Goat herding is an ancient practice that has been integral to human agriculture for thousands of years. This sustainable form of animal husbandry involves raising goats for various purposes, including milk, meat, fiber, and land management. With their adaptability and hardy nature, goats have become popular livestock choices for both small-scale farmers and larger agricultural enterprises.
Unlike many other livestock, goats can thrive in diverse environments, from arid regions to lush pastures, making them a viable option for many farmers worldwide.
The goat is known for its curiosity and intelligence, which can make them engaging and rewarding animals to work with. As social animals, goats prefer to live in herds, exhibiting behaviors that strengthen their social bonds.
This aspect of their nature not only influences their management practices but also enhances their welfare. Proper goat herding requires an understanding of these social dynamics, as well as knowledge of their dietary needs, health management, and breeding practices.
In recent years, there has been a resurgence of interest in goat herding, spurred by the increasing demand for organic and locally sourced food. Goat milk, for instance, is often hailed for its health benefits and is a staple in many cultures.
Similarly, goat meat, particularly from specific breeds, is celebrated for its flavor and lean qualities. The versatility of goats also extends to their ability to control weeds and manage land, providing an eco-friendly solution for landowners looking to reduce brush and improve soil health.
This complete guide to goat herding aims to equip aspiring and current goat herders with essential knowledge and practical advice to ensure the successful management of their herds. It will cover various aspects of goat husbandry, including selecting the right breeds, understanding nutritional requirements, implementing effective healthcare practices, and optimizing breeding strategies.
Furthermore, the guide will address the importance of proper housing and fencing, highlighting how to create a safe and comfortable environment for goats. It will also explore common challenges faced in goat herding, such as predator control, disease management, and seasonal care needs. By offering a comprehensive overview of these critical areas, readers will gain the confidence to make informed decisions about their goat farming practices.
Moreover, goat herding is not just a means of subsistence; it can also be a profitable business venture. With the right marketing strategies, goat products can command high prices in local and niche markets.
This guide will touch on effective marketing techniques and how to connect with potential customers, enabling herders to maximize their profits while maintaining ethical practices.
Choosing the Right Goat Breed

Selecting the appropriate breed of goat is crucial for meeting your farming goals. Here are key considerations to guide your choice:
1. Purpose of Farming: Determine the primary purpose of your goat farm, such as milk production, meat production, fiber (like cashmere or mohair), or as pets. Different breeds are suited for different purposes.
2. Dairy Goat Breeds: If you aim to produce milk, consider dairy breeds like Saanen, Nubian, or Alpine. These breeds are known for their high milk yield and quality.
3. Meat Goat Breeds: For meat production, look into breeds such as Boer or Kiko goats, which are known for their growth rates and carcass quality.
4. Fiber Goat Breeds: If fiber is your goal, consider Angora or Cashmere goats, which are valued for their high-quality fibers used in textiles.
5. Adaptability: Choose breeds that are well-suited to your local climate and conditions. Some breeds are more resilient to specific environmental stresses, such as heat or cold.
Setting Up Your Goat Farm
Creating a suitable environment for your goats is vital for their health and productivity. Here are key points to consider when setting up your farm:
1. Location and Land Requirements: Select a location with ample space for grazing, shelter, and access to clean water. Goats require adequate space to roam and forage, so plan for a minimum of 200 square feet per goat.
2. Shelter and Housing: Provide proper shelter to protect goats from extreme weather conditions. Structures should have adequate ventilation, insulation, and space to accommodate the herd comfortably.
3. Fencing: Install strong fencing to keep goats safe from predators and prevent them from wandering off. Stock fencing with barbed wire or electric fencing is commonly used for goat farms.
4. Grazing Areas: Designate grazing areas with diverse vegetation to meet their dietary needs. Rotate grazing areas to prevent overgrazing and maintain pasture health.
Read Also: Siamese Cats: All You Need to Know About Them
Essential Equipment for Goat Herding

Having the right equipment is essential for effective goat herding and farm management. Here are some key tools and equipment to consider:
1. Feeding Equipment: Invest in feeders that can accommodate your goats’ dietary needs, such as hay racks and grain troughs. This helps minimize waste and ensures that all goats have access to food.
2. Water Supply: Ensure a reliable source of clean water for your goats. Use troughs or automatic waterers to provide fresh water, checking them regularly to prevent contamination.
