have prompted a closer look at cotton production. Organic and sustainable cotton practices aim to minimize the ecological footprint associated with conventional cultivation methods, addressing issues like pesticide use and water consumption.
In addition, Cotton, with its rich history, economic importance, and versatility, stands as a testament to the enduring relationship between humanity and the natural world. Its journey from the fields to the fabric is a fascinating exploration of agriculture, industry, and innovation, making cotton an integral part of our daily lives and global heritage.
Read Also: Storage Life of Harvested Crop Materials
Uses of Cotton
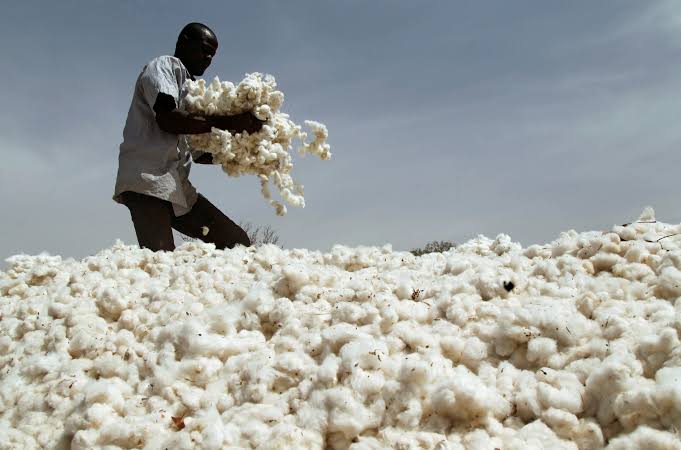

Cotton finds a multitude of uses across various aspects of our daily lives. Its versatility makes it a preferred choice for an array of products. Here are some of the common uses of cotton:
1. Clothing: Cotton is a popular fabric for clothing due to its breathability and comfort.
It is used in the production of T-shirts, shirts, dresses, jeans, underwear, and various other types of apparel.
2. Home Textiles: Cotton is widely used in the production of bed sheets, pillowcases, and duvet covers for its softness and comfort.
Towels, bathrobes, and washcloths are often made from cotton due to its absorbent nature.
3. Medical Products: Cotton is used in the manufacturing of medical supplies such as bandages, gauze, and cotton balls due to its hypoallergenic properties.
4. Personal Care Products: Cotton is a common material for hygiene products like cotton swabs and cotton pads.
5. Industrial Uses: Cottonseed oil, a byproduct of cotton processing, is used in cooking and various industrial applications. Cotton fibers are utilized in the creation of industrial products such as filters and thread.
6. Art and Craft: Cotton is used in art and craft projects, including canvas for painting and various DIY projects.
7. Paper Products: Cotton fibers are sometimes used in the production of high-quality paper, contributing to its durability and texture.
8. Furniture: Cotton upholstery fabric is commonly used in furniture manufacturing for its softness and durability.
9. Cottonseed Meal: Cottonseed meal, a byproduct of cottonseed oil extraction, is used as a fertilizer in agriculture.
10. Banknotes: Some countries use a blend of cotton and linen fibers in the production of banknotes to enhance their durability.
11. Automotive Industry: Cotton is used in car interiors, including seat covers and upholstery, providing comfort and a natural feel.
12. Fashion Accessories: Cotton is utilized in the creation of various fashion accessories like scarves, hats, and gloves.
13. Sports Equipment: Cotton is sometimes incorporated into sports-related products such as sweatbands and athletic apparel.
14. Footwear: Cotton fabrics are used in the manufacturing of socks and casual footwear.
15. Toys and Stuffed Animals: Cotton is often used as stuffing material in the production of toys and stuffed animals.
These diverse uses highlight the significance of cotton as a versatile and indispensable natural resource in our daily lives and various industries.
Read Also: The Advantages of Being a Rice Farmer
Benefits of Cotton

