The Rice Nodes: Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products
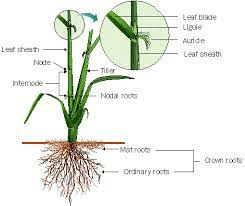
Rice nodes are the points along the stem of a rice plant where leaves, branches, and reproductive structures emerge. In the botanical context of Oryza sativa, rice nodes play a vital role in the overall growth and development of the plant.
Each node consists of a small swelling or protrusion on the stem where a leaf is attached. The area around the node contains specialized tissues responsible for the formation of new plant parts, such as shoots, roots, and flowers. Nodes serve as important sites for nutrient and water transport throughout the plant.
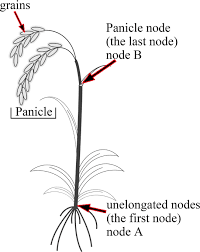
During the vegetative stage of growth, rice nodes primarily produce leaves, which are essential for photosynthesis and the production of carbohydrates. As the plant transitions to the reproductive stage, nodes give rise to floral structures, including spikelets, where rice grains develop.
The number and arrangement of nodes along the rice stem vary depending on factors such as genetic characteristics, environmental conditions, and management practices. Varieties with more nodes may exhibit greater branching and canopy development, potentially influencing yield and grain quality.
Nodes also play a role in determining the overall architecture and height of the rice plant. Breeders and researchers often study node characteristics to develop rice varieties with desired traits, such as improved lodging resistance, efficient nutrient uptake, and adaptation to specific growing conditions.
Rice nodes are critical anatomical features that contribute to the growth, development, and productivity of the rice plant. Understanding their structure and function is essential for optimizing crop management practices and enhancing rice cultivation worldwide.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Rice Nodes
Rice nodes, the points on the rice stem where leaves, branches, and reproductive structures attach, hold significant economic importance and serve various purposes across different industries. Let’s explore the economic significance and diverse uses of rice nodes:
1. Structural Support: Rice nodes provide structural support to the rice plant, allowing it to stand upright and support the weight of leaves, branches, flowers, and grains. This structural integrity is crucial for preventing lodging and maximizing sunlight exposure for photosynthesis.
2. Resource Transport: Nodes facilitate the transport of water, nutrients, and sugars throughout the rice plant. Vascular bundles within the nodes carry water and minerals absorbed by the roots upward to the leaves, while phloem tissues transport sugars produced during photosynthesis to other parts of the plant.
3. Reproductive Function: Nodes play a vital role in the reproductive process of rice plants. They serve as attachment points for panicles, where flowers develop and grains form after pollination. Healthy nodes ensure successful pollination and grain filling, contributing to crop yield and quality.
4. Biomass Production: Rice nodes contribute to biomass production, which is essential for various industrial applications such as bioenergy, bioplastics, and biocomposites. Biomass-derived from rice nodes can be converted into renewable energy sources or used as raw materials for manufacturing.
5. Fodder and Animal Feed: Rice nodes, along with other parts of the rice plant, are utilized as fodder and animal feed. They provide a source of nutrition for livestock such as cattle, sheep, and poultry, contributing to livestock production and agricultural livelihoods.
6. Mulching Material: Nodes trimmed during rice cultivation can be used as mulching material in agricultural fields. Mulching helps conserve soil moisture, suppress weed growth, and improve soil fertility, promoting sustainable agriculture practices.
7. Craft and Art: In some cultures, rice nodes are used in traditional crafts and art forms. They are woven into baskets, mats, and decorative items, showcasing the cultural significance and creativity associated with rice cultivation.
8. Soil Erosion Control: Rice nodes, when incorporated into soil or used as erosion control barriers, help prevent soil erosion on slopes and embankments. Their fibrous structure stabilizes the soil, reduces water runoff, and protects against erosion caused by rainfall and wind.
9. Bioremediation: Nodes, along with other plant parts, can contribute to bioremediation efforts by absorbing and metabolizing pollutants from the soil and water. They help detoxify contaminated environments and restore ecological balance in areas affected by pollution.
10. Ethnobotanical Uses: In traditional medicine and folklore, rice nodes are sometimes used for their medicinal properties. Extracts or preparations derived from nodes are believed to have therapeutic effects and are used to treat various ailments in certain cultures.
