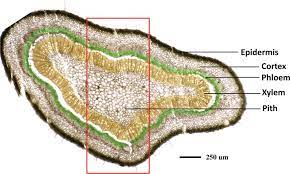
The grapefruit phloem is a critical component of the vascular system in grapefruit (Citrus × paradisi), a citrus fruit belonging to the Rutaceae family. The phloem is one of the two primary vascular tissues in plants, the other being xylem. The grapefruit phloem plays a fundamental role in transporting sugars, nutrients, and other important substances throughout the plant.
The grapefruit phloem is composed of various specialized cells, including sieve tube elements, companion cells, phloem parenchyma cells, and phloem fibers. Sieve tube elements are the main conducting cells responsible for transporting sugars and other nutrients.
Sieve tube elements are elongated, tube-like cells arranged end to end, forming a continuous pipeline for the transportation of sugars (such as glucose and fructose), amino acids, hormones, and other organic compounds. These cells have thin walls to facilitate efficient nutrient transport.
Companion cells are intimately associated with sieve tube elements and play a vital supportive role. They help in loading sugars into the sieve tube elements, as sieve tube elements themselves lack certain organelles required for cellular processes.
Phloem parenchyma cells surround the sieve tube elements and companion cells. They provide structural support and participate in various metabolic activities, such as storage of nutrients and synthesis of certain compounds. Phloem fibers are long, slender cells that provide additional structural support to the phloem tissue. They are particularly important in maintaining the integrity and strength of the phloem.
The primary function of the grapefruit phloem is to transport photosynthetic products, primarily sugars produced in the leaves during photosynthesis, to various parts of the plant where they are utilized for growth, energy production, and storage. This includes transporting sugars from source leaves (e.g., mature leaves) to sink tissues (e.g., roots, developing fruits, and growing stems).
The transport of sugars and other nutrients in the grapefruit phloem occurs through a process called translocation. Sugars are actively loaded into the sieve tube elements by companion cells and are then transported through pressure-driven flow along the concentration gradient. This movement of nutrients is known as mass flow.
Understanding the structure and function of grapefruit phloem is crucial for comprehending how grapefruit trees efficiently distribute nutrients and sustain their growth and development.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Grapefruit Phloem
Grapefruit (Citrus paradisi) is a popular citrus fruit known for its juicy, tangy flavor and numerous health benefits. The phloem is a vascular tissue in plants that plays a crucial role in transporting sugars, nutrients, and other essential substances throughout the plant.
Here are the economic importance and uses of grapefruit phloem:
1. Nutrient Transport and Growth: The phloem in grapefruit plays a vital role in transporting essential nutrients, sugars, and organic compounds (e.g., sugars, amino acids) from the leaves, where they are produced via photosynthesis, to various parts of the plant, including the roots and developing fruits. This efficient nutrient transport is critical for the growth and development of the grapefruit tree.
2. Fruit Development and Quality: The phloem transports sugars from the leaves to the developing fruits, including grapefruits. This sugar transport is fundamental for the development and sweetness of the fruit. Adequate sugar transport via the phloem contributes to the overall quality and taste of grapefruits.
3. Economic Value through Fruit Production: Grapefruits are a major agricultural product with significant economic value. The efficient functioning of the phloem system ensures healthy fruit development, leading to higher yields and improved economic returns for farmers and stakeholders in the grapefruit industry.
Read Also: Grapefruit Pedicel: Economic Importance, Uses And By-Products
4. Nutritional Value for Human Consumption: Grapefruits are a rich source of vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. The sugars and nutrients transported through the phloem contribute to the nutritional value of the fruit, making it a valuable addition to a healthy diet.
5. Commercial Products: Grapefruits and grapefruit by-products are used to create a variety of commercial products. These include juices, jams, marmalades, essential oils, and dietary supplements. The efficient phloem transport system ensures an adequate supply of raw materials for these products.
6. Pharmaceutical Uses: Grapefruit seed extract, which can be derived from grapefruit phloem, is used in various pharmaceutical and herbal preparations. It is believed to have antimicrobial properties and is used in products like dietary supplements and topical ointments.
7. Research and Agriculture: Studying the phloem in grapefruits and other plants helps researchers and agricultural scientists understand plant physiology and develop strategies to improve crop yields and fruit quality. Insights into phloem transport mechanisms can guide the development of more efficient agricultural practices.
8. Contribution to Food Industry: The juice extracted from grapefruits is a significant product in the food and beverage industry. The phloem transports sugars and compounds that contribute to the taste, flavor, and nutritional content of grapefruit juice. It is a popular beverage and a versatile ingredient in various culinary dishes.
