Plant reproduction is the process by which plants produce offspring, ensuring their survival and continuation. This guide covers what plant reproduction is, the types of reproduction, and the processes involved in sexual and asexual reproduction, including pollination and fertilization.
Plant reproduction is the biological mechanism by which plants create new individuals, continuing their species. This can occur through sexual reproduction, involving the fusion of male and female gametes, or asexual reproduction, where new plants arise from a single parent without the need for gamete fusion.
Types of Plant Reproduction
1. Sexual Reproduction: Involves the fusion of male and female gametes (sex cells) to form a zygote, leading to genetic diversity among offspring. Example: Flowering plants produce seeds through sexual reproduction.
2. Asexual Reproduction: Does not involve gametes. New plants are produced from a single parent through methods such as vegetative propagation or cloning. Example: Plants like potatoes and strawberries reproduce asexually through tubers and runners, respectively.
Sexual Reproduction in Plants
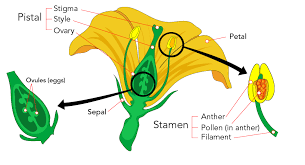
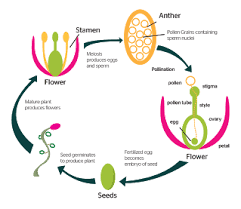
1. Gamete Formation: Male gametes (pollen) and female gametes (ovules) are formed in the flower’s reproductive organs. Example: Pollen is produced in the anthers, and ovules are located in the ovary.
2. Pollination: The transfer of pollen from the male anther to the female stigma. This can be facilitated by wind, insects, or other animals. Example: Bees pollinate flowers by transferring pollen while collecting nectar.
3. Fertilization: Pollen germinates on the stigma, growing a pollen tube to the ovule, where sperm cells fertilize the egg. This results in the formation of a zygote. Example: After fertilization, the ovule develops into a seed.
4. Seed Development: The fertilized ovule matures into a seed, while the ovary develops into a fruit that protects and disperses the seed. Example: An apple develops from the ovary and contains seeds inside.
5. Seed Dispersal: Seeds are spread from the parent plant to reduce competition and enhance germination chances. Example: Dandelion seeds are dispersed by the wind.
Asexual Reproduction in Plants
1. Vegetative Propagation: Involves new plants growing from vegetative parts like stems, leaves, or roots. Example: A rose bush can be propagated from stem cuttings.
2. Cloning: Producing genetically identical plants from a single parent through methods like tissue culture. Example: Orchids can be cloned using tissue culture techniques.
3. Apomixis: Seeds are produced without fertilization, leading to offspring that are genetic clones of the parent. Example: Some dandelion species reproduce via apomixis.
Pollination and Fertilization Processes
1. Pollination: The transfer of pollen to the stigma of a flower, which can occur via insects, wind, birds, or water. Example: Hummingbirds transfer pollen while feeding on nectar from tubular flowers.
2. Fertilization: Pollen germinates on the stigma and grows a pollen tube down to the ovule. Sperm cells travel through the tube to fertilize the egg cell. Example: In flowering plants, fertilization results in seed formation.
3. Double Fertilization: In many plants, one sperm cell fertilizes the egg cell, and another sperm cell fuses with two other cells to form endosperm, which nourishes the embryo. Example: In many flowering plants, this process ensures the development of both the seed and the surrounding nutrient tissue.
The Role of Flowers and Fruits
1. Flowers: Flowers are the reproductive structures of flowering plants (angiosperms). They contain the plant’s reproductive organs, including stamens (male parts) and pistils (female parts). Function: Flowers facilitate pollination by attracting pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and birds with their color, scent, and nectar.
2. Fruits: Fruits develop from the ovary of a flower after fertilization. They protect and nourish developing seeds and aid in their dispersal. Function: Fruits can be fleshy, like apples and tomatoes, or dry, like nuts and grains. They enhance seed dispersal by attracting animals or by mechanical means.
