This article contains the complete and innovative step-by-step guide on how to use rice husk to produce electricity. Rice husk also known as rice hull is a byproduct of rice milling, and it is often disposed of as waste. However, rice husk is a valuable resource that can be used to produce electricity.
Rice husk is a renewable energy source, which means that it can be replaced naturally once it is used.
Using rice husk to produce electricity is an innovative and environmentally sustainable approach that not only helps in the effective management of agricultural waste but also contributes to the generation of renewable energy.
This process involves the utilization of the abundant rice husk, which is the outer covering of the rice grain that is removed during the milling process.
Think about how rice husk power plants could be used to benefit your own communities. For example, think about where a rice husk power plant is located in your community and how it could be used to provide electricity and jobs.
Rice husk is a valuable resource that can be used to produce electricity. Rice husk power plants can help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and provide clean energy to rural communities.
According to research, rice husk contains about 30–50% of organic carbon and have high heat value of 13–16 MJ per kg. It can be used to generate fuel, heat, or electricity through thermal, chemical, or bioprocesses.
The energy conversion processes of rice husk are presented in a diagram below;

Rice husk has some specific characteristics which has made it easy to be used as an energy source, for instance;
1. The average caloric value of rice husk is 3410 K Cal/kg.
2. 1 ton of rice paddy can produce 220 kg of rice husk.
3. Rice husk is easily collectable at a very low cost.
A typical analysis of the chemical composition of given in the table below:
| Property | Range |
| Bulk density (kg/m3) | 96-160 |
| Hardness (Mohr’s scale) | 5-6 |
| Ash,% | 22-29 |
| Carbon, % | ≈ 35 |
| Hydrogen,% | 4 – 5 |
| Oxygen,% | 31 – 37 |
| Nitrogen,% | 0.23 – 0.32 |
| Sulphur,% | 0.04 – 0.08 |
| Moisture,% | 8 – 15 |
Read Also: 22 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Malpighia Emarginata (Acerola Cherry)
Steps on How to Use Rice Husk to Produce Electricity
Now let us discuss the detailed steps and mechanisms involved in the process:
Step 1: Rice Husk Collection and Storage
The first step is the collection and proper storage of rice husk. After the rice milling process, the husk is collected and stored in a dry and secure area to prevent it from getting damp or decomposing.
Step 2: Pre-processing
The collected rice husk needs to undergo pre-processing to prepare it for the electricity generation process.
This involves cleaning and sorting to remove impurities and any unwanted materials that might hinder the subsequent steps.
Step 3: Conversion to Biomass
The processed rice husk is then converted into biomass, which involves breaking down the husk into smaller particles or chips.
This step enhances the combustion efficiency and ensures a consistent and high-quality feedstock for the subsequent stages.
Step 4: Combustion or Gasification
These are two main ways to use rice husk to produce electricity: combustion and gasification.
The biomass obtained from the rice husk is then either combusted or gasified in a controlled environment.
a. Combustion
Combustion is the process of burning rice husk to produce heat. The heat can then be used to generate steam, which can drive a turbine to produce electricity.
Combustion involves burning the biomass directly to produce heat, which is then used to generate steam. The steam, in turn, drives a turbine connected to a generator to produce electricity.
b. Gasification
Gasification is the process of converting rice husk into a combustible gas. The gas can then be used to generate electricity in a gas turbine or gas engine.
Gasification, on the other hand, involves converting the biomass into a combustible gas, which is then utilized similarly to produce electricity.
Which of these two methods is better?
Gasification is generally considered to be a more efficient way to produce electricity from rice husk than combustion.
This is because gasification produces a cleaner gas, which can be burned more efficiently. Gasification also produces less ash than combustion.
Among some effective ways, here power generation by rice husk gasification is adopted and the system is designed in such a greener way so that the system evolves absolute zero emission.
To discuss elaborately the entire process involved, a basic block diagram is shown in the diagram below;
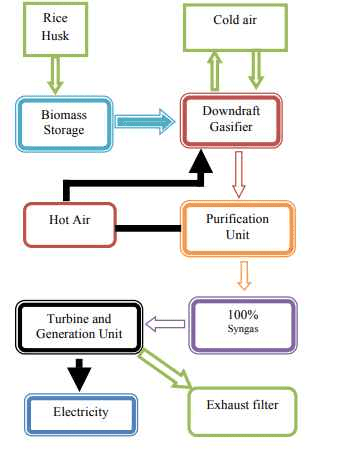
Step 5: Power Generation
The steam or gas produced from the combustion or gasification process is utilized to drive turbines that generate electricity.
This electricity can be used for various purposes, including powering agricultural machinery, providing energy to rural communities, or even feeding back into the national grid.
Read Also: When to Feed each Poultry Feed Types to Birds
Step 6: Ash Disposal and Environmental Impact
Proper management of the ash generated during the combustion or gasification process is crucial.
This ash can be rich in minerals and can be utilized as a valuable fertilizer or disposed of in an environmentally friendly manner.
Step 7: Maintenance and Optimization
Regular maintenance of the equipment involved in the process is essential to ensure its efficient and continuous operation.
Furthermore, continuous research and development are required to optimize the process, improve efficiency, and minimize any negative environmental impacts.
By effectively utilizing rice husk to produce electricity, we can not only reduce the environmental burden caused by its disposal but also contribute to the sustainable production of renewable energy.
This process aligns with the principles of a circular economy, where waste is repurposed to generate valuable resources, promoting a more sustainable and ecologically friendly agricultural practice.
