Natural Mating and Artificial Insemination are two primary methods of breeding animals. Both techniques have their unique advantages and challenges, playing a vital role in livestock reproduction. Understanding the differences between natural mating and artificial insemination helps farmers and animal breeders make informed decisions on which method best suits their breeding goals.
Natural mating involves direct contact between a male and a female animal for reproduction. In this method, the male mounts the female and transfers semen naturally. This is the traditional method of breeding, commonly used in nature and on farms. Natural mating relies heavily on the health, fertility, and physical ability of the animals.
For many species, this method is instinctive and occurs without human intervention. It allows for genetic diversity as the mating process is based on natural selection. However, natural mating comes with limitations. Animals may face physical incompatibilities, and in cases where large herds are involved, it may be difficult to monitor successful fertilization. Additionally, diseases can be transmitted during physical contact between animals, leading to health risks within the herd.
Artificial insemination (AI), on the other hand, is a controlled and scientific method of reproduction, where semen is collected from a male and manually inserted into the reproductive tract of a female. This method allows breeders to bypass the need for natural mating and offers several benefits, especially for large-scale livestock operations.
Artificial insemination enables the use of semen from genetically superior males, which can be transported over long distances to inseminate multiple females. This allows for greater genetic control and improvement of animal breeds. AI also reduces the risk of transmitting diseases, as there is no direct contact between animals during breeding.
The key differences between these two methods lie in their processes, control over breeding, and associated risks. Natural mating is a less expensive option that requires minimal human involvement but may present challenges in controlling the genetic traits of offspring.
In contrast, artificial insemination offers more precision in breeding programs, with the ability to select specific sires and traits, making it an ideal choice for improving livestock quality. While AI requires expertise and initial investment in equipment, it has become increasingly popular due to its efficiency and flexibility.
In conclusion, both natural mating and artificial insemination have their distinct roles in animal reproduction. Natural mating remains the default option for small-scale operations or when seeking minimal intervention, while artificial insemination is favored for larger herds and those looking to enhance specific genetic traits.
Choosing between the two depends on factors such as breeding goals, herd size, and resources available for managing the reproduction process.
Definition of Natural Mating
Natural mating is the process by which animals breed without human intervention. It involves a male and female engaging in courtship behaviors that lead to copulation and fertilization. In natural mating, the male typically displays certain behaviors to attract the female, and mating occurs when the female is receptive. This method is commonly observed in many animal species, including livestock, wildlife, and pets.
Definition of Artificial Insemination
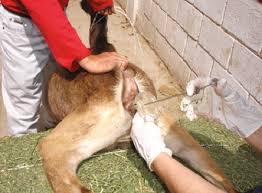
Artificial insemination (AI) is a reproductive technique that involves the deliberate introduction of sperm into a female’s reproductive tract by human intervention rather than through natural mating.
Artificial insemination is commonly used in livestock breeding, where semen collected from a male is deposited into the female’s uterus or cervix using specialized equipment. This method allows for controlled breeding, genetic selection, and improved reproductive efficiency.
Historical Background of Reproductive Techniques
The use of reproductive techniques has evolved over centuries:
1. Natural Mating: For thousands of years, natural mating has been the primary method of animal reproduction. Early farmers and breeders observed animal behaviors and utilized natural mating to improve the quality and productivity of their herds.
2. Artificial Insemination Development: The first recorded use of artificial insemination dates back to the 18th century, but it gained traction in the 20th century with advances in reproductive science. In 1930, the first successful artificial insemination of cattle was achieved, marking a significant milestone in livestock breeding. Over the years, AI techniques have improved with the development of semen preservation methods and the use of hormones to synchronize estrus cycles.
3. Modern Techniques: Today, artificial insemination is widely used in various animal species, including cattle, pigs, sheep, and horses. Techniques like in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer have also emerged as advanced reproductive technologies, further enhancing breeding capabilities.
Key Differences Between Natural Mating and Artificial Insemination
| Aspect | Natural Mating | Artificial Insemination |
|---|---|---|
| Method of Fertilization | Occurs through copulation between male and female. | Involves manually introducing sperm into the female’s reproductive tract. |
| Control Over Breeding | Limited control over which male mates with which female. | Allows for selection of specific males with desirable traits. |
| Timing and Efficiency | Depends on the natural estrus cycle; may lead to missed opportunities. | Can be timed precisely with ovulation, increasing success rates. |
| Health and Disease Management | Higher risk of transmitting sexually transmitted diseases. | Minimizes disease transmission risks; sperm can be screened. |
| Logistics and Accessibility | Requires proximity of males and females, which can be logistically challenging. | Enables breeding across greater distances without transporting animals. |
Advantages of Natural Mating
Natural mating refers to the traditional method of breeding animals, where a male and female mate without human intervention. This approach offers several benefits:
1. Genetic Diversity: Natural mating allows for a wider gene pool as animals mate based on their instincts. This can help maintain genetic diversity within a herd or flock, reducing the risks of inbreeding.
2. Lower Costs: This method typically incurs fewer costs compared to artificial insemination (AI). There are no expenses for semen collection, storage, or insemination equipment, making it more economical for small-scale farmers.
