A concrete fish pond is a man-made structure designed specifically for raising fish, utilizing reinforced concrete for its construction. This material is renowned for its durability and strength, making it ideal for creating long-lasting and stable ponds.
Concrete fish ponds are advantageous for both small-scale and commercial fish farming due to their ability to retain water and withstand various environmental stressors. These ponds provide a controlled environment, which significantly reduces risks associated with natural water bodies, such as predators, fluctuations in water quality, and the spread of diseases.
Concrete fish ponds also facilitate easier monitoring and management of fish, making them suitable for both novice and experienced farmers. Furthermore, the use of concrete allows for the construction of ponds in different shapes and sizes, catering to various farming needs and space constraints.
As fish farming continues to grow as a sustainable and profitable venture, concrete fish ponds emerge as a reliable option for maximizing yields and ensuring the health of the fish. When planning the construction of a concrete fish pond, several critical steps must be taken to ensure the pond’s effectiveness and efficiency.
The first step involves selecting an appropriate location. The site should receive adequate sunlight, as light is essential for the growth of plankton, which serves as food for the fish. It should also be easily accessible for feeding, monitoring, and harvesting the fish. Proximity to a water source is crucial for filling the pond and maintaining water levels.
Once the location has been determined, the next step is to decide on the size and shape of the concrete fish pond based on the type and number of fish to be reared. Common shapes for concrete fish ponds include rectangular, square, and circular designs, each offering unique benefits.
Rectangular concrete fish ponds, for instance, are easier to manage and harvest, while circular concrete fish ponds promote better water circulation, which can be beneficial for fish health.
The depth of the concrete fish pond is another important consideration. For most fish species, a depth of 1.2 to 1.5 meters is recommended. This depth provides sufficient space for the fish to swim and grow while allowing for efficient oxygen distribution throughout the water.
Shallow concrete fish ponds may overheat quickly, particularly in warm climates, while deeper concrete fish ponds can experience oxygen depletion, which can be detrimental to fish health.
It is also essential to plan for effective drainage and water inlet systems. Proper drainage facilitates the easy removal of waste and old water, which is crucial for maintaining high water quality and ensuring the health of the fish. The inlet system should allow for controlled water flow to prevent sudden changes in water levels, which can stress the fish and potentially lead to health issues.
Constructing a concrete fish pond requires specific materials and tools to ensure a sturdy and long-lasting structure. The primary material used is reinforced concrete, which is made by mixing cement, sand, gravel, and water.
Reinforcement bars, commonly known as rebar, are embedded in the concrete to provide additional strength and prevent cracking over time. A high-quality waterproofing agent is also necessary to prevent water seepage, ensuring that the concrete fish pond retains water effectively.
In addition to concrete and rebar, other essential materials include PVC pipes for the inlet and outlet systems, drainage valves, and mesh or nets to cover the concrete fish pond and protect the fish from predators.
The construction process of a concrete fish pond involves several steps. It begins with the excavation of the pond area to the desired shape and depth. Following excavation, formwork is installed to hold the concrete in place as it sets.
The rebar is then positioned within the formwork to provide the necessary reinforcement. Once the formwork and rebar are in place, concrete is poured and evenly spread to form the pond walls and floor.
It is crucial to ensure that the concrete is properly mixed and cured to avoid weak spots and potential leaks in the pond structure. During construction, various tools are required, including shovels, trowels, levels, and wheelbarrows.
A concrete mixer can be particularly beneficial for mixing large quantities of concrete efficiently. After the concrete has cured, the pond should be coated with a waterproofing agent to seal any pores and prevent water loss. Once the concrete fish pond is constructed and waterproofed, it can be filled with water and stocked with fish.
Read Also: Introduction and Feasibility Study on Fish Farming
Benefits of Using Concrete for Fish Ponds

Concrete fish ponds have become a popular choice among fish farmers due to their numerous advantages over other types of ponds. These benefits range from durability and maintenance to water quality control and flexibility in design. Here is an in-depth look at the benefits of using concrete for fish ponds.
1. Durability and Longevity: One of the most significant benefits of using concrete for fish ponds is the material’s durability and longevity. Concrete is a strong and robust material that can withstand various environmental stressors, including extreme weather conditions.
