Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products of Cocoa/Cacao Roots
Cocoa/Cacao Roots are the underground part of the cocoa tree (Theobroma cacao), which is native to the tropical regions of Central and South America. These roots play a vital role in providing stability and nutrients to the cocoa tree, supporting its growth and development.
Cocoa roots are typically fibrous and branching, extending horizontally in the soil. They can spread out over a considerable area, forming an extensive network that helps the tree absorb water and essential minerals from the soil. The root system also aids in anchoring the cocoa tree securely in the ground, enabling it to withstand wind and other environmental stresses.
The roots of the cocoa tree possess a symbiotic relationship with certain soil fungi, particularly species of mycorrhizal fungi. These fungi form a mutually beneficial association with the roots, extending their hyphae (thread-like structures) into the root cells. This symbiosis enhances the cocoa tree’s ability to absorb nutrients, especially phosphorus, from the soil. In return, the tree provides carbohydrates to the fungi, promoting their growth and survival.
Cocoa roots are an essential component for cocoa cultivation and the production of chocolate. They absorb nutrients from the soil, including nitrogen, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and trace elements, which are vital for the tree’s overall health and the development of cocoa pods.
It is worth noting that while cocoa roots are important for cocoa production, the primary part of the tree used for commercial purposes is the cocoa pod, which contains the cocoa beans used to make chocolate. Nevertheless, the health and vigor of the roots directly impact the tree’s productivity and its ability to withstand diseases, pests, and adverse environmental conditions. Therefore, maintaining healthy cocoa roots is crucial for sustainable cocoa farming.
Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products of Cocoa/Cacao Roots
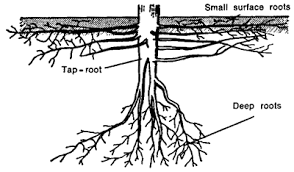
The economic importance of cocoa/cacao roots lies in their various uses and benefits within the cocoa industry. While the primary economic value of cocoa/cacao is derived from its beans, the roots also have some significance. Here are some economic uses and importance of cocoa/cacao roots:
1. Propagation: Cocoa/cacao roots are crucial for propagation and the establishment of new cocoa plantations. By using root cuttings or rootstocks, farmers can efficiently multiply and propagate cocoa trees to expand their plantations or replace older trees. This helps in meeting the increasing demand for cocoa beans and sustaining the cocoa industry.
2. Disease resistance: Cocoa/cacao roots play a significant role in developing disease-resistant cocoa varieties. Through root grafting or rootstock selection, researchers and breeders can introduce desired traits, such as resistance to common cocoa diseases like black pod disease or witches’ broom disease. Disease-resistant cocoa varieties improve crop productivity and reduce losses, ensuring a stable and profitable cocoa industry.
Read Also : Introducing “Agric4Profit Cocoa Farm Set-Up”
3. Soil erosion control: The extensive root system of cocoa/cacao trees helps in preventing soil erosion, especially in regions with hilly or sloping terrains. The dense network of roots holds the soil together, reducing the risk of erosion caused by heavy rainfall or wind. This is essential for maintaining the quality of cocoa plantations and preserving fertile soil, which is vital for sustained cocoa production.
4. Agroforestry systems: Cocoa/cacao roots contribute to the establishment of agroforestry systems, where cocoa trees are intercropped with other beneficial plants or trees. The roots provide stability to the cocoa trees and help in the nutrient cycling process within the agroforestry system. This diversification of crops enhances biodiversity, improves soil health, and provides additional economic opportunities for farmers through the cultivation of companion crops like plantains, bananas, or timber trees.
5. Soil fertility enhancement: The roots of cocoa/cacao trees contribute to soil fertility by improving its structure and nutrient content. The roots can reach deep into the soil, accessing nutrients that are otherwise unavailable to shallower-rooted crops. Furthermore, cocoa roots can fix atmospheric nitrogen through symbiotic relationships with nitrogen-fixing bacteria, enriching the soil with this essential nutrient.
6. Waste utilization: Although not directly related to the economic value of cocoa/cacao roots, it’s worth mentioning that the waste material generated during cocoa processing, such as cocoa pod husks, can be used as a source of organic matter and energy. These waste materials can be composted to produce organic fertilizers or used as biomass for energy generation, reducing waste and providing additional economic benefits to cocoa processing industries.
7. Water management: The extensive root system of cocoa/cacao trees helps in water management within cocoa plantations. The roots absorb water from the soil, reducing excess water runoff and promoting efficient water use. This is particularly valuable in regions with limited water resources, where cocoa/cacao roots aid in conserving water and optimizing irrigation practices.
