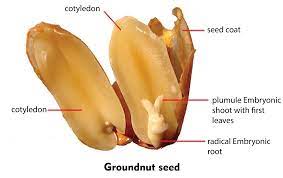
Groundnuts/Peanuts Cotyledons also commonly known as peanuts, are edible legume seeds that develop underground in the roots of the peanut plant (Arachis hypogaea). The cotyledons are the first leaves that emerge from the seed upon germination. In the case of groundnuts or peanuts, the cotyledons are an essential part of the seed structure.
The cotyledons are generally oval or heart-shaped and may have a slightly pointed tip. They are usually pale cream or light yellow in color.
The cotyledons have a soft and fleshy texture, making them easy to chew and digest.
Groundnut cotyledons are packed with nutrients, such as proteins, healthy fats (including monounsaturated fats), dietary fiber, vitamins (like vitamin E, B-complex vitamins), and minerals (such as magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc). They are particularly known for their high protein content.
Groundnuts or peanuts are widely used in various culinary applications. They can be roasted, boiled, or consumed as a raw snack. They are also used to make peanut butter, which is a popular spread. Groundnut oil is extracted from the cotyledons and is used for cooking and frying in many cuisines.
Due to their rich nutritional profile, groundnuts are considered a healthy food choice when consumed in moderation. They can provide a good source of energy, promote heart health, and support overall well-being.
It’s important to note that groundnuts are one of the most common food allergens, and some people can have severe allergic reactions to them.
Groundnuts are a versatile and nutritious food, enjoyed by people around the world. They play a significant role in various cuisines, and their cotyledons are at the core of their nutritional value and culinary appea
Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products of Groundnuts/Peanuts Cotyledons
Groundnuts, also known as peanuts, are a significant crop globally and their cotyledons (seed leaves) have several economic importance and uses due to their nutritional and industrial properties. Here are some of the key economic importance and uses of groundnuts/peanuts cotyledons:
1. Food and Nutrition: Groundnut cotyledons are rich in essential nutrients and provide a valuable source of dietary protein, healthy fats, vitamins (such as niacin, folate, and vitamin E), and minerals (like magnesium, phosphorus, and potassium). They are widely used in human diets and various food products.
Example: Groundnuts are commonly eaten as snacks, roasted or boiled. They are also used to make peanut butter, which is popularly consumed spread on bread or used as an ingredient in various recipes.
2. Oil Production: Groundnut cotyledons contain a high oil content, making them a significant source of vegetable oil. Groundnut oil is stable at high temperatures and has a longer shelf life compared to some other vegetable oils.
Example: Groundnut oil is used in cooking, frying, salad dressings, and in the food industry for baking and confectionery.
3. Animal Feed: Groundnut cotyledons, along with the leftover seed hulls after oil extraction (groundnut meal), are used as animal feed due to their high protein content.
Example: Groundnut meal is a valuable component in livestock and poultry feed formulations to enhance the protein content and overall nutritional value of the diet.
4. Industrial Uses: Groundnut cotyledons have various industrial applications due to their oil and protein content. They are used in the production of several industrial products.
Example: Groundnut oil is used in the manufacture of soaps, cosmetics, and lubricants. Groundnut protein isolates are utilized in the production of adhesive formulations and as an emulsifier in the textile and paper industries.
5. Health Benefits and Medicine: Groundnut cotyledons contain bioactive compounds, such as resveratrol and phytosterols, which have potential health benefits. Additionally, groundnuts are a source of antioxidants, which may help combat oxidative stress.
Example: Groundnuts are incorporated into various health foods and dietary supplements due to their antioxidant properties and potential health benefits.
6. Biodiesel Production: Groundnut oil can be converted into biodiesel, an eco-friendly alternative to fossil fuels, through transesterification.
Example: Biodiesel derived from groundnut oil can be used as a renewable and cleaner energy source for vehicles and machinery.
7. Cosmetics and Skincare: Groundnut oil is used in the cosmetics industry as a natural moisturizer and skin softener.
Example: Groundnut oil is an ingredient in skincare products like lotions, creams, and lip balms.
Read Also : Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products of Groundnuts/Peanuts Seeds (peanuts)
8. Traditional and Culinary Uses: In various cultures, groundnut cotyledons are utilized in traditional dishes, adding unique flavors and textures.
Example: In some Asian cuisines, groundnuts are used in sauces and curries to enhance taste and provide a crunchy texture.
9. Confectionery and Snack Industry: Groundnut cotyledons are a popular ingredient in the confectionery industry, particularly in the production of candies and chocolates.
Example: Chocolate-covered peanuts and peanut brittle are well-known confectionery products that incorporate groundnuts.
10. Flour and Bakery Products: Groundnut cotyledons can be ground into flour, which is used in various bakery products, such as bread, cakes, and cookies.
Example: Groundnut flour is used as a gluten-free alternative in baking, providing a nutty flavor and enhancing the nutritional profile of the products.
11. Nutritional Supplements: Groundnut cotyledons are used as a base for nutritional supplements and powdered protein formulations.
Example: Groundnut protein powder is used by athletes, bodybuilders, and individuals seeking additional protein intake to support muscle growth and recovery.
12. Peanut Shells and By-products: Apart from the cotyledons, the shells and other by-products of groundnuts are also utilized in various applications.
Example: Peanut shells are used as animal bedding material, in composting, and in the manufacturing of particleboards.
13. Traditional Medicine: In some cultures, groundnut cotyledons have been used in traditional medicine for their potential medicinal properties.
Example: Groundnut extracts have been used to treat certain skin conditions and as remedies for coughs and sore throats in traditional medicine practices.