Unlike earthen ponds, which can erode over time, concrete ponds maintain their structural integrity for many years. This longevity makes concrete fish ponds a cost-effective investment in the long run, as they require fewer repairs and less frequent rebuilding compared to ponds made from other materials.
2. Low Maintenance: Concrete fish ponds are relatively low maintenance. The solid and smooth surfaces of concrete ponds make them easier to clean compared to earthen or liner ponds, which can accumulate debris and algae in crevices.
Regular maintenance tasks, such as removing waste and cleaning the pond walls, are more straightforward and less time-consuming with concrete ponds. Additionally, the non-porous nature of concrete helps prevent the growth of unwanted plants and algae, reducing the need for chemical treatments and manual cleaning.
3. Water Quality Control: Another critical advantage of concrete fish ponds is the ability to maintain consistent water quality. Concrete ponds can be designed with efficient drainage and filtration systems, allowing for better control over water parameters such as temperature, pH, and oxygen levels.
This control is essential for the health and growth of fish, as it helps create a stable and suitable environment. In earthen ponds, water quality can fluctuate due to soil composition and external factors, but concrete ponds provide a more predictable and manageable setting for fish farming.
4. Pest and Predator Prevention: Concrete fish ponds offer superior protection against pests and predators compared to other types of ponds. The solid walls and floors of a concrete pond create a barrier that prevents burrowing animals and insects from entering.
Additionally, concrete ponds can be covered with nets or mesh to keep out birds and other predators that might prey on the fish. This level of protection ensures that the fish remain safe, reducing losses and improving overall farm productivity.
5. Flexibility in Design: Concrete fish ponds provide great flexibility in terms of design and customization. They can be constructed in various shapes and sizes to fit specific farming needs and available space. Whether a farmer needs a small backyard pond or a large commercial setup, concrete can be molded to meet those requirements.
This flexibility extends to the installation of features such as water inlets, outlets, and aeration systems, which can be integrated into the pond’s design to optimize water flow and fish health. Furthermore, the ability to design a pond according to precise specifications allows farmers to maximize the use of their land and resources.
6. Improved Fish Health and Growth: The stable environment provided by concrete fish ponds contributes to improved fish health and growth. The smooth surfaces of the pond reduce the risk of injuries and infections that fish might suffer in rough or uneven environments.
Additionally, the controlled water quality helps prevent diseases and stress caused by poor water conditions. Fish in concrete ponds often exhibit better growth rates and higher survival rates, leading to increased yields and profitability for the farmer.
7. Ease of Harvesting: Harvesting fish from concrete ponds is generally easier than from earthen or liner ponds. The smooth and solid surfaces allow for efficient use of nets and other harvesting equipment, reducing the time and labor required.
Additionally, the design of concrete ponds can include features such as sloped floors and drainage systems that facilitate the easy collection of fish. This ease of harvesting translates to lower operational costs and quicker turnaround times for the farmer.
8. Environmental Impact: Concrete fish ponds can have a lower environmental impact compared to other pond types. Because they are less prone to erosion, they do not contribute to sediment runoff, which can pollute nearby water bodies.
The controlled environment of concrete ponds also reduces the need for chemical treatments, which can be harmful to the surrounding ecosystem. By minimizing these environmental risks, concrete ponds offer a more sustainable option for fish farming.
9. Versatility in Usage: Concrete fish ponds are versatile and can be used for various aquaculture applications. They are suitable for raising a wide range of fish species, including tilapia, catfish, and ornamental fish.
Additionally, concrete ponds can be used for breeding, hatching, and grow-out phases, making them a comprehensive solution for different stages of fish farming. This versatility makes concrete ponds an attractive option for farmers looking to diversify their aquaculture operations.
10. Economic Benefits: The combination of durability, low maintenance, improved fish health, and ease of harvesting leads to significant economic benefits for fish farmers. Concrete fish ponds reduce the need for frequent repairs and replacements, lowering long-term costs.
The enhanced fish health and growth rates result in higher yields and better-quality produce, increasing the farm’s profitability. Moreover, the ability to control water quality and prevent losses due to predators and pests ensures a more consistent and reliable output.