3. Increased Behavioral Interaction: Natural mating encourages natural behaviors in animals, promoting social interactions that are crucial for their well-being. This can lead to healthier animals that are less stressed.
4. Reduced Technical Skill Requirements: Farmers do not need specialized training or equipment for natural mating, making it more accessible for those without experience in AI techniques.
Read Also: Things You Should Know About Medicinal Plants
Advantages of Artificial Insemination

Artificial insemination is a breeding technique where semen is manually introduced into a female’s reproductive tract. This method offers several advantages:
1. Improved Genetic Quality: AI enables farmers to use semen from genetically superior males, which can enhance the overall quality of the offspring and lead to improved traits such as growth rates, disease resistance, and reproductive performance.
2. Control Over Breeding Timing: Farmers can better manage the timing of breeding, leading to more predictable and efficient production schedules. This is particularly useful for synchronizing breeding within a herd or flock.
3. Disease Control: AI reduces the risk of transmitting diseases that can occur with natural mating, as it minimizes direct contact between animals. This is especially important in large-scale operations or when introducing new animals to a herd.
4. Extended Breeding Options: AI allows farmers to access semen from a wider geographical area, providing opportunities to breed with outstanding animals that are not locally available.
Disadvantages of Natural Mating
While natural mating has its advantages, it also comes with several disadvantages:
1. Limited Genetic Selection: Farmers may have fewer options for selecting high-quality sires. This can lead to a less efficient breeding program and reduced genetic improvement over time.
2. Risk of Disease Transmission: Natural mating can facilitate the spread of diseases among animals, particularly in cases where animals from different herds are brought together. This risk is exacerbated in herds with poor health management practices.
3. Uncontrolled Breeding: Farmers have less control over which animals mate, which can result in unwanted pairings and a lack of planned genetic improvement. This can lead to issues like inbreeding and the proliferation of undesirable traits.
4. Management Challenges: Natural mating can be more challenging to manage, as it requires close monitoring of animals for signs of estrus and successful mating. This can be time-consuming and may not always yield desired results.
Disadvantages of Artificial Insemination
Artificial insemination (AI) is a widely used method in livestock breeding, but it has some disadvantages that farmers should consider:
1. Costly Setup: The initial costs of AI can be high. Farmers need to invest in equipment, storage facilities for semen, and training to effectively perform AI procedures.
2. Skill Requirements: Successful AI requires training and skill. Improper technique can lead to low conception rates and wasted resources, which may discourage some farmers.
3. Timing Challenges: Accurate timing of insemination is crucial for success. Misjudging the timing can result in missed opportunities for breeding, leading to reduced productivity.
4. Semen Quality Variability: The quality of frozen or cooled semen can vary. Factors such as handling, thawing, and storage conditions can impact the viability of the sperm, affecting fertility rates.
5. Reduced Animal Interaction: AI can reduce natural mating behaviors and interactions between animals. This may lead to behavioral issues or stress among animals that thrive on social dynamics.
Read Also: History and Uses of Herbal Remedies
Ethical Considerations in Reproductive Practices

When it comes to reproductive practices in livestock farming, several ethical considerations arise:
1. Animal Welfare: Ethical concerns often focus on the welfare of the animals involved. Practices like AI can be seen as invasive, and the potential stress on animals during the process should be minimized.
2. Genetic Manipulation: The use of AI can lead to selective breeding, raising concerns about the long-term effects of concentrating specific traits at the expense of others. This could impact genetic diversity and overall health.
3. Handling Practices: Ensuring that animals are handled humanely during AI procedures is essential. The conditions under which they are kept and bred must prioritize their welfare and comfort.
4. Transparency in Practices: Farmers should be transparent about their reproductive practices and their impact on animal health. Ethical breeding programs should include clear communication with consumers regarding how animals are bred and raised.
Choosing the Right Reproductive Method
Selecting the appropriate reproductive method depends on various factors that farmers should consider:
1. Farm Goals: Farmers need to clearly define their goals, whether it is improving herd genetics, maximizing production efficiency, or maintaining animal welfare. Different reproductive methods may align better with specific objectives.
2. Resources Available: Assessing available resources is crucial. This includes financial capacity for AI setups, knowledge and skills of the farm personnel, and access to quality semen and breeding stock.
3. Breed and Species Considerations: The choice of reproductive method may vary depending on the species and breed of livestock. Some breeds may respond better to natural mating, while others may thrive with AI techniques.
4. Management Capabilities: Consideration of the farm’s management practices is essential. Effective monitoring of estrus cycles, breeding timing, and animal health management are critical for the success of the chosen method.
5. Ethical Values: Farmers should reflect on their ethical values regarding animal treatment and reproductive practices. Aligning methods with personal and industry-wide ethical standards can lead to better practices and consumer trust.
Do you have any questions, suggestions, or contributions? If so, please feel free to use the comment box below to share your thoughts. We also encourage you to kindly share this information with others who might benefit from it. Since we can’t reach everyone at once, we truly appreciate your help in spreading the word. Thank you so much for your support and for sharing!