9. Export and Trade: Grapefruits and grapefruit products are traded internationally, contributing to global agricultural and economic markets. Efficient phloem functioning ensures the availability of quality grapefruit products for both domestic consumption and export, boosting the economy through trade.
10. Employment and Livelihoods: The grapefruit industry, supported by healthy grapefruit trees with efficient phloem systems, provides employment opportunities for a wide range of individuals, including farmers, harvesters, processors, distributors, and retailers. It supports livelihoods in both rural and urban areas.
11. Environmental Benefits: Healthy grapefruit trees with well-functioning phloem play a role in environmental sustainability. They absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis and contribute to overall carbon sequestration, aiding in mitigating climate change and improving air quality.
12. Research and Innovation: The study of grapefruit phloem and its functions provides insights into plant physiology and anatomy, aiding ongoing research and innovation in the field of agriculture and biotechnology. This knowledge can lead to the development of improved cultivation techniques, disease-resistant varieties, and more sustainable agricultural practices.
13. Biofuel Potential: Phloem transports sugars, which can potentially be utilized for biofuel production. Research is ongoing to harness the sugar content in plant phloem for biofuel purposes, providing an alternative and renewable energy source.
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Grapefruit Phloem
The phloem of a grapefruit tree primarily transports sugars, nutrients, and other substances throughout the plant. However, deriving products directly from grapefruit phloem is not a common practice due to its vital role in the tree’s physiological processes. Instead, grapefruit trees are typically utilized for their fruits, leaves, and seeds, which are processed to create a range of products and by-products. Here are some of them:
1. Grapefruit Fruit (Primary Product): The main product derived from a grapefruit tree is the fruit itself, commonly used for fresh consumption, juices, jams, marmalades, and other culinary purposes. It’s a significant source of vitamin C and other essential nutrients.
2. Grapefruit Peel (By-product): The peel of grapefruit is a by-product of fruit processing. It is utilized to make essential oils, which find applications in aromatherapy, flavorings, and fragrances. The peel can also be dried and used in herbal teas and culinary recipes.
3. Grapefruit Seed Extract (By-product): Extracts from grapefruit seeds are used for their potential antimicrobial and antioxidant properties. Grapefruit seed extract is often incorporated into natural health and personal care products, such as skincare, mouthwashes, and dietary supplements.
4. Grapefruit Seed Oil (By-product): Grapefruit seed oil is derived from the seeds and is used in the production of cosmetics, soaps, and hair care products. It’s valued for its potential antibacterial and antifungal properties.
5. Grapefruit Leaf Extract (By-product): Extracts from grapefruit leaves may have potential health benefits and can be used in dietary supplements or herbal remedies. However, research on its efficacy and safety is ongoing.
6. Grapefruit Pulp (By-product): After extracting the juice, the remaining pulp can be used as a livestock feed or for composting to enrich soil.
7. Grapefruit Juice (By-product): When grapefruits are processed for juice, the juice itself is the primary product, and the pulp and other solids become by-products. Grapefruit juice is a popular beverage consumed globally.
8. Grapefruit Essential Oil (By-product): Essential oil extracted from grapefruit peels is used in aromatherapy, as a natural flavoring agent, and in the manufacturing of skincare and cosmetic products.
Read Also: Dates Stamen: Economic Importance, Uses and By-Products
9. Grapefruit Dietary Supplements (By-product): Grapefruit seed extract and grapefruit leaf extract can be used to create dietary supplements that are marketed for their potential health benefits, including immune support and antioxidant properties.
10. Grapefruit Bioactive Compounds (Research Product): Ongoing research explores the bioactive compounds within grapefruit, such as flavonoids and polyphenols, for potential health benefits. These could lead to the development of specialized nutritional supplements or functional foods.
11. Grapefruit Infused Beverages (Product): The flavors and aromas of grapefruit can be used to infuse various beverages, including teas, sparkling water, and alcoholic beverages like grapefruit-flavored beer or cocktails.
12. Grapefruit Seed Powder (By-product): The seeds can be dried, ground, and processed into a fine powder. This powder can be utilized in dietary supplements or as an additive in cosmetic and personal care products.
13. Grapefruit Biodegradable Packaging (Potential Product): Research is being conducted to extract natural polymers from grapefruit by-products, which could potentially be used to create biodegradable packaging materials, contributing to sustainable packaging solutions.
In conclusion, the phloem in grapefruit plays a vital role in nutrient transport, fruit development, and economic value. It contributes to the growth of healthy fruits, enhances their nutritional value, and supports various industries, including agriculture, food production, and pharmaceuticals.
Read Also: Feeding the World: The Importance of Sustainable Crop Farming

