Olive phloem refers to the phloem tissue found in olive trees (Olea europaea), a species known for its economic and cultural importance due to olive oil production and culinary uses. Phloem is one of the vascular tissues in plants, responsible for transporting sugars, organic nutrients, and other essential substances throughout the plant.
Olive phloem is composed of specialized cells, primarily sieve elements (sieve tubes) and companion cells. Sieve elements are elongated cells that form tubes, allowing for the efficient transport of sugars and other nutrients. Companion cells provide metabolic support to sieve elements.
The primary function of the phloem in olive trees is the transport of sugars (mostly sucrose), amino acids, hormones, and other organic compounds produced during photosynthesis. These substances are transported from the leaves (the primary site of photosynthesis) to various parts of the plant, including roots, stems, and developing fruits.
Transport in the phloem occurs through pressure-driven flow. Sucrose and other nutrients are actively loaded into sieve elements in source tissues (e.g., leaves) and are then transported via pressure gradients to sink tissues (e.g., roots, developing fruits) where they are unloaded and utilized.
Phloem sap is the fluid transported within the phloem. It contains sugars, amino acids, hormones, vitamins, and minerals. The sugars are the major components and are transported in the form of sucrose.
The phloem tissue is distributed throughout the plant, forming a network of tubes that run alongside xylem vessels. In olive trees, the phloem is found in the vascular bundles of the stems, leaves, and other plant organs. Olive phloem is adapted to the specific needs of the olive tree, optimizing the transport of nutrients for growth, fruit development, and oil production. The transport efficiency is crucial for supporting the development of olives, which are harvested for oil production.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Olive Phloem
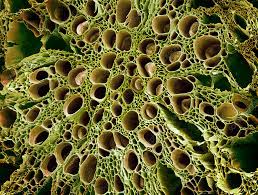
The phloem in plants, including olive trees (Olea europaea), is a critical tissue responsible for transporting sugars, nutrients, and other essential substances throughout the plant. While the economic importance and uses of olive phloem specifically may not be as extensively studied or recognized compared to other parts of the olive tree, I can provide information on the general economic importance and uses of the olive tree as a whole, which indirectly involves the phloem.
1. Olive Oil Production: Olive oil is a significant product derived from olives and is a staple in Mediterranean cuisine. The olive fruit, which contains the phloem tissue, is pressed to extract olive oil. Olive oil is not only a cooking oil but also used in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and various industrial applications.
2. Food Industry: Olives themselves are used in various culinary applications, including salads, spreads, and snacks. The phloem is an integral part of the olive fruit, facilitating the transport of nutrients and sugars that contribute to the overall quality and taste of the fruit.
3. Pharmaceuticals: Certain compounds extracted from olives, including those found in the phloem, may have potential health benefits. Olive leaves, for instance, are used in traditional medicine and can be a source of bioactive compounds that possess antioxidant and antimicrobial properties.
Read Also: Olive Calyx: Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products
4. Biomedical Research: Olive phloem and other plant tissues are subjects of scientific research aimed at understanding plant biology and potentially developing new technologies, medicines, or bioproducts. The study of phloem can contribute to a broader understanding of plant physiology and biochemistry.
5. Fertilizers and Soil Amendments: The phloem, like other plant tissues, contains essential nutrients that can be utilized in producing organic fertilizers or soil amendments. These organic products can enhance soil fertility and promote plant growth.
6. Bioenergy and Biomass Production: Plant materials, including olive trees, can be used for bioenergy production through processes such as anaerobic digestion or combustion. The phloem, being part of the plant biomass, contributes to these energy production processes.
7. Environmental Applications: Olive trees, including their phloem, play a role in soil conservation and erosion control. The roots and overall structure of the tree help stabilize the soil, preventing erosion and maintaining soil health.
8. Economic Sustainability: The cultivation and harvesting of olive trees, which includes utilizing the phloem indirectly, contribute significantly to the economy of regions where olive cultivation is prevalent. Olive farming supports livelihoods, generates employment, and stimulates local economies.
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Olive Phloem
Olive phloem is a part of the plant’s vascular system that transports nutrients, sugars, and other important substances throughout the plant. However, extracting products directly from olive phloem is not a common practice. Olive trees are primarily cultivated for their fruits (olives) and the products derived from them. The phloem is essential for nutrient transportation within the olive tree, but it is not typically used as a direct source for specific products.
Instead, the main products and by-products derived from olives and olive trees include:
1. Olives (Fruits): Olives are the primary product derived from olive trees. They are used for various purposes, including culinary consumption, oil production, and as table olives. Olives can be processed in different ways, such as brining, curing, or pressing to extract olive oil.
2. Olive Oil: Olive oil is a major product derived from the pressing of olives. It is widely used in cooking, salad dressings, and various culinary applications. Olive oil is also a valuable ingredient in cosmetics, soaps, and traditional medicine.
3. Olive Pomace: Olive pomace is a by-product generated during the olive oil extraction process. It consists of the leftover pulp, skin, and pit fragments. Olive pomace can be further processed to extract additional oil using solvents or other methods.
4. Olive Leaf Extract: Olive leaf extract is a by-product obtained from the leaves of the olive tree. It contains compounds such as oleuropein and is used in dietary supplements, herbal medicines, and skincare products due to its potential health benefits.
5. Olive Wood: Olive wood is a by-product from pruning and trimming olive trees. It is valued for its attractive appearance and durability, making it suitable for crafting furniture, utensils, decorative items, and woodwork.
Read Also: 23 Medicinal Health Benefits of Citrus latipes (Khasi Papeda)
6. Olive Leaf Tea: Dried olive leaves can be used to make olive leaf tea. This tea is believed to have various health benefits and is consumed as a herbal beverage.
7. Olive Pits (or Olive Stones): Olive pits, the hard seeds found inside olives, can be ground down to produce olive pit powder. This powder can be used in some industrial applications, such as abrasives or as an additive in animal feed.
8. Olive Husks: The husks of olives, the outer layer of the fruit, can be used as biomass fuel, animal bedding, or compost.
9. Olive Residues (Pulp and Skins): Leftover residues from olive processing, including pulp and skins, can be used for composting, animal feed, or as a source of biogas through anaerobic digestion.
10. Olive Leaf Mulch: Olive leaves and other plant parts can be used as mulch in gardens and agricultural applications to improve soil quality and water retention.
In conclusion, it is important to note that while olive phloem plays a crucial role in the overall health and growth of the olive tree, it is not typically utilized as a direct source for specific products. The valuable products from olive trees are primarily derived from the fruits (olives), leaves, and other parts of the tree.
Read Also: All You Need to Know About Cosmos Flower

