Chickpea/Gram pea Cotyledons are an essential part of the plant’s anatomy, serving as the primary storage tissue for nutrients during germination. Chickpea cotyledons are typically small, oval-shaped, and somewhat asymmetrical. They have a convex appearance on one side and a slightly concave side on the other, resembling a rounded triangle or a heart shape.
The color of chickpea cotyledons seeds varies depending on the variety, but they are commonly beige, cream, or light yellow. Some varieties may have a slightly darker hue. The cotyledons have a smooth and firm texture when dry. Once cooked or soaked, they become soft and have a creamy consistency.
Chickpea cotyledons are rich in essential nutrients, making them a valuable source of plant-based protein, dietary fiber, complex carbohydrates, vitamins (such as B vitamins), and minerals (including iron, potassium, magnesium, and zinc).
Chickpea cotyledons are a staple ingredient in various cuisines around the world. They are commonly used in soups, stews, salads, and curries. In some regions, chickpea flour is made from grinding dried chickpea cotyledons and is used in baking and cooking. Due to their high protein content, chickpea cotyledons are a popular choice for vegetarians and vegans as a meat alternative. They also contribute to heart health and may help regulate blood sugar levels and support digestive health due to their fiber content.
Before using chickpea cotyledons, they are often soaked in water to rehydrate and soften them. This reduces cooking time and improves digestibility. The soaked or boiled chickpea cotyledons can be added to various dishes or ground into flour for various recipes. Chickpea cotyledons seeds are not only delicious but also offer a wide range of nutritional benefits, making them a valuable addition to a balanced and healthy diet.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Chickpea/Gram Pea Cotyledons
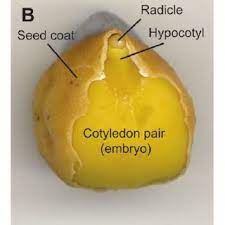
Chickpea, also known as gram pea or garbanzo bean, is a highly nutritious and economically important legume crop. Its cotyledons, the seed leaves present within the seed, play a significant role in its economic importance.
Here are some of the economic importance and uses of chickpea cotyledons:
1. Food Source: Chickpea cotyledons are a staple food in many cultures around the world. They are a rich source of protein, dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals. The cotyledons are commonly used in various culinary applications, such as soups, stews, salads, and as an essential ingredient in dishes like hummus and falafel.
2. Nutritional Value: Chickpea cotyledons are a valuable source of essential nutrients, including protein, carbohydrates, dietary fiber, folate, iron, magnesium, and phosphorus. As a result, they contribute to food security and play a vital role in addressing malnutrition in regions where they are a dietary staple.
3. Animal Feed: Chickpea cotyledons are also used as a feed source for livestock, particularly for poultry and cattle. They provide a nutritious and cost-effective feed option, contributing to the growth and productivity of animals.
4. Health Benefits: Consumption of chickpea cotyledons has been associated with several health benefits, including improved heart health, weight management, and better blood sugar control. The dietary fiber in chickpeas helps promote healthy digestion and reduce the risk of certain gastrointestinal disorders.
5. Export and Trade: Chickpea cotyledons are a valuable commodity in international trade. Countries that produce chickpeas in surplus can export them to regions with high demand, contributing to foreign exchange earnings and strengthening trade relations.
6. Crop Rotation and Nitrogen Fixation: Chickpeas are an important component of crop rotation systems. As legumes, they have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen through a symbiotic relationship with nitrogen-fixing bacteria in their roots. This helps improve soil fertility and reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers in subsequent crops, leading to sustainable agricultural practices.
7. Industrial Uses: Chickpea cotyledons are also used in the food processing industry for making flour and protein isolates. Chickpea flour, also known as gram flour or besan, is used in various culinary preparations, while protein isolates find applications in the production of protein-rich foods and as a supplement in the food industry.
8. Medicinal Uses: In some cultures, chickpea cotyledons have been used in traditional medicine for various purposes, including wound healing, as a diuretic, and for improving lactation in nursing mothers.