Step-By-Step Guide to Constructing a Concrete Fish Pond
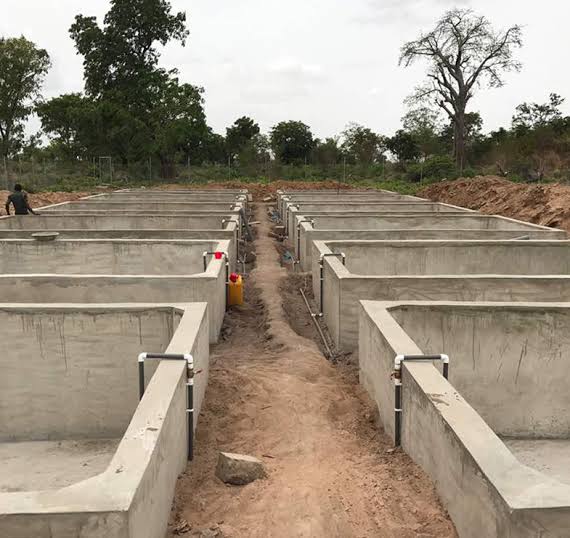

Building a concrete fish pond involves several steps, each requiring careful planning and execution to ensure a durable and functional structure. Here is a detailed step-by-step guide to constructing a concrete fish pond.
Step 1: Planning and Design
Before construction begins, thorough planning is crucial. Decide on the size, shape, and depth of the pond based on the type and number of fish you plan to raise. Consider factors like sunlight, accessibility, and proximity to a water source. A typical depth for most fish species ranges from 1.2 to 1.5 meters. Ensure the design includes efficient drainage and water inlet systems to maintain water quality.
Step 2: Selecting the Location
Choose a suitable location for your concrete fish pond. The site should receive adequate sunlight, which is essential for the growth of plankton that serves as food for the fish. It should also be easily accessible for feeding, monitoring, and harvesting the fish. Ensure the location is close to a water source for easy filling and maintaining water levels.
Step 3: Marking and Excavation
Mark the outline of the pond using stakes and string based on your planned dimensions. Once the area is marked, begin excavation. Dig to the required depth, ensuring the bottom is level. The sides should be slightly sloped to prevent collapsing. Excavate trenches for the drainage and inlet pipes as well.
Step 4: Installing Formwork
Formwork is a temporary mold into which concrete is poured to form the pond walls and floor. Construct the formwork using wooden boards or metal panels, ensuring it matches the shape and size of the pond. Secure the formwork firmly to prevent it from shifting during the pouring of concrete.
Step 5: Placing Reinforcement Bars (Rebar)
Reinforcement bars, commonly known as rebar, are essential for adding strength to the concrete structure. Place the rebar grid within the formwork, ensuring it is evenly spaced and elevated slightly off the ground using rebar chairs or small concrete blocks. The rebar should be placed in both the walls and the floor of the pond to prevent cracking and increase durability.
Step 6: Mixing and Pouring Concrete
Mix the concrete using cement, sand, gravel, and water. A concrete mixer can be used for efficiency. The concrete mixture should have a smooth, workable consistency. Begin pouring the concrete into the formwork, starting with the floor and then the walls. Ensure the concrete is evenly spread and free of air pockets by using a vibrating tool or tapping the sides of the formwork. Smooth the surface with a trowel.
Step 7: Curing the Concrete
Curing is the process of allowing the concrete to harden and gain strength. This step is crucial for the durability of the pond. Cover the concrete with plastic sheets or burlap to retain moisture and prevent cracking. Keep the concrete moist by sprinkling water regularly for at least a week. Avoid disturbing the concrete during this period to ensure proper curing.
Step 8: Removing the Formwork
Once the concrete has cured adequately, usually after a week, carefully remove the formwork. Check the pond walls and floor for any cracks or weak spots. If any are found, repair them using a concrete patching compound. Smooth out any rough edges to prevent injury to the fish.
Step 9: Applying Waterproofing
To ensure the pond retains water effectively, apply a waterproofing agent to the concrete surfaces. Waterproofing helps seal any pores and prevents water seepage. Use a brush or roller to apply the waterproofing compound evenly on the walls and floor. Allow it to dry completely before filling the pond with water.
Step 10: Installing Drainage and Inlet Systems
Install PVC pipes for the drainage and inlet systems. The drainage system should include a valve for easy removal of old water and waste. Position the inlet pipe to allow for controlled water flow into the pond. Ensure that the pipes are securely fitted and do not leak.