14. Groundnut Allergen: Although not a positive economic aspect, the presence of allergenic proteins in groundnut cotyledons has led to the development of allergen testing and labeling in the food industry.
Example: Proper labeling of groundnut allergens on food products helps individuals with peanut allergies avoid potentially harmful ingredients.
15. Soil Improvement: Groundnut plants are legumes, which means they have the ability to fix nitrogen in the soil, thus enhancing soil fertility and reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
Example: Farmers may include groundnut crops in their rotations to improve soil health and boost the yield of subsequent crops.
16. Crop Rotation and Pest Management: Groundnuts can be used in crop rotation to break pest cycles and reduce pest pressures for other crops.
Example: Rotating groundnuts with cereal crops can help manage nematode populations and improve soil structure.
17. Sustainable Farming Practices: Groundnuts are relatively resilient to drought and require fewer inputs like water and pesticides, making them suitable for sustainable farming practices.
Example: Groundnut cultivation can be part of sustainable agriculture initiatives to conserve resources and promote environmental conservation.
The economic importance and uses of groundnut cotyledons make them a versatile and valuable crop with applications in various industries, from food and agriculture to industrial and healthcare sectors. As consumer preferences and demands evolve, groundnuts continue to play a significant role in meeting nutritional, industrial, and economic needs worldwide.
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Groundnuts/Peanuts Cotyledons
The cotyledons contain a significant amount of oil, protein, and other nutrients, making them valuable for various applications. Here are some of the main products and by-products that can be obtained from groundnuts/peanuts cotyledons:
1. Peanut Oil: Process: Peanut oil is extracted from the groundnut cotyledons through mechanical pressing or solvent extraction.
Example: Refined peanut oil used for cooking, frying, and various culinary applications.
2. Peanut Butter: Process: Peanut butter is made by grinding roasted groundnut cotyledons until they form a smooth and creamy paste.
Example: Creamy or crunchy peanut butter used as a spread, in baking, or for making peanut-based sauces.
3. Peanut Flour: Process: Peanut flour is obtained by finely grinding roasted groundnut cotyledons.
Example: Used in baking, as a thickener in sauces and soups, or as a gluten-free alternative in recipes.
4. Peanut Protein Isolate/Concentrate: Process: Peanut protein isolate or concentrate is obtained by extracting the protein from groundnut cotyledons and further processing it to increase protein content.
Example: Used as a protein supplement in sports nutrition products, protein bars, and shakes.
5. Peanut Meal: Process: After oil extraction, the remaining groundnut cotyledons are ground into a meal.
Example: Used as animal feed for livestock and poultry due to its high protein content.
6. Peanut Husks and Shells: Process: After the cotyledons are removed for processing, the husks and shells are the outer protective layers of the groundnut seed.
Example: Used as animal bedding, in composting, or as a fuel source.
7. Peanut Skins: Process: Peanut skins are the thin reddish-brown covering on the cotyledons and are often removed during processing.
Example: Used in animal feed, antioxidants, or as a natural food coloring.
Read Also : Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products of Grape Flowers
8. Peanut Snacks: Process: Groundnut cotyledons can be roasted, seasoned, or coated to make various peanut snacks.
Example: Roasted peanuts, flavored peanuts, peanut brittle, etc.
9. Peanut Milk: Process: Peanut milk is made by blending groundnut cotyledons with water and straining to obtain a milk-like liquid.
Example: A dairy-free alternative used in beverages, smoothies, and cereal.
10. Peanut Sauce: Process: Groundnut cotyledons can be ground and combined with other ingredients to make peanut sauce.
Example: Used in dishes like satay, stir-fries, and peanut-based dressings.
11. Peanut Ice Cream: Process: Groundnut cotyledons can be incorporated into ice cream formulations to add a nutty flavor and texture.
Example: Peanut butter ice cream, peanut brittle ice cream, etc.
12. Peanut Energy Bars: Process: Groundnut cotyledons can be combined with other ingredients to make energy bars.
Example: Peanut and date bars, peanut and chocolate bars, etc.
13. Peanut Flavored Beverages: Process: Groundnut cotyledons or peanut flavoring can be used to enhance the taste of various beverages.
Example: Peanut-flavored shakes, smoothies, and hot beverages.
14. Peanut Soap: Process: Groundnut oil can be used in soap-making to add moisturizing properties.
Example: Peanut oil soap for skincare benefits.
15. Peanut Cosmetics: Process: Groundnut oil and extracts can be used in cosmetics and personal care products.
Example: Peanut oil-based moisturizers, lip balms, and hair products.
16. Peanut Biodiesel: Process: Groundnut oil can be converted into biodiesel through a transesterification process.
Example: Biodiesel used as a renewable fuel source for diesel engines.
17. Peanut Biomass for Bioenergy: Process: Peanut shells and other residual biomass can be used to produce bioenergy through combustion or gasification.
Example: Biomass power plants using peanut shells as a renewable energy source.
18. Peanut Composites: Process: Peanut shells can be incorporated into composite materials for various applications.
Example: Peanut shell-filled plastic composites for non-structural components.
19. Peanut Fertilizer: Process: Peanut meal or waste can be processed into organic fertilizer.
Example: Organic peanut meal fertilizer used in agriculture.
20. Peanut Glue: Process: Peanut flour can be used to produce adhesive or glue for various applications.
Example: Eco-friendly peanut-based glue for woodworking or crafts.
It’s important to mention that while groundnuts/peanuts have numerous products and by-products, their safety for consumption and suitability for different applications should be carefully considered. Also, the regulations and standards governing the production and use of these products may vary from one region to another. Additionally, some by-products may be more regionally specific or used in niche industries.
Read Also : Comprehensive Corn Farming Guide