In general, rice husk is collected after rice milling, with moisture content of about 8 –15%. This fits the requirement for further pretreatment or processing. Thermal processes, including combustion, gasification, and pyrolysis, are applied for rice husk processing.
The Energy products from rice husk are heat, electricity, and biofuel (solid or liquid). Heat generated from this could be used for house heating and cooking, industrial boilers, drying, and generating electricity.
The diagram below shows a schematic diagram of a combined system for processing biomass, including mechanical pretreatment, pyrolysis, gasification, and gas refinery. This system has been observed in the UK recently and known as the newest technology for biofuel conversion from biomass.
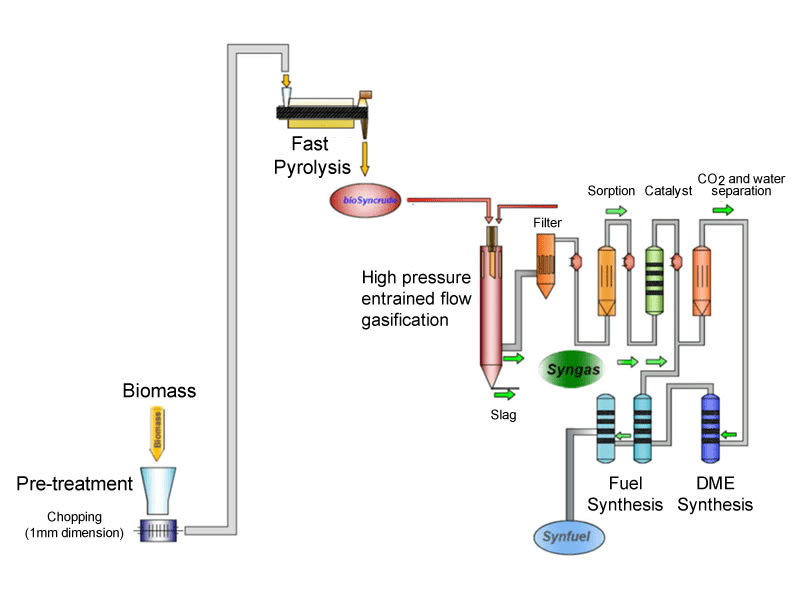
The following is a summary of the characteristics of rice husk compared with other solid fuels in terms of energy use:
1. Its high silica content causes the wearing of the components in processing machines, such as the chopper or grinder. Content of volatile matter in rice husk is higher than in wood and much higher than in coal, whereas fixed carbon is much lower than in coal. Ash content in rice husk is much higher than in wood and coal, which cause barriers for energy conversion (Jenkins 1998).
2. Its high content of ash, alkali, and potassium causes agglomeration, fouling, and melting in the components of combustors or boilers (Baker 2000).
Available solution to solve barriers in energy conversion from rice husk is pretreatment. Rice husk could be pretreated through mechanical, physical, and chemical means and through bioprocessing, or a combination of these processes to increase efficiency in further energy conversion.
These pretreatment technologies can be referred to in Klass (1998), Baker (2000), and Sadaka and Negi (2009). Other solutions for ash-related problems in rice husk are: to combine this with other fuels that are lower in alkali and chlorine (Tillman, 2000), to reduce the temperature in combustion systems, and to use other types of conversion systems such as Organic Rankin Cycle (ORC) and two-stage combustion.
Now this brings us to the next question, how to build a rice husk power plant and the benefits as well as the challenges of using rice husk to produce electricity.
Read Also: Poultry Housing Management: Site Selection Guide
How to Build a Rice Husk Power Plant
To build a rice husk power plant, you will need the following equipment:
- A gasifier
- A turbine or gas engine
- A generator
- Other equipment, such as boilers, condensers, and pumps
The gasifier is used to convert rice husk into a combustible gas. The gas is then fed to the turbine or gas engine, which drives the generator to produce electricity.
Benefits and Challenges of Using Rice Husk to Produce Electricity
a. Benefits of Using Rice Husk to Produce Electricity
There are many benefits to using rice husk to produce electricity and they include the following:
1. Rice husk is a renewable energy source.
2. Rice husk is a waste product, so using it to produce electricity reduces the amount of waste that goes to landfills.
3. Rice husk power plants can be small and decentralized, which means that they can be located close to where the rice is grown. This can reduce the need for long-distance transmission lines.
4. Rice husk power plants can provide jobs and economic benefits to rural communities.
b. Challenges of Using Rice Husk to Produce Electricity
There are also some challenges to using rice husk to produce electricity and they include the following:
1. Rice husk is a bulky material, so it can be expensive to transport.
2. Rice husk can contain impurities, such as sand and grit, which can damage the gasifier and other equipment.
3. Rice husk power plants can produce emissions, such as nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide, which can contribute to air pollution.
References
Baker R. 2000. Biomass fuel leaching for the control of fouling, slagging, and agglomeration in biomass power generation. PhD Dissertation, University of Califonia.
Jenkins BM. 1998. Physical properties of biomass. In: Kitani O, Hall CW, editors. Biomass Handbook. Gordon and Breach, New York.
Klass L. 1998. Biomass for Renewable Energy and Fuels. Barrington, Illinois (United States): Entech International, Inc.
Sadaka S, Negi S. 2009. Improvements of biomass physical and thermochemical characteristics via torrefaction process. Environ. Prog. Sustainable Energ. 28(3). http://www.scopus.com/inward/record.url?eid=2-s2.0.
Tillman DA. 2000. Biomass co-firing: the technology, the experience, the combustion consequences. Biomass Bioenergy 19:365-384.
Read Also: Ways to Make Money from Biodegradable Waste Materials