Step 11: Filling the Pond
Before filling the pond with water, rinse it thoroughly to remove any debris or dust from construction. Fill the pond slowly, checking for any leaks. Monitor the water level and quality, ensuring it meets the requirements for the type of fish you plan to raise.
Step 12: Stocking the Pond
After the pond is filled and the water quality is stabilized, it is time to stock it with fish. Introduce the fish gradually to allow them to acclimate to the new environment. Monitor their behavior and health closely in the initial days to ensure they adapt well.
Step 13: Maintaining the Pond
Regular maintenance is essential for the health of the fish and the longevity of the pond. This includes monitoring water quality, feeding the fish appropriately, and cleaning the pond to remove waste and debris. Check the drainage and inlet systems regularly to ensure they are functioning correctly.
Step 14: Harvesting the Fish
When the fish reach the desired size, it is time to harvest them. Use nets and other harvesting equipment to collect the fish efficiently. The design of the concrete pond, with its smooth surfaces and efficient drainage system, facilitates easier harvesting compared to other types of ponds.
Read Also: How to Market your Matured Fishes for Profit
Diagram of a Concrete Fish Pond
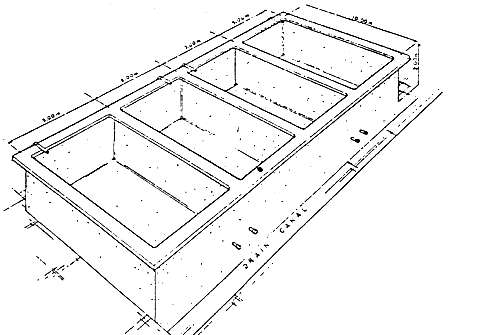
Creating a diagram of a concrete fish pond involves more than just illustrating the structure; it includes a detailed explanation of each component and its function within the pond system. Below is a comprehensive description of a concrete fish pond, focusing on the different parts and how they contribute to the pond’s overall functionality.
1. Overview of a Concrete Fish Pond: A concrete fish pond is a man-made water body constructed using reinforced concrete. It is designed to provide a controlled environment for raising fish.
The diagram of a concrete fish pond typically includes various components such as the pond basin, inlet and outlet pipes, drainage system, and possibly an aeration system. Each of these elements plays a crucial role in maintaining the pond’s ecosystem and ensuring the health and growth of the fish.
2. Pond Basin: The pond basin is the primary component of a concrete fish pond. It is a large, open area where the fish live and swim. The basin’s size and shape can vary depending on the intended use and the number of fish it will hold.
Typically, the basin is rectangular or oval, which facilitates easy cleaning and efficient water flow. The depth of the basin is also important; it usually ranges from 1.2 to 1.5 meters, providing sufficient space for the fish to move and grow while maintaining an optimal oxygen level.
3. Reinforced Concrete Walls and Floor: The walls and floor of the pond basin are made from reinforced concrete, which is strong and durable. The reinforcement usually involves a grid of steel bars (rebar) placed within the concrete to provide additional strength and prevent cracking. This reinforcement is crucial for maintaining the structural integrity of the pond over time, especially under the pressure of the water.
4. Inlet Pipe: The inlet pipe is responsible for supplying fresh water to the pond. It is usually positioned at a higher point to ensure gravity-fed flow, which helps distribute water evenly across the pond.
The inlet pipe is connected to a water source, such as a well or a reservoir, and can be equipped with a filter to prevent debris and contaminants from entering the pond. Fresh water is essential for maintaining water quality and ensuring the fish have a healthy environment.
5. Outlet Pipe and Drainage System: The outlet pipe and drainage system are crucial for removing excess water and waste from the pond. The outlet pipe is typically positioned at the bottom of the pond to facilitate the removal of settled waste and debris.
This pipe leads to a drainage system that directs the water away from the pond, preventing flooding and maintaining a stable water level. The drainage system often includes a valve that allows for easy control of water flow, enabling periodic cleaning and water changes.
6. Aeration System: An aeration system is sometimes included in concrete fish ponds to ensure adequate oxygen levels in the water. This system can consist of air pumps, diffusers, or fountains that introduce air into the water.
Oxygen is vital for the respiration of fish and the breakdown of organic matter by aerobic bacteria. Proper aeration helps prevent the buildup of harmful gases and supports the overall health of the pond ecosystem.