Cotton offers a range of benefits across different aspects, from its impact on the environment to its comfort in daily use. Here are some key benefits of cotton:
1. Natural Fiber: Cotton is a natural fiber derived from the cotton plant, making it biodegradable and environmentally friendly.
2. Breathability: Cotton fabrics are breathable, allowing air to circulate, which makes them comfortable to wear in various climates.
3. Softness and Comfort: Cotton is known for its soft and comfortable feel against the skin, making it a preferred choice for clothing and home textiles.
4. Absorbency: Cotton has high absorbent properties, making it suitable for products like towels and bathrobes that need to quickly absorb moisture.
5. Hypoallergenic: Cotton is often hypoallergenic, making it a good choice for individuals with sensitive skin or allergies.
6. Versatility: Cotton’s versatility allows it to be used in a wide range of products, from clothing and home furnishings to medical supplies and industrial applications.
7. Durable: Cotton fibers are durable and can withstand wear and tear, contributing to the longevity of products made from cotton.
8. Easy to Dye: Cotton readily absorbs dyes, allowing for vibrant and long-lasting colors in textiles and clothing.
9. Renewable Resource: Cotton is a renewable resource, as it can be harvested annually, providing a sustainable material for various industries.
10. Economic Impact: Cotton cultivation supports the livelihoods of millions of farmers and workers worldwide, contributing significantly to the global economy.
11. Cottonseed Byproducts: The byproducts of cotton processing, such as cottonseed oil and cottonseed meal, find uses in cooking, industrial applications, and agriculture.
12. Biodegradable: Cotton products decompose naturally, reducing the environmental impact compared to synthetic materials.
13. Cooling Properties: Cotton fabrics have cooling properties, making them suitable for warm weather and promoting comfort during physical activities.
14. Cotton Gin Efficiency: The invention of the cotton gin by Eli Whitney in the 18th century revolutionized cotton processing, significantly increasing efficiency and production.
15. Cultural and Historical Significance: Cotton has played a crucial role in the cultural and historical development of societies, influencing economies and trade routes.
These benefits collectively underscore the importance of cotton as a sustainable, comfortable, and versatile resource that has a positive impact on various aspects of our lives and industries.
Economic Impact of Cotton

The economic impact of cotton is substantial and extends across multiple sectors, contributing significantly to the global economy. Here are key aspects of the economic impact of cotton:
1. Employment: Cotton cultivation and the entire cotton value chain provide employment opportunities for millions of people worldwide. Farmers, farm laborers, textile workers, and those involved in related industries all contribute to the workforce.
2. Agricultural Sector: Cotton cultivation is a major component of the agricultural sector in many countries. The income generated from cotton farming supports rural economies and livelihoods.
3. Textile Industry: The textile industry, which heavily relies on cotton, is a major contributor to the global economy. Cotton is a primary raw material for the production of textiles, including clothing, home furnishings, and industrial products.
4. Trade and Export: Cotton is a significant commodity in international trade. Countries that are major cotton producers often export their cotton, contributing to foreign exchange earnings and trade balances.
5. Small and Large Scale Enterprises: Cotton processing and textile manufacturing support both small-scale enterprises and large-scale industries, fostering economic diversity and development.
6. Technological Advancements: Innovations in cotton farming practices and processing technologies contribute to increased productivity, efficiency, and competitiveness, further enhancing the economic impact.
7. Infrastructure Development: The economic importance of cotton cultivation often leads to investments in infrastructure, such as irrigation systems, transportation networks, and processing facilities, benefiting both rural and urban areas.
8. Research and Development: The cotton industry invests in research and development to improve crop yields, resist diseases, and develop more sustainable cultivation practices, contributing to long-term economic growth.
9. Global Supply Chain: Cotton is an integral part of the global supply chain, linking farmers, manufacturers, retailers, and consumers across different countries and regions.
10. Job Creation in Downstream Industries: Beyond farming and textile production, cotton contributes to job creation in downstream industries, such as fashion, retail, and marketing.
11. Contribution to GDP: The economic value generated by the entire cotton value chain, including farming, processing, and manufacturing, significantly contributes to the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of many countries.
12. Trade Relationships: Cotton trade fosters economic relationships between countries, promoting cooperation and collaboration in the global marketplace.
13. Income Diversification: For many developing countries, cotton cultivation provides a source of income diversification, reducing dependency on a single agricultural product.
14. Social Impact: The economic impact of cotton extends to social aspects, improving living standards and supporting education and healthcare initiatives in cotton-producing regions.
In summary, the economic impact of cotton is extensive, influencing agriculture, industry, trade, and employment on a global scale. The cultivation and processing of cotton contribute to the economic well-being of nations and play a crucial role in shaping regional and global economic dynamics.
Read Also: Advantages of Waste Recycling