3. Hoof Care Tools: Regular hoof trimming is essential for goat health. Invest in hoof trimmers, and consider having a hoof trimming stand to make the process easier and safer.
4. Health Management Supplies: Equip your farm with basic veterinary supplies, such as dewormers, vaccinations, and first aid kits. Regular health checks and preventive care are vital for maintaining herd health.
5. Transport Equipment: Depending on your needs, consider investing in a livestock trailer for transporting goats, especially if you plan to attend shows or sell animals.
Feeding and Nutrition for Goats
Proper nutrition is vital for the health and productivity of goats. Here are some key aspects to consider:
1. Balanced Diet: Goats require a balanced diet that includes forage, grains, minerals, and vitamins. High-quality forage, such as hay or pasture, should make up the majority of their diet.
2. Nutritional Requirements: Nutritional needs can vary by age, breed, and production purpose (milk, meat, fiber). Consult with a veterinarian or animal nutritionist to formulate a diet that meets the specific needs of your herd.
3. Protein Sources: Protein is essential for growth, reproduction, and milk production. Consider incorporating protein-rich supplements like soybean meal, alfalfa, or commercial goat feed.
4. Mineral and Vitamin Supplements: Ensure that goats have access to mineral blocks or supplements to meet their calcium, phosphorus, and other vitamin needs. This is especially important during lactation and growth periods.
5. Water Access: Goats need constant access to clean, fresh water. Dehydration can lead to serious health issues, so make sure their water supply is reliable.
Housing and Shelter Requirements
Providing appropriate housing and shelter for your goats is essential for their well-being. Here are important considerations:
1. Shelter Design: Goats require a clean, dry place to stay protected from weather extremes. Shelters should be well-ventilated and spacious enough for all goats to move freely.
2. Bedding: Use appropriate bedding materials, such as straw or wood shavings, to absorb moisture and provide comfort. Regularly clean the bedding to maintain hygiene and prevent disease.
3. Space Requirements: Each goat needs adequate space to thrive. Aim for at least 15 to 20 square feet per goat in the shelter, with additional space for grazing and exercise.
4. Fencing: Strong fencing is crucial to protect goats from predators and prevent them from escaping. Use sturdy materials and regularly inspect fences for damage.
5. Temperature Control: Ensure the shelter can provide temperature control to keep goats comfortable during hot or cold weather. Provide shade in summer and insulation in winter.
Read Also: 10 Medicinal Health Benefits of Podocarpus henkelii (Henkel’s Yellowwood)
Health Care and Veterinary Considerations
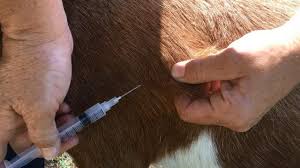
Regular health care is vital for maintaining a productive goat herd. Here are key points to consider:
1. Routine Check-ups: Schedule regular veterinary check-ups for vaccinations, deworming, and health assessments. Preventive care helps detect issues early and maintains herd health.
2. Common Health Issues: Be aware of common health issues in goats, such as respiratory infections, mastitis, and digestive problems. Monitor for signs of illness, including lethargy, coughing, or changes in appetite.
3. Hoof Care: Regular hoof trimming is essential to prevent foot rot and other hoof-related issues. Trim hooves every 6 to 8 weeks, depending on the goat’s living conditions.
4. Vaccination Protocol: Follow a vaccination schedule based on your veterinarian’s recommendations to protect goats from common diseases like CD&T (Clostridium perfringens and tetanus).
5. Emergency Preparedness: Have a plan in place for emergencies, including access to veterinary care and supplies for first aid. Familiarize yourself with common goat ailments and their treatments.
Breeding and Reproduction in Goats
Understanding breeding and reproduction is crucial for herd management. Here are important considerations:
1. Breeding Goals: Determine your breeding goals, whether for milk production, meat quality, or specific traits. Choose breeding stock that meets your objectives.
2. Reproductive Cycle: Understand the reproductive cycle of goats, including estrus (heat) cycles, which typically occur every 21 days. Monitor for signs of heat to time breeding effectively.
3. Mating Methods: Consider your breeding methods, such as natural breeding or artificial insemination. Each method has its advantages and considerations based on your goals and resources.