9. Climate Resilience: Chickpeas are well-adapted to a wide range of climatic conditions, including semi-arid and arid regions. They can thrive in areas with limited water availability, making them an essential crop in regions facing water scarcity and climate change challenges.
10. Income Generation for Farmers: Chickpea cultivation can be economically beneficial for farmers. Due to their high demand and various uses, chickpeas can provide a stable source of income for farmers, especially those in regions with suitable agro-climatic conditions for chickpea production.
11. Biodiversity Conservation: Chickpeas exhibit considerable genetic diversity, with various landraces and wild relatives. The conservation and sustainable utilization of this genetic diversity are vital for maintaining crop resilience and adapting to changing environmental conditions.
Read Also: Chickpea/Gram pea Flowers: Economic Importance, Uses and By-Products
12. Value-Added Products: Apart from fresh or dried cotyledons, chickpeas can be processed into various value-added products. These include roasted chickpeas, canned chickpeas, chickpea snacks, and chickpea-based pasta and noodles. The production of these products adds value to the crop and provides additional income streams for processors and manufacturers.
13. Cultural and Culinary Importance: Chickpeas have deep cultural significance in many regions. They are an integral part of traditional dishes and festivals, contributing to cultural heritage and culinary diversity.
14. Biological Research and Biotechnology: Chickpeas serve as an essential model organism for biological research and biotechnology studies. Researchers use chickpeas to study various aspects of plant genetics, physiology, and biochemistry, leading to advancements in crop improvement and sustainable agriculture practices.
Example: Genetic studies in chickpeas have helped identify key genes responsible for important agronomic traits, such as disease resistance and drought tolerance, enabling breeders to develop improved varieties.
15. Climate Change Mitigation: Chickpeas, like other legumes, have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen through their symbiotic relationship with nitrogen-fixing bacteria. This process reduces the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers, which are energy-intensive to produce and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. By incorporating chickpeas into cropping systems, farmers can play a role in mitigating climate change.
16. Employment Opportunities: Chickpea production, processing, and value-added product manufacturing create employment opportunities in rural areas. From farm labor to processing and distribution, chickpea-related activities contribute to rural livelihoods and economic development.
17. Food Security and Diversification: Chickpeas are an important source of plant-based protein, which can be especially crucial in regions with limited access to animal protein sources. The cultivation of chickpeas can diversify food options and contribute to food security. In parts of Africa and Asia where chickpeas are grown and consumed, they provide a nutritious and affordable protein source for local populations.
18. Market Demand and Price Stability: The growing popularity of plant-based diets and the increasing demand for protein-rich foods have contributed to the rising popularity of chickpea-based products. This demand can create price stability for farmers and traders, encouraging consistent cultivation and trade of chickpeas.
19. Disease and Pest Management: Chickpeas are susceptible to various diseases and pests. Research focused on chickpea cotyledons has helped identify resistance traits, leading to the development of disease-resistant varieties. This contributes to more sustainable pest management practices, reducing the reliance on chemical pesticides.
20. Potential for Genetic Modification: As a crop with significant economic importance, chickpeas have attracted interest in genetic modification for specific traits, such as improved nutritional content, disease resistance, and abiotic stress tolerance. While this technology remains a subject of debate, it offers potential opportunities for further enhancing the crop’s economic value and sustainability.
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Chickpea/Gram pea Cotyledons Seeds
The cotyledons, which are the embryonic seed leaves found within the chickpea seed, can be processed to produce a range of products and by-products.
Here are some examples along with their processes:
1. Chickpea Flour: Chickpea flour, also known as gram flour or besan, is a popular gluten-free flour widely used in culinary applications. The process involves grinding dried chickpea cotyledons into a fine powder. This flour is commonly used in making traditional dishes like Indian pakoras, flatbreads, and as a thickening agent in various recipes.
2. Chickpea Protein Isolate: Chickpea protein isolate is a protein-rich powder extracted from chickpea cotyledons. The process involves removing the starch and other components, leaving behind a high-protein concentrate. It can be used in protein bars, shakes, and other food products as a plant-based protein source.