8. Carbon sequestration: Cocoa/cacao roots contribute to carbon sequestration, a process where carbon dioxide is captured and stored in the soil. The extensive root system facilitates the transfer of carbon compounds from the atmosphere into the soil, promoting carbon storage and mitigating climate change. This ecological service has gained attention due to its potential economic value in carbon markets and initiatives focused on reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
9. Traditional medicine: In some cultures, cocoa/cacao roots have been used for their medicinal properties. Although the commercial utilization of these roots in traditional medicine is limited, there is potential for further exploration and development of medicinal applications. Extracts or compounds derived from cocoa/cacao roots may have antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, or antioxidant properties, opening up possibilities for the pharmaceutical or nutraceutical industries.
10. Research and development: Cocoa/cacao roots play a role in ongoing research and development efforts within the cocoa industry. Scientists and researchers study the physiology and genetics of cocoa roots to improve understanding and optimize root development, nutrient uptake, and overall plant health. This knowledge informs breeding programs, cultivation practices, and soil management techniques, contributing to the continuous improvement of cocoa production systems.
11. Biotechnology applications: Cocoa/cacao roots have potential applications in biotechnology, particularly in the field of genetic engineering. Researchers may use root tissue culture techniques to produce transgenic cocoa plants with desirable traits, such as increased yield, disease resistance, or improved quality characteristics. This research and the resulting innovations can have long-term economic implications for the cocoa industry.
12. Waste water treatment: In some cases, cocoa/cacao roots have been explored for their potential in treating wastewater from cocoa processing facilities. The roots can help in the removal of organic pollutants and nutrients from wastewater, contributing to the reduction of environmental impacts and providing a sustainable solution for wastewater management in cocoa processing regions.
13. Erosion control and slope stabilization: The extensive root system of cocoa/cacao trees helps in preventing soil erosion on slopes and hilly terrains. This is particularly beneficial in regions where cocoa plantations are established on sloping land. By anchoring the soil, cocoa/cacao roots minimize the risk of soil erosion, safeguarding the productivity and longevity of the cocoa plantation.
14. Research for improved rootstock selection: Researchers and breeders are continually studying cocoa/cacao roots to identify and select improved rootstocks. These rootstocks exhibit desirable traits such as enhanced resistance to diseases, improved adaptation to different soil types and climates, or increased nutrient absorption. The development of superior rootstocks helps in achieving higher yields, improved crop quality, and overall productivity gains.
15. Root-based agroforestry products: In addition to cocoa beans, cocoa/cacao roots have the potential to be utilized in the production of value-added products. For example, roots can be processed into herbal teas, dietary supplements, or extracts that are used in the food, beverage, or cosmetic industries. This diversification of product offerings provides additional revenue streams and economic opportunities for farmers and processors.
16. Carbon credits and ecosystem services: The role of cocoa/cacao roots in carbon sequestration, water management, and biodiversity conservation can generate carbon credits and other ecosystem services. These ecosystem services can be monetized through carbon markets, conservation schemes, or certification programs that promote sustainable cocoa production. This creates economic incentives for farmers to implement sustainable practices and protect the natural environment.
17. Bioengineering applications: Cocoa/cacao roots have potential applications in bioengineering and environmental restoration projects. Their extensive root systems and ability to adapt to different soil conditions make them valuable for stabilizing riverbanks, reclaiming degraded lands, or restoring ecosystems. This opens up opportunities for cocoa/cacao farmers to engage in environmental restoration initiatives and leverage their expertise in root propagation and planting techniques.
18. Livelihood diversification: The utilization of cocoa/cacao roots in various applications can contribute to livelihood diversification for cocoa farmers. By exploring value-added products, such as root-based herbal teas or supplements, farmers can generate additional income streams and reduce their reliance solely on cocoa bean production. This diversification can enhance resilience, improve socio-economic conditions, and provide stability in the face of market fluctuations.
These points highlight the multi-faceted economic importance of cocoa/cacao roots, showcasing their potential for sustainable land management, ecosystem services, product diversification, and livelihood improvement. The continued exploration and utilization of cocoa/cacao roots contribute to a more holistic and economically viable cocoa industry.
Overall, while cocoa/cacao roots may not have a direct market value like the beans themselves, their economic importance lies in their contribution to propagation, disease resistance, soil conservation, agroforestry systems, soil fertility enhancement, and waste utilization within the cocoa industry. These benefits help ensure sustainable cocoa production, enhance farmer livelihoods, and maintain a robust cocoa industry worldwide.