4. Pregnancy Care: Monitor pregnant goats closely for signs of pregnancy and provide proper nutrition and care. Regular veterinary check-ups during this time are essential for ensuring a healthy pregnancy.
5. Caring for Kids: After birth, ensure that kids receive colostrum within the first few hours for optimal immunity. Provide a safe environment for the mother and her young, and monitor their health closely.
Managing Goat Behavior and Training
Understanding and managing goat behavior is crucial for a harmonious farm environment. Here are important considerations:
1. Understanding Goat Behavior: Goats are social animals that thrive in herds. They can exhibit various behaviors such as curiosity, playfulness, and even stubbornness. Understanding these behaviors helps in managing them effectively.
2. Socialization: Introduce new goats gradually to minimize stress and aggression. Goats establish a hierarchy within their social structure, so it’s essential to monitor interactions.
3. Basic Training Techniques: Basic commands like “come,” “stay,” and “no” can be taught through positive reinforcement. Use treats or rewards to encourage desired behaviors.
4. Leash Training: Training goats to walk on a leash can be helpful for handling them during vet visits or transportation. Start by getting them comfortable with the leash in a safe space.
5. Addressing Behavioral Issues: Common behavioral problems include aggression and excessive bleating. Identifying triggers and providing enough stimulation can help mitigate these issues.
Pasture Management and Foraging
Effective pasture management is essential for the health and productivity of goats. Here are key practices:
1. Rotational Grazing: Implement rotational grazing to prevent overgrazing and allow pastures to recover. Move goats between different grazing areas to maintain healthy forage growth.
2. Forage Quality: Ensure goats have access to high-quality forage, including grasses, legumes, and shrubs. Monitor pasture health and reseed as necessary to improve forage quality.
3. Supplemental Feeding: During periods of low pasture growth, provide supplemental feed, such as hay or grains, to meet nutritional needs. This ensures goats receive adequate nutrients year-round.
4. Weeds and Pests Control: Regularly monitor pastures for weeds and pests that can affect forage quality. Implement integrated pest management strategies to control infestations without harming the environment.
5. Water Access: Ensure goats have constant access to clean water in grazing areas. Proper hydration is essential for their health and productivity.
Common Diseases and Prevention Strategies
Preventing diseases is crucial for maintaining a healthy goat herd. Here are important points to consider:
1. Common Diseases: Be aware of common goat diseases such as foot rot, mastitis, and pneumonia. Monitor your herd regularly for signs of illness.
2. Vaccination Schedule: Follow a vaccination protocol recommended by a veterinarian. Vaccines can protect against diseases like CD&T, rabies, and others.
3. Nutritional Support: A balanced diet supports the immune system, making goats less susceptible to diseases. Ensure proper nutrition to promote overall health.
4. Regular Health Checks: Conduct routine health checks to identify potential issues early. Look for signs of illness, such as changes in behavior, appetite, or physical appearance.
5. Biosecurity Measures: Implement biosecurity measures to prevent the introduction of diseases. Quarantine new animals before introducing them to the herd and practice good hygiene.
Marketing and Selling Goat Products
Successfully marketing goat products can enhance your farm’s profitability. Here are some strategies:
1. Identifying Your Products: Determine which goat products you want to market, such as meat, milk, cheese, fiber (like mohair or cashmere), or breeding stock.
2. Local Market Research: Research local demand for goat products. Attend farmers’ markets, craft fairs, or agricultural events to gauge consumer interest and preferences.
3. Value Addition: Consider processing goat milk into cheese or yogurt, or creating specialty products to increase value. Value-added products can attract more customers and enhance profitability.
4. Online Presence: Establish an online presence through social media and a website to reach a broader audience. Share information about your farm, products, and sustainable practices.
5. Networking: Build relationships with local restaurants, grocery stores, and specialty shops that may be interested in sourcing goat products. Networking can open new market opportunities.
Do you have any questions, suggestions, or contributions? If so, please feel free to use the comment box below to share your thoughts. We also encourage you to kindly share this information with others who might benefit from it. Since we can’t reach everyone at once, we truly appreciate your help in spreading the word. Thank you so much for your support and for sharing!
Read Also: Living a Zero Waste Lifestyle: A Complete Guide
Frequently Asked Questions
We will update this section soon.