7. Waterproofing and Sealing: To prevent water leakage, the concrete surfaces of the pond are treated with waterproofing agents. These agents seal the pores in the concrete, ensuring that the pond retains water effectively. Waterproofing is applied to both the walls and the floor of the pond, providing a protective barrier against water seepage and structural damage.
8. Protective Features: Concrete fish ponds often include protective features to safeguard the fish from predators and environmental factors. For example, nets or mesh covers can be installed over the pond to prevent birds and other animals from preying on the fish. Additionally, shade structures may be added to protect the fish from excessive sunlight, which can cause overheating and stress.
9. Maintenance Access: Easy access for maintenance is an important consideration in the design of a concrete fish pond. This can be achieved by incorporating walkways or platforms around the pond, allowing for easy cleaning, feeding, and monitoring of the fish. Proper access ensures that routine maintenance tasks, such as checking water quality and cleaning the pond, can be performed efficiently.
10. Illustration of a Concrete Fish Pond: While a written description provides a comprehensive understanding, an actual diagram helps visualize the structure and components of a concrete fish pond. Picture a rectangular or oval basin with reinforced concrete walls and floor.
At one end, there is an inlet pipe connected to a water source, positioned to allow fresh water to flow into the pond. The other end features an outlet pipe at the bottom, leading to a drainage system for waste removal.
Inside the pond, you might see a grid of rebar embedded in the concrete for reinforcement. The surface of the concrete is coated with a waterproofing agent, ensuring it holds water without leaking. An aeration system, possibly consisting of air pumps and diffusers, is installed to maintain oxygen levels.
Around the pond, walkways or platforms provide easy access for maintenance. Protective nets or mesh covers are installed overhead to keep predators away, and shade structures offer protection from direct sunlight. The entire setup is designed to create a controlled, sustainable environment for raising healthy fish.
Frequently Asked Questions on Concrete Fish Pond Construction and Farming Guide
1. What is a concrete fish pond?
A concrete fish pond is a man-made water body constructed using reinforced concrete. It is designed to provide a controlled environment for raising fish. The pond’s structure includes a basin made from concrete, with walls and a floor reinforced by steel bars to ensure durability and prevent cracking. Concrete fish ponds are favored for their strength, low maintenance, and ability to maintain stable water conditions, which are crucial for fish farming.
2. Why should I choose a concrete fish pond over other types?
Concrete fish ponds offer several advantages over other types of ponds, such as earthen or plastic-lined ponds. The key benefits include:
- Durability: Concrete ponds are long-lasting and resistant to wear and tear.
- Low Maintenance: They require less frequent repairs and maintenance compared to other types.
- Water Quality Control: The concrete structure makes it easier to manage water quality, crucial for fish health.
- Predator Protection: Smooth surfaces and secure construction help prevent predators from harming the fish.
- Ease of Cleaning: The solid structure allows for easier cleaning and waste removal.
3. How do I plan the construction of a concrete fish pond?
Planning is the first and most crucial step in constructing a concrete fish pond. Here’s what you need to consider:
- Size and Shape: Determine the dimensions based on the type and number of fish you plan to raise.
- Location: Choose a site with adequate sunlight, easy access, and proximity to a water source.
- Depth: Typically, a depth of 1.2 to 1.5 meters is ideal for most fish species.
- Drainage and Inlet Systems: Plan for efficient water management systems to maintain water quality.
4. What materials and tools are needed for constructing a concrete fish pond?
For constructing a concrete fish pond, you will need:
- Materials: Cement, sand, gravel, steel bars (rebar), waterproofing agent, PVC pipes for drainage and inlet, and possibly air pumps for aeration.
- Tools: Concrete mixer, trowels, shovels, rebar cutter, measuring tape, stakes, string, and a level.
5. How do I select the location for my concrete fish pond?
Choosing the right location is essential for the success of your fish pond. Consider the following:
- Sunlight: The site should receive adequate sunlight to promote plankton growth, which serves as food for the fish.
- Accessibility: Ensure the pond is easily accessible for feeding, monitoring, and maintenance.
- Proximity to Water Source: A nearby water source is crucial for filling and maintaining the pond’s water levels.
- Protection from Elements: Consider natural or artificial structures to protect the pond from strong winds and excessive sunlight.
6. What is the step-by-step construction process for a concrete fish pond?
The construction process includes several steps:
- Planning and Design: Define the pond’s size, shape, and depth.
