Cats breeding and reproduction are fascinating topics that reveal the complexities of feline behavior and biology. Understanding these processes is essential for responsible cat owners, breeders, and enthusiasts who wish to ensure the health and well-being of both the mother cat and her kittens.
Breeding cats involves more than simply allowing them to mate; it requires careful planning, knowledge of genetics, and awareness of the physical and emotional needs of the animals involved.
The reproductive cycle of cats, also known as the estrous cycle, plays a critical role in breeding. Female cats, or queens, typically reach sexual maturity between five to twelve months of age, depending on their breed and individual development.
This cycle consists of several stages: proestrus, estrus (heat), metestrus (diestrus), and anestrus. The most notable stage for breeding is estrus, during which the queen is receptive to mating.
This period lasts about one week and can occur multiple times a year, with some queens going into heat as often as every three weeks during the breeding season. Recognizing the signs of estrus such as increased vocalization, affectionate behavior, and restlessness is crucial for successful breeding.
Once a queen is in heat, she will attract male cats, or toms, with her pheromones. Successful mating involves the tom biting the queen’s neck and holding her in place, which can appear aggressive but is a natural part of feline mating behavior. After mating, the queen can become pregnant.
The gestation period for cats is approximately 63 to 65 days, during which the developing embryos undergo significant changes. Cat breeders should provide a safe and comfortable environment for the queen during this time, ensuring she receives proper nutrition and veterinary care to support her health and the health of her kittens.
As the time for delivery approaches, queens often seek out quiet and secure places to give birth. This process, known as queening, can involve several kittens, typically ranging from one to six, though larger litters are not uncommon. After birth, the mother cat plays a crucial role in nurturing her kittens.
She will nurse them, clean them, and keep them warm. It’s essential for breeders to monitor the mother and her litter during the early weeks to ensure all kittens are feeding well and developing properly.
Breeding cats also comes with ethical considerations. Responsible breeders prioritize the health and temperament of their cats, aiming to produce well-adjusted kittens that meet breed standards.
This includes screening for genetic disorders, providing appropriate veterinary care, and ensuring that all cats involved in the breeding process are well-socialized. Furthermore, breeders must be aware of the risks of overpopulation and consider the importance of spaying and neutering when breeding is not intended.
Understanding Cat Breeding Basics

Breeding cats involves more than just pairing two felines. It requires careful consideration of genetics, health, and breed standards.
1. Purpose of Breeding: Many breeders aim to improve specific traits in a breed, such as temperament, appearance, or health. Understanding the goals of breeding can help guide decisions throughout the process.
2. Ethical Considerations: Responsible breeding focuses on the health and well-being of both the parent cats and the kittens. Avoid breeding cats with known genetic health issues or undesirable traits to ensure healthier offspring.
3. Commitment to Care: Breeding cats is a significant commitment. It involves time, effort, and financial resources for health screenings, veterinary care, and proper nutrition.
The Reproductive Cycle of Cats
Understanding the reproductive cycle of cats is crucial for successful breeding.
1. Estrous Cycle: Female cats have an estrous cycle, also known as the heat cycle, which typically occurs every 2 to 3 weeks. During this period, they are receptive to mating.
2. Signs of Heat: Common signs that a female cat is in heat include increased vocalization, restlessness, affectionate behavior, and assuming a mating position when petted. Recognizing these signs is essential for timing the breeding process.
3. Duration of Heat: The heat cycle lasts about 7 to 10 days. If a female cat does not mate during this period, she will go out of heat and return to it in a few weeks.
Selecting Breeding Cats: Traits to Consider
Choosing the right cats for breeding is essential to produce healthy, well-tempered kittens.
1. Health Screening: Prioritize health screenings for both the male and female cats. Common tests include checking for feline leukemia virus (FeLV), feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV), and other genetic conditions.
2. Breed Standards: Familiarize yourself with breed standards to ensure the cats meet the criteria for conformation, coat color, and temperament. This helps maintain breed integrity.