3. Chickpea Starch: The starch obtained from chickpea cotyledons can be used as a thickening agent in food products, similar to cornstarch or potato starch. The process involves separating the starch from the cotyledons through washing, drying, and milling.
4. Chickpea Fiber: Chickpea cotyledons contain dietary fiber, which can be extracted and used in various food products to increase their fiber content. The process involves isolating the fiber through milling and sieving.
5. Chickpea Oil: Chickpea oil, also known as gram oil, can be extracted from chickpea cotyledons. The process involves mechanically pressing the cotyledons to extract the oil, which can be used for cooking, as a salad dressing, or in various beauty products.
6. Chickpea Snacks: Roasted or fried chickpeas are a popular and nutritious snack. The process involves coating the chickpeas in oil and seasoning before roasting or frying until they become crispy. These snacks can be flavored with various spices or sweeteners.
7. Chickpea By-Products (e.g., Chickpea Husks and Bran): During the processing of chickpeas to obtain the various products mentioned above, there will be by-products such as husks and bran. These can be used as animal feed, as ingredients in the production of composite flours, or in the agricultural industry for soil enrichment.
Read Also: Chickpea/Gram pea Seeds: Economic Importance, Uses and By-Products
8. Chickpea Milk: Chickpea milk is a dairy-free alternative to cow’s milk. The process involves blending soaked chickpeas with water and then straining the mixture to obtain a creamy milk-like liquid. Chickpea milk can be used in coffee, smoothies, and various recipes as a milk substitute.
9. Chickpea Puree: Chickpea cotyledons can be processed into a smooth puree, which can be used as a base for dips, spreads, and sauces.
10. Chickpea Noodles/Pasta: Chickpea flour can be used to make gluten-free noodles or pasta. The process involves mixing chickpea flour with water and other ingredients to form a dough, which is then extruded into various shapes and dried.
11. Chickpea Baby Food: Chickpea cotyledons can be processed into a nutritious and baby-friendly food. The process involves cooking and pureeing chickpeas to create a smooth and easily digestible baby food option.
12. Chickpea Soup Mix: Chickpea cotyledons can be processed into a dry soup mix with other ingredients like spices, vegetables, and grains. Consumers can rehydrate and cook the mix to make a hearty and flavorful chickpea soup.
13. Chickpea Desserts: Chickpea flour can be used as an alternative in baking, creating gluten-free desserts like cookies, cakes, and brownies. Chickpea puree or aquafaba (the liquid from canned chickpeas) can be used as an egg replacement in vegan baking.
14. Chickpea Fermented Products: Chickpea cotyledons can be used to create fermented products like tempeh or fermented chickpea paste. Fermentation enhances the nutritional profile and digestibility of chickpeas while adding a unique flavor to the products.
15. Chickpea Face Mask: Chickpea flour is known for its skin-friendly properties. It can be mixed with other ingredients like yogurt, honey, or turmeric to create a natural face mask that helps cleanse and brighten the skin.
16. Chickpea Biodegradable Packaging: Researchers are exploring the use of chickpea proteins and starches to create biodegradable packaging materials, reducing plastic waste and environmental impact.
17. Chickpea Coffee Substitute: Roasted and ground chickpeas can be used as a coffee substitute or coffee additive, offering a caffeine-free alternative with a slightly nutty flavor.
18. Chickpea Pet Food: Chickpea cotyledons, along with other ingredients, can be used in the production of nutritious and protein-rich pet food for dogs and other animals.
In conclusion, the economic importance of chickpea cotyledons extends far beyond their role as a nutritious food source. Their impact on agriculture, trade, employment, and food security highlights the significance of chickpeas in both local and global contexts. As the world faces challenges related to climate change, population growth, and sustainable development, chickpeas and their cotyledons continue to play a crucial role in addressing these issues and ensuring a more sustainable future for all.
Read Also: Sheep 101: Wool Production Complete Guide