Read Also: Moon Flowers (Ipomoea Alba): All You Need To Know About
Seed Formation and Dispersal
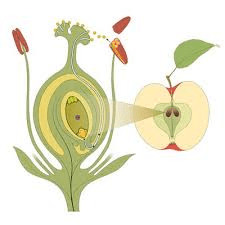
1. Seed Formation: After fertilization, the ovule develops into a seed, which contains the embryo (the young plant), endosperm (nutrient supply), and a protective seed coat. Process: Seeds develop within the fruit and are designed to withstand various conditions until they reach a suitable environment for germination.
2. Seed Dispersal: Seeds are dispersed from the parent plant to reduce competition and increase the likelihood of successful germination. Methods: Dispersal methods include wind (e.g., dandelion seeds), animals (e.g., seeds with hooks that cling to fur), water (e.g., coconuts), and mechanical means (e.g., exploding seed pods).
Factors Affecting Plant Reproduction
1. Pollination: Effective pollination is critical for successful reproduction. Factors affecting pollination include the availability of pollinators, timing of flower blooming, and the presence of pollinator attractants. Solution: Plant a variety of flowering species to attract diverse pollinators and ensure that plants are pollinated during their blooming period.
2. Soil Quality: Soil fertility and structure impact the health of plants and their ability to produce seeds. Solution: Regularly test and amend soil to ensure it has adequate nutrients, pH, and drainage.
3. Climate and Weather: Temperature, rainfall, and seasonal changes influence plant growth and reproduction. Solution: Choose plant varieties suited to your local climate and consider microclimates within your garden to provide optimal growing conditions.
4. Pests and Diseases: Pests and diseases can hinder pollination and damage reproductive structures. Solution: Implement pest control measures and practice good garden hygiene to prevent and manage diseases.
Common Reproductive Challenges and Solutions
1. Poor Pollination: Inadequate pollination can lead to poor fruit and seed production. Solution: Increase the presence of pollinators by planting a diverse range of flowering plants and avoiding the use of pesticides that harm beneficial insects.
2. Low Seed Viability: Seeds that fail to germinate can be due to poor seed quality or environmental conditions. Solution: Use high-quality seeds, store them properly, and ensure optimal germination conditions, such as proper temperature and moisture levels.
3. Seedling Diseases: Seedlings can suffer from diseases that affect their development. Solution: Use disease-resistant plant varieties, provide adequate spacing for air circulation, and avoid overwatering to reduce disease risks.
4. Inadequate Fruit Set: Some plants may produce flowers but fail to set fruit. Solution: Ensure proper pollination, maintain optimal growing conditions, and provide sufficient nutrients to support fruit development.
Read Also: Hawaiian Flowers (Hibiscus Brackenridgei): All You Need To Know About
Strategies to Enhance Plant Reproduction
1. Enhance Pollination: Attract and support pollinators by planting diverse flowers and providing habitat. Use techniques such as hand pollination for crops that require it.
2. Improve Soil Health: Regularly enrich soil with compost and organic matter to support healthy plant growth and reproductive processes. Test soil and adjust nutrient levels as needed.
3. Optimize Growing Conditions: Ensure plants are grown in appropriate light, temperature, and moisture conditions. Use greenhouse or shade cloths to control environmental factors when necessary.
4. Implement Pest Management: Monitor plants for pests and diseases and use integrated pest management (IPM) strategies to control infestations while minimizing harm to beneficial organisms.
5. Select Appropriate Varieties: Choose plant varieties known for their strong reproductive capabilities and suitability to your local climate. Consider varieties with high yields, disease resistance, and efficient pollination.
6. Practice Proper Plant Care: Regularly prune and maintain plants to encourage healthy growth and reproduction. Provide adequate water, nutrients, and support structures as needed.
Understanding plant reproduction is crucial for successful gardening and agriculture. By comprehending the roles of flowers and fruits, seed formation and dispersal, and the factors affecting reproduction, you can better manage and enhance plant growth.
Addressing common reproductive challenges and implementing strategies to improve reproduction will help ensure healthy, productive plants and a thriving garden.
Read Also: Kirby Plush: The Best Plush Toys for Imaginative Play
Frequently Asked Questions
We will update this section soon.