Shifting Cultivation is one of the farming methods that has been practiced by man to meet his/her food needs. So, Shifting Cultivation is described as an agricultural system where a farmer haven farmed a piece of land for a short period of time, say 1 – 3 years abandons the land and goes to another to continue his farming activity.
The decision whether to return to the former piece of land after the abandoning period remains his/her decision. The main aim of practicing Shifting Cultivation is to look for an area where there is abundant land with good level of soil fertility that can guarantee him/her (farmer) his intended level of farm production.
Concept and Definition of Shifting Cultivation
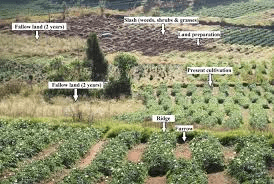
Shifting Cultivation is known as system of agricultural practice where a farmer farms on a piece of land for a while (which may be a period of 1 – 3 years) and thereafter leaves or abandon the land and goes to another land to continue his/her farming activities or operations (Lar, 2005).
Shifting Cultivation – Wikipedia stated that the system involves clearing a piece of land which is then followed by several years of farming until the soil begins to lose nutrients / fertility.
The system is such that the land is farmed until productivity is noticed to be declining through loss of soil fertility. Then the soil is left to regain its fertility through natural means that involves regeneration of the vegetation.
It is of note that Shifting Cultivation is a system that due to its nature is practiced by individual farmer or family. In rear cases it be practiced by a village of small community.
Shifting Cultivation – Science Daily Report advanced that Shifting cultivation is an elusive term to define, since it is perceived and used by different people in different contexts in widely differing ways. Nevertheless, some of the definition here stated; According to FAO Shifting Cultivation is defined as an agricultural or farm system in which relatively short periods of cultivation are followed by relatively long periods of fallow.
Shifting Cultivation is also defined as an agricultural system in which plots of land are cultivated temporarily, then abandoned and allowed to revert to their natural vegetation while the cultivator or farmers move to another plot to continue his/her farming activity.
From the definition, Shifting Cultivation is preparing ground in a large plot or area and cultivating mostly food grains and vegetables fruits etc till the soil fertility is lost. Then the field is burnt and cultivation shifted to another place or area.
Emphases are that the land is left at the point where production from the farm begins to fall or decline and that the period of fallow is usually longer than the period of cultivation.
The main importance or reason why farmers practice Shifting Cultivation is that, it is a farming system that helps to restore soil fertility through long periods of fallowing (Shifting Cultivation – Science Daily).
Read Also : Permanent Crops Cultivation and Characteristics of Permanent Plants
This method of regaining nutrient is preferred to the use of farm inputs like inorganic fertilizers and amendments. During Shifting Cultivation, nutrients are recycled between natural vegetation and crops; and ecological balance is maintained by adopting diverse and complex practices.
Adebowale (2018) pointed out the effects of Shifting Cultivation are of two folds. They are;
- Forest degradation and deforestation, and
- Land degradation.
An Overview of Shifting Cultivation

Shifting cultivation is an agricultural system in which plots of land are cultivated temporarily, then abandoned and allowed to revert to their natural vegetation while the cultivator of farmer moves on to another plot of land to continue with his/her farming (Shifting Cultivation – Science Daily)
Shifting cultivation is the most ancient system of agriculture in which soil fertility is restored by natural means that involves long periods of fallowing rather than the use of farm inputs like inorganic fertilizers and amendments.
Shifting cultivation as an agricultural system involves an alternation between cropping for a few years on selected and cleared plots.
A few years of cropping or cultivation is followed by a lengthy period of fallow. Then the land is assumed to have rested and be able to regain its lost nutrients that were original in the soil before first cultivation started or took place.
Shifting Cultivation is a technology that has been practiced in those regions were the population is scanty It is particularly popular in forested and derived savanna areas of tropical Asia where there is expanse of land for cultivation.
Shifting Cultivation refers to a technique of rotational farming in which land is cleared for cultivation mostly with the use of cutlass and possibly other simple farm tools, the debris are then burnt and the land is then farmed on.

After some time when the land may have be known to be declining in nutrients availability and subsequently crop productivity, it is then left to regenerate for a period of few years. Another name for Shifting Cultivation is “swidden agriculture” (Shifting Cultivation – Wikipedia)
Shifting Cultivation often involves clearing of a piece of land and cultivating it for the period it can product crop at its peak, followed by several years of wood harvesting or farming until the soil loses fertility (that is the fallow period).
Once the land becomes inadequate for crop production or seen not to be meeting up with its potentials, it is then left to be reclaimed by natural vegetation, or sometimes converted to a different long term cyclical farming practice.
Lal (2005) noted that across the globe, Shifting Cultivation is known to be practiced as many as an estimated population exceeding 250 million people derive subsistence from the practice of shifting cultivation, and ecological consequences are often deleterious.
Sadly, Shifting Cultivation is considered devastating and disadvantageous as it does not only cause harm to the ecosystem but also exerts negative impacts on economy. On the contrary, many studies concluded that tribal or practitioners of Shifting Cultivation are part of conservation.
In summary, shifting Cultivation is known as an age long practice that involves the farmer farming a piece of land and then leaving or vacating the land for another place on the ground of loss of fertility.
Amongst the several definitions advanced, Shifting Cultivation is an agricultural system in which plots of land are cultivated temporarily, then abandoned and allowed to revert to their natural vegetation while the cultivator or farmers move to another plot to continue his/her farming activity.
Read Also: 12 Management Tips for better Poultry Performance Potential
Frequently Asked Questions
We will update this section soon.