3. Temperament: Consider the temperament of the breeding cats. Friendly, sociable, and well-adjusted cats are more likely to produce kittens with similar traits.
Read Also: Bedbugs: Description, Damages Caused, Control and Preventive Measures
Preparing for Cat Breeding

Preparation is key to a successful breeding experience.
1. Creating a Safe Environment: Set up a quiet, safe space for the breeding process. This area should be clean, comfortable, and free from disturbances.
2. Veterinary Care: Schedule a veterinary check-up for both cats to ensure they are in good health before breeding. Discuss vaccinations and any necessary medications.
3. Nutritional Needs: Provide a balanced diet with high-quality cat food to support the health of the breeding cats. Proper nutrition is vital for successful breeding and the health of the kittens.
4. Timing the Mating: Once the female cat shows signs of being in heat, arrange for mating with the selected male cat. Monitor the cats during this period to ensure successful breeding.
Mating Process and Timing
Successful cat breeding starts with the mating process.
1. Timing the Mating: The best time for mating is during the female cat’s heat cycle. Heat usually lasts about 7 to 10 days, and mating should occur during this window.
2. Natural Behavior: Male cats will often show interest in females during her heat cycle. You may notice increased vocalization, affectionate behavior, and the female assuming a mating position.
3. Mating Behavior: During mating, the male cat may bite the female gently on the neck to hold her in place. After mating, the female may exhibit behaviors like rolling or grooming.
4. Repeated Mating: It is common for cats to mate multiple times during the heat cycle to ensure successful fertilization.
Pregnancy in Cats: Signs and Duration
Once mating occurs, pregnancy will begin if fertilization is successful.
1. Signs of Pregnancy: Some signs that a female cat is pregnant include:
i. Change in Appetite: She may experience increased hunger or decreased appetite during the early stages.
ii. Behavioral Changes: Pregnant cats may become more affectionate or seek solitude.
iii. Nipple Changes: The nipples may become enlarged and more prominent, a condition known as “pinking up.”
2. Duration of Pregnancy: The average gestation period for cats is about 63 to 65 days. However, it can range from 58 to 70 days.
3. Veterinary Confirmation: A visit to the veterinarian can confirm pregnancy through ultrasound or other examinations, providing reassurance about the health of the mother and kittens.
Read Also: 10 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Jakhya (Cleoma viscosa)
Caring for Pregnant Cats
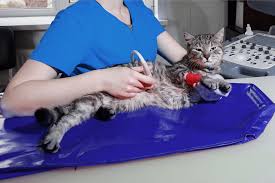
Caring for a pregnant cat is essential for her health and the health of her kittens.
1. Nutrition: Ensure that she receives a balanced diet that meets her increased nutritional needs. High-quality kitten food is recommended during pregnancy, as it provides the necessary nutrients for both the mother and developing kittens.
2. Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular veterinary check-ups to monitor the cat’s health and the development of the kittens. Vaccinations and preventive treatments should be discussed with the veterinarian.
3. Comfortable Environment: Provide a safe and comfortable living space for the pregnant cat. A quiet area where she can relax is essential for her well-being.
4. Monitor Behavior: Pay attention to any changes in her behavior. If she shows signs of distress or discomfort, consult a veterinarian promptly.
Preparing for Kitten Birth
As the due date approaches, preparation is key for a smooth delivery.
1. Whelping Area: Create a safe, quiet area for the cat to give birth. This area, known as a whelping box, should be clean, soft, and free from disturbances. It can be lined with clean towels or blankets.
2. Gather Supplies: Have essential supplies ready, such as clean towels, scissors, and a heating pad for warmth. Also, keep a box handy to place the kittens after birth.
3. Understanding Labor Signs: Familiarize yourself with signs of labor, including nesting behavior, restlessness, and increased vocalization. This knowledge can help you provide support during the birthing process.
4. Be Prepared for Complications: While many cats give birth without issues, be prepared to contact a veterinarian if complications arise, such as prolonged labor or distress.
Neonatal Care for Kittens
Caring for newborn kittens is crucial for their survival and development.
