Cinnamon stigma: Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products
Cinnamon stigma typically refers to the reproductive structure found in flowers of plants, particularly those in the Cinnamomum genus. Cinnamomum is a genus of flowering plants in the laurel family (Lauraceae) that includes several species known for producing the spice cinnamon.
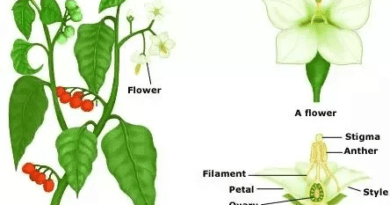
The stigma is a part of the female reproductive organs of a flower, specifically the pistil, which is composed of three main parts: the stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is the receptive surface at the top of the pistil where pollen grains land and germinate, facilitating the process of fertilization.
In the context of Cinnamomum plants, the stigma plays a crucial role in the reproductive process, allowing the plant to produce seeds for future generations. The flowers of Cinnamomum species possess stigmas that are receptive to pollen, aiding in the pollination process and subsequent development of seeds.
Cinnamon is obtained from the bark of Cinnamomum trees, and the reproductive structures of the flowers, including the stigma, contribute to the overall reproductive cycle of these plants. The stigma’s function is essential for successful reproduction and seed production in Cinnamomum species.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Cinnamon stigma
Cinnamon stigma, also known as saffron or the stigma of the Crocus sativus flower, is a valuable spice used in various culinary, medicinal, and industrial applications.
1. Culinary Use: Cinnamon is a popular spice used in cooking and baking. Its distinct and aromatic flavor enhances the taste of both sweet and savory dishes. It’s used in desserts, beverages, curries, stews, and more.
2. Food Preservation: Cinnamon has natural antimicrobial properties, making it historically valuable for preserving food. It helps prevent spoilage and extend the shelf life of food products.
3. Health and Medicinal Uses: Cinnamon has potential health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It’s used in traditional medicine for various ailments like digestive issues, colds, and diabetes management. Research is ongoing to explore its medicinal potential.

4. Perfumes and Aromatherapy: The aroma of cinnamon is used in perfumes, candles, and other fragrance products. It’s also utilized in aromatherapy for its calming and soothing effects.
5. Flavoring and Beverages: Cinnamon is used to flavor a wide range of beverages, including teas, coffees, and cocktails.
6. Confectionery: Cinnamon is a common ingredient in candies, chewing gums, and other confectionery items.
7. Saffron (Crocus sativus): Saffron is obtained from the stigma of the Crocus sativus flower. It’s one of the most expensive spices due to its labor-intensive harvesting process. Here are its economic importance and uses:
8. Culinary Use: Saffron is a highly prized spice known for its distinct flavor, aroma, and vibrant yellow color. It’s used in various dishes such as paella, risottos, biryanis, and desserts. It adds both flavor and color to the food.
9. Dyeing and Coloring: Saffron is used as a natural dye for fabric and food. Its vibrant color is utilized in textiles and culinary applications.
10. Traditional Medicine: Saffron has been used in traditional medicine for its potential medicinal properties, including as an antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antidepressant. It’s believed to have a range of health benefits, although scientific research is ongoing to substantiate these claims.
11. Cosmetics and Perfumery: Saffron’s aroma and color make it a desirable ingredient in perfumes, cosmetics, and skincare products.
12. Beverages: Saffron is used to flavor and color beverages such as saffron-infused teas and drinks.
Read Also: 24 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Linaria vulgaris (Butter and Eggs)
13. Ceremonial Use: In some cultures, saffron is used in religious ceremonies and rituals.
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived FromCinnamon stigma
Cinnamon stigma, also known as cinnamon flowers or saffron of India, refers to the female flower parts of the Cinnamomum tree. The main product derived from cinnamon stigma is saffron, which is highly valued for its unique flavor, aroma, and various uses.
Here are the primary products and by-products that can be derived from cinnamon stigma:
1. Saffron (Crocus sativus): Saffron is the main product derived from cinnamon stigma. It is a spice known for its distinct flavor, fragrance, and vibrant red color. It is primarily used for culinary purposes, including flavoring and coloring various dishes such as rice, desserts, and beverages.
2. Saffron Extract: Saffron extract is obtained by extracting the active components from the cinnamon stigma. It is used in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries for its potential health benefits, including its antioxidant properties and potential mood-enhancing effects.
3. Saffron Oil: Saffron oil is an essential oil extracted from cinnamon stigma. It is used in perfumery, aromatherapy, and for its medicinal properties, such as being an antispasmodic and anti-inflammatory agent. It can also be used in culinary applications to impart saffron flavor and aroma.
4. Saffron Powder: Ground saffron is used in cooking and baking to infuse dishes with the distinctive flavor and color of saffron. It’s commonly used in various cuisines to add depth and richness to the taste of the dishes.
5. Saffron Tea: Infusions made from cinnamon stigma can be used to make saffron tea, which is known for its potential health benefits, including its antioxidant properties, potential mood enhancement, and digestive support.
6. Saffron Infused Water: Infusing water with cinnamon stigma can create a saffron-infused water, which can be used for various purposes, including drinking or as an ingredient in beverages and culinary dishes.
7. Saffron Dyes: Saffron can be used as a natural dye for textiles and other materials due to its vibrant color. It has been historically used for dyeing fabrics, although this use is less common today due to the high cost of saffron.
8. Saffron Residues and By-products: After saffron extraction or processing, there may be residues or by-products, including plant material and waste. These residues can potentially be used for composting, animal feed, or in the extraction of additional compounds for various purposes.
In conclusion, it is important to note that the production and extraction methods for these products and by-products may vary, and the yield and quality of the derivatives can depend on factors such as the quality of the cinnamon stigma, the extraction process, and the intended use of the end products.
Read Also: What is Daisy Flower? Benefits, Uses and Importance