- Site Selection: Choose an appropriate location.
- Marking and Excavation: Outline the pond and excavate to the required depth.
- Installing Formwork: Build the formwork for shaping the pond.
- Placing Rebar: Insert reinforcement bars to strengthen the structure.
- Mixing and Pouring Concrete: Prepare and pour the concrete mix.
- Curing the Concrete: Allow the concrete to harden and gain strength.
- Removing Formwork: Carefully remove the formwork after curing.
- Applying Waterproofing: Seal the concrete to prevent water leakage.
- Installing Drainage and Inlet Systems: Set up pipes for water management.
- Filling the Pond: Rinse and fill the pond with water.
- Stocking the Pond: Introduce fish to the pond.
- Maintenance: Regularly monitor water quality and fish health.
7. How do I maintain a concrete fish pond?
Maintaining a concrete fish pond involves several tasks to ensure the health of the fish and the longevity of the pond. Key maintenance activities include:
- Monitoring Water Quality: Regularly check parameters such as pH, temperature, oxygen levels, and ammonia levels. Use water testing kits to ensure the water remains within the optimal range for the fish species.
- Feeding the Fish: Provide the right amount of food to avoid overfeeding, which can lead to water pollution.
- Cleaning: Remove waste, uneaten food, and debris from the pond to prevent the buildup of harmful substances.
- Water Changes: Periodically replace a portion of the pond water to maintain water quality. Use the drainage system to remove old water and add fresh water through the inlet pipe.
- Inspecting Infrastructure: Regularly check the pond structure for cracks or leaks and repair any damages promptly. Ensure that the drainage and inlet systems are functioning correctly.
- Controlling Algae: Monitor algae growth and control it using appropriate methods to prevent it from overwhelming the pond and depleting oxygen levels.
8. How do I stock my concrete fish pond with fish?
Stocking your concrete fish pond involves introducing fish into the newly prepared pond environment. Follow these steps:
- Acclimatization: Before releasing the fish, acclimate them to the pond water by gradually mixing pond water into their transport container over a period of time. This helps them adjust to the new water conditions and reduces stress.
- Gradual Introduction: Introduce the fish in small batches rather than all at once. This reduces the shock to the pond’s ecosystem and allows you to monitor the fish for any signs of stress or illness.
- Monitoring: After stocking, closely observe the fish for a few days to ensure they are adapting well to their new environment. Look for signs of healthy behavior, such as active swimming and feeding.
9. What are common issues faced in concrete fish ponds and how can they be addressed?
Common issues in concrete fish ponds include water quality problems, algae growth, fish diseases, and structural issues. Here’s how to address them:
- Water Quality Problems: Regularly test and monitor water quality. Perform partial water changes and use water conditioners if necessary.
- Algae Growth: Manage algae by controlling nutrient levels, reducing sunlight exposure, and using algicides if needed. Avoid overfeeding, which can contribute to algae growth.
- Fish Diseases: Maintain good water quality and avoid overcrowding to reduce the risk of diseases. Quarantine new fish before adding them to the pond. If diseases occur, identify the issue and treat the pond with appropriate medications.
- Structural Issues: Inspect the pond for cracks or leaks regularly. Repair minor cracks with concrete patching compounds and consider professional assistance for significant structural problems.
10. How can I ensure the sustainability and productivity of my concrete fish pond?
To ensure the sustainability and productivity of your concrete fish pond, focus on the following practices:
- Regular Monitoring: Keep a close eye on water quality, fish health, and pond infrastructure.
- Proper Feeding: Follow a balanced feeding regimen to promote healthy fish growth and minimize waste.
- Water Management: Maintain clean water through regular partial water changes and effective filtration.
- Predator Control: Use protective nets or covers to keep predators away from the pond.
- Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of water quality tests, feeding schedules, and any treatments or changes made to the pond. This helps in identifying patterns and making informed management decisions.
In conclusion, constructing and maintaining a concrete fish pond involves a series of well-planned steps and ongoing management practices. From initial planning and site selection to construction and regular maintenance, each phase is crucial for creating a productive and sustainable fish farming system. By following the outlined guidelines and addressing common issues promptly, you can ensure the success of your concrete fish pond and achieve optimal fish growth and health.
Read Also: How to Grow Tomatoes in Containers





