Animal rearing is an age-long activity that man carries out basically for food and the production of raw materials for agro-industries. Meat or flesh, milk, and eggs are primarily obtained directly from farm animals for consumption by man. Wool, fur, hides and skin are other products from farm animals for industrial use as raw materials.
Animals are categorized into ruminants and non-ruminants based on anatomical and physiological differences. Apart from being a source of meat as other animals, ruminant animals are the main sources of raw materials such as wool, fur, hides and skin, milk, and many others for the production of clothing materials, leather materials (such as footwear like shoes, belt, shawl), milk products like yogurt, butter, cheese, and many other products. Ruminant animals, especially bulls or camels are also used as draught animals for transportation and traction.
Definition of Ruminant Animals
Ruminant animals are mammals that belong to the order Artiodactyla. They are animals with complex stomachs, unlike the non-ruminants that have simple stomachs. They eat and digest forages or plant-based feed by swallowing it first and allowing it to get moistened in the rumen which is the first compartment of the complex stomach.
The swallowed food is later regurgitated by the animal and re-chewed to break down the plant materials for digestion. This process is called rumination or chewing the cud. The cud is a semi-solid and semi-degraded digesta usually in a bolus form which is regurgitated from the reticulorumen of the animal.
Examples of ruminant animals are cattle, sheep, goats, camel, water buffalo, giraffes, and antelopes to mention but a few. However, we shall limit our discussion in this study to cattle, sheep, and goats that are commonly found in our environment.
The diagrams below show the labeled parts of cattle and goat:
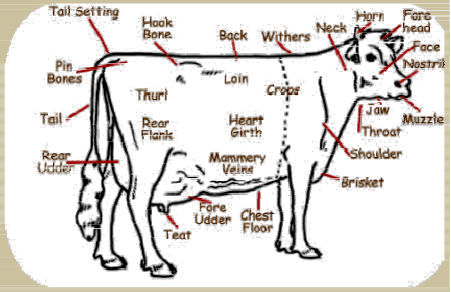
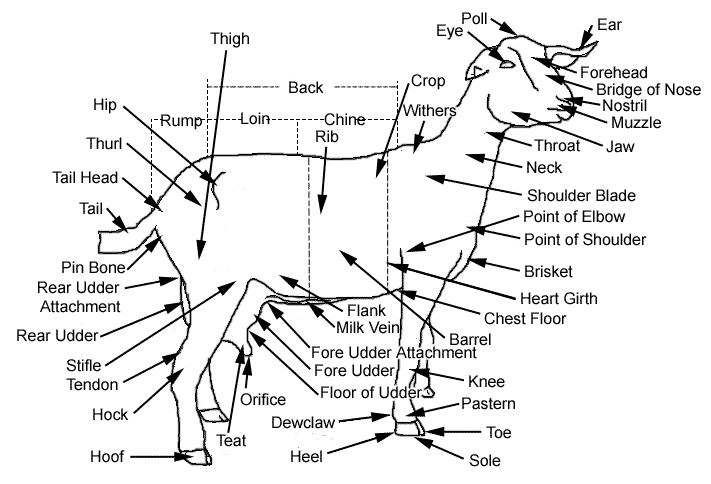
Read Also Internal Parasites of Ruminants and the Control Measures
The Differences between Ruminant and Non-ruminant Animals
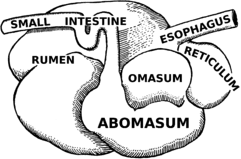
As mentioned above, the main difference between ruminant animals and non-ruminants is the anatomy of their stomach. Contrary to the belief of many, ruminants have only one stomach and not four.
However, the stomach is divided into four compartments or chambers, unlike the simple stomach of the non-ruminants which has no division. The compartments are rumen, reticulum, omasum, and abomasum.
The last of the compartments is the true stomach in ruminants while the rumen and reticulum perform the function of moistening the swallowed forage. In the omasum, water and inorganic materials are absorbed before the digest is passed into the true stomach. Another major physical difference is the possession of spilled hooves by ruminant animals.
Read Also Nutrient Requirements and Feeding of Ruminants
Classes of Ruminant Animals
Ruminant animals are categorized into two main classes based on their body size namely, the large ruminant animals and small ruminant animals.
Examples of large ruminants are cattle, water buffalo, giraffes, camel, etc while small ruminants are sheep, goats, antelope etc. Ruminants have the advantage of the ability to eat and utilize low-quality fibrous food that cannot be eaten by humans or non-ruminants.
Economic Importance of Keeping Ruminant Animals
Ruminant animals and their products as mentioned in the introduction have tremendous nutritional and economic value to man as stated below:
1. Meat and milk of cattle, sheep, goats, and other ruminants are good sources of animal protein to man which are of better quality than plant protein.
2. They serve as sources of raw materials used in industries e.g. leather goods respectively. Goat hair is also used for making carpets, bags, and ropes. Wool is a raw material for the production of clothing for human wear.
3. They serve as a means of foreign exchange earning. For instance, some countries in Europe such as Denmark and Botswana in the Southern region of Africa export beef to earn foreign exchange. Others export dairy products from milk to earn foreign exchange.
4. They serve as a source of income for subsistence farmers. In Nigeria, cattle, sheep, and goats are kept at the subsistence level by farmers.
5. These animals can survive on fallow lands and others that are not good for arable crop farming thereby maximizing the use of the available land resource.
6. They are also used as gifts or bride prices which serve as family wealth.
7. They are sources of gainful employment.
8. The manure/dung from these animals can be used as a source of organic fertilizer.
9. The skin of the Red Sokoto breed of goats in Nigeria commands a high premium in the international market because of its superior quality
10. In the South-Western part of Nigeria, goats are relished as meat and as barbecued during ceremonies. Generally, under the organized production system, ruminant animals are slaughtered during festive seasons all over the world.
Blood and bones obtained from the slaughtering of these animals are often recycled and processed into blood meal, and bone meal which are used as components of animal feed.
11. Cattle and some other ruminants can also be used as “beasts of burden”
In summary, ruminant animals are those that feed on plant-based feed by swallowing it and later regurgitating the forage for proper mastication or chewing to reduce the semi-solid digest to particle size for digestion.
Ruminant animals differ from non-ruminants because they possess only one stomach with four compartments which are the rumen, reticulum, omasum, and abomasum.
The fourth compartment called the abomasum is the true stomach, ruminants also differ from non-ruminants because they have spilt-hooved toes and are divided into large and small based on their body size, they also have tremendous nutritional and economic value. They serve as a source of foreign exchange earnings and also raw materials for agro-allied-industries.
Read Also Complete Composting Guide for Beginners