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Cocoa/Cacao Roots
Cocoa, also known as cacao, is a tropical plant whose seeds are used to produce chocolate and cocoa-based products. While the seeds are the most commonly used part of the cocoa plant, various products and by-products can be derived from its roots as well. Here are some examples:
1. Cocoa Powder: The main product derived from cocoa beans is cocoa powder, which is obtained by grinding roasted cocoa beans. Cocoa powder is widely used in baking, confectionery, and beverage industries to add flavor and color to various products like chocolate cakes, cookies, hot chocolate, and more.
2. Cocoa Butter: Cocoa butter is a natural fat extracted from cocoa beans. It is commonly used in the production of chocolate, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. Cocoa butter gives chocolate its smooth texture and is often used in skincare products due to its moisturizing properties.
3. By-products for Animal Feed: The roots of cocoa plants can be processed into by-products that are suitable for animal feed. After extracting cocoa butter from the beans, the remaining material, known as cocoa meal or cocoa press cake, can be dried and ground into a powder. This powder can then be used as a high-protein ingredient in animal feed, providing nutrition to livestock.
4. Medicinal and Health Supplements: Cocoa roots have been traditionally used for their medicinal properties in some cultures. Extracts from cocoa roots are believed to have various health benefits, such as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. These extracts can be processed and incorporated into dietary supplements or herbal remedies.
Read Also : Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products of Oil Palm Mesocarp
5. Natural Dyes: Cocoa roots contain pigments that can be used as natural dyes for fabrics and other materials. These dyes can provide a range of warm, earthy tones, depending on the processing and application techniques. Some artisanal or sustainable textile manufacturers utilize cocoa root dyes to create unique and eco-friendly products.
6. Soil Conditioner: The roots of cocoa plants can be composted and used as a natural soil conditioner. The decomposed roots add organic matter and nutrients to the soil, improving its fertility and structure. This can benefit other plants grown in the same area and contribute to sustainable agriculture practices.
7. Herbal Tea: Cocoa roots can be dried, ground, and used as an ingredient in herbal teas. The tea made from cocoa roots is believed to have various health benefits, including relaxation, digestion aid, and antioxidant properties. It can be enjoyed on its own or blended with other herbs and flavors.
8. Natural Cosmetics: Extracts from cocoa roots can be used in the formulation of natural cosmetics and skincare products. They can be incorporated into creams, lotions, and serums, providing moisturizing, soothing, and anti-aging effects. Cocoa root extracts may help improve skin elasticity, reduce inflammation, and protect against environmental damage.
9. Artisanal Crafts: In some regions where cocoa is cultivated, the roots are creatively repurposed for artisanal crafts. The sturdy and fibrous nature of cocoa roots makes them suitable for weaving baskets, mats, and other handicrafts. These unique products can be used for home decor, gifts, or sold as part of local artisanal traditions.
10. Traditional Medicine: In certain cultures, cocoa roots have been used in traditional medicine for their potential therapeutic properties. The roots may be prepared as infusions, decoctions, or extracts and used to alleviate various ailments such as stomachaches, fever, or coughs. However, it’s important to note that scientific research is still limited in this area, and the use of cocoa roots in traditional medicine should be approached with caution.
11. Natural Insecticides: Some studies have shown that extracts from cocoa roots possess insecticidal properties. These extracts can be used as a natural alternative to synthetic pesticides in agricultural practices. They may help repel or control pests that commonly affect cocoa crops, contributing to more sustainable and environmentally friendly farming methods.
12. Biomass Energy: Cocoa roots, along with other agricultural waste, can be utilized as a source of biomass energy. The roots can be processed and converted into biogas or used as fuel for biomass power plants. This helps to reduce waste, generate renewable energy, and mitigate the environmental impact of traditional energy sources.
These examples showcase the potential versatility and utilization of cocoa roots beyond their primary use for cocoa beans. However, it’s important to consider local customs, regulations, and scientific research when exploring the extraction and application of products and by-products from cocoa/cacao roots.
t’s important to note that while cocoa roots can potentially yield these products, the primary focus of cocoa cultivation is on the seeds and the production of cocoa beans. The utilization of cocoa roots for specific purposes may vary depending on cultural practices, regional traditions, and industrial demands.
Read Also : How to Grow Sugar Cane Minecraft in a Sugar Cane Farm Minecraft