1. Immediate Care After Birth: After the kittens are born, ensure they are breathing and nursing. If a kitten is not breathing, gently rub it with a clean towel to stimulate it. The mother should lick the kittens to clean them and encourage them to nurse.
2. Keeping Kittens Warm: Newborn kittens cannot regulate their body temperature effectively. Keep them warm by providing a heat source, such as a heating pad set on low, placed under half of their bedding area so they can move away if they get too warm.
3. Nutrition Needs: Kittens should nurse from their mother every 2-3 hours during the first few weeks. If the mother is unable to nurse, use a commercial kitten milk replacer to feed them using a bottle.
4. Monitoring Weight and Growth: Weigh the kittens daily to monitor their growth. Kittens should gain approximately 10-15 grams daily. If a kitten is not gaining weight or is lethargic, consult a veterinarian.
5. Cleaning the Litter: The mother will usually clean the kittens, but you may need to help. If they are not kept clean, they can develop infections. Ensure their living area is clean and dry.
Socializing Kittens for Adoption
Proper socialization is vital for helping kittens become well-adjusted adults.
1. Early Socialization: Begin socializing kittens as early as 3 weeks of age. Gently handle them, exposing them to various people and gentle interactions to help them get used to human touch and voices.
2. Gradual Exposure to Environments: Introduce them to different environments and experiences, such as different sounds, textures, and smells. This exposure helps them adjust to various situations and reduces fear.
3. Playtime and Interaction: Engage the kittens in play using toys and encourage interaction with each other. This helps develop their hunting instincts and social skills.
4. Encourage Positive Experiences: Ensure that all interactions are positive. Avoid overwhelming them with too many stimuli at once. Offer treats and affection to create positive associations with humans and their environment.
5. Preparing for Adoption: When the kittens are around 8-12 weeks old, they should be ready for adoption. Provide potential adopters with information on the kittens’ personalities, behaviors, and any special needs.
Health Considerations for Breeding Cats
Maintaining the health of breeding cats is crucial for successful breeding.
1. Regular Veterinary Check-ups: Schedule regular veterinary visits to monitor the health of the breeding cats. Vaccinations and parasite control should be up-to-date.
2. Nutrition: Provide a balanced diet formulated for pregnant or nursing cats. High-quality food will ensure the mother cat receives the necessary nutrients for herself and her kittens.
3. Stress Management: Minimize stress in the breeding environment. Stress can negatively impact the health of the mother and her kittens. Create a calm and safe space for them.
4. Observe for Health Issues: Watch for any signs of illness or discomfort in the breeding cats. Prompt veterinary care is essential if any health issues arise.
5. Spaying and Neutering: Consider spaying or neutering the cats after they have completed their breeding to prevent unwanted litters and contribute to the overall health and well-being of the cats.
Responsible Breeding Practices
Responsible breeding is essential to promote the health and welfare of cats.
1. Ethical Breeding: Breed cats only for the purpose of improving the breed and ensuring the health of the kittens. Avoid breeding for profit or to meet demand without considering the welfare of the animals.
2. Selecting Healthy Breeding Cats: Choose breeding cats based on their health, temperament, and genetic background. Ensure they are free from hereditary diseases to promote healthy kittens.
3. Education and Research: Stay informed about best practices in cat breeding. Attend workshops, seminars, or read reputable sources to continuously improve your knowledge.
4. Finding Good Homes: Screen potential adopters to ensure they can provide a loving and responsible home for the kittens. Be prepared to take back any kittens if the new owners cannot care for them.
5. Commitment to Lifelong Care: Be committed to the welfare of the kittens throughout their lives. Offer support and advice to adopters and be available to help if they face challenges.
Do you have any questions, suggestions, or contributions? If so, please feel free to use the comment box below to share your thoughts. We also encourage you to kindly share this information with others who might benefit from it. Since we can’t reach everyone at once, we truly appreciate your help in spreading the word. Thank you so much for your support and for sharing!
Read Also: The Different Types of Manure and How they Work
Frequently Asked Questions
We will update this section soon.