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Rice Nodes

Rice nodes offer the potential for deriving various products and by-products that contribute to agricultural, industrial, and medicinal sectors. Let’s explore the diverse range of products derived from rice nodes along with their production processes:
1. Bioenergy Production: Rice nodes can be processed into biofuels such as bioethanol and biogas. Through biochemical or thermochemical conversion processes, the cellulose and hemicellulose present in nodes are broken down into fermentable sugars or converted into gaseous fuels.
2. Biocomposites: Node fibers can be used as reinforcement in biocomposite materials. When combined with resins or matrices derived from natural or synthetic sources, node fibers enhance the mechanical properties of composites used in construction, automotive, and aerospace industries.
3. Bioplastics: Node fibers can be utilized in the production of biodegradable plastics. When processed into polymer matrices, node fibers enhance the biodegradability and sustainability of plastic products, reducing environmental pollution and waste.
4. Paper and Pulp: Node fibers, when pulped and processed, can be used in the production of paper and pulp. They contribute to the manufacturing of packaging materials, stationery, and cardboard, offering a renewable and eco-friendly alternative to conventional paper products.
5. Animal Bedding: Node fibers can be used as bedding material for livestock and poultry. Their absorbent properties help maintain dry and clean bedding conditions, promoting animal health and welfare in agricultural operations.
6. Bioremediation Medium: Node fibers, when incorporated into bioremediation systems, serve as a medium for microbial activity and pollutant degradation. They provide a substrate for beneficial microorganisms to colonize and metabolize pollutants, facilitating the cleanup of contaminated environments.
7. Mulch and Soil Amendment: Node fibers, when shredded or chopped, can be used as mulch or soil amendment in agricultural and landscaping applications. They help conserve soil moisture, suppress weed growth, and improve soil structure, promoting sustainable soil management practices.
8. Construction Materials: Node fibres can be incorporated into construction materials such as particleboard, fiberboard, and insulation panels. Their fibrous structure enhances the mechanical strength and thermal insulation properties of building materials, contributing to energy efficiency and environmental sustainability.
9. Craft and Art Supplies: Node fibres are used in traditional crafts and art forms. They are woven into baskets, mats, and decorative items, showcasing the cultural heritage and creativity associated with rice cultivation.
10. Medicinal Extracts: Certain components of rice nodes may have medicinal properties. Extracts obtained from nodes are studied for their potential antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and other therapeutic effects in traditional medicine and modern pharmacology.
Read Also: 18 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Maytenus aquifolia (Toothed Mayten)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Rice Nodes
1. What are rice nodes?
Rice nodes are the points on the rice stem where leaves, branches, and reproductive structures attach, providing structural support and facilitating resource transport within the rice plant.
2. How do rice nodes contribute to crop production?
Rice nodes play a vital role in supporting the rice plant’s structure, facilitating water and nutrient transport, and contributing to biomass production, which is essential for crop yield and quality.
3. Can rice nodes be utilized for non-agricultural purposes?
Yes, rice nodes have applications beyond agriculture. They are utilized in industries such as bioenergy, bioplastics, construction, and bioremediation, contributing to economic diversification and sustainability.
4. Are there any environmental benefits associated with rice nodes?
Rice nodes contribute to environmental sustainability by promoting soil conservation, reducing soil erosion, and supporting bioremediation efforts to clean up contaminated environments.
5. Do rice nodes have any medicinal properties?
Certain components of rice nodes may possess medicinal properties and are studied for their potential therapeutic effects. Extracts obtained from nodes are investigated for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and other bioactive properties in traditional medicine and modern pharmacology.
6. How are rice nodes processed into bioenergy and bioproducts?
Rice nodes can be processed through biochemical or thermochemical conversion processes to produce biofuels, biocomposites, bioplastics, and other value-added products. These processes involve breaking down the cellulose and hemicellulose present in nodes into usable forms.
7. What are the cultural traditions associated with rice nodes?
In some cultures, rice nodes are used in traditional crafts and art forms, showcasing the cultural heritage and creativity associated with rice cultivation. They are woven into baskets, mats, and decorative items, reflecting the significance of rice in local customs and traditions.
8. How do environmental factors affect rice node development?
Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, soil fertility, and water availability influence rice node development and plant growth. Optimal environmental conditions promote healthy node formation and stem growth, leading to robust crop performance and yield.
9. What research is being conducted on rice nodes?
Ongoing research on rice nodes encompasses various disciplines such as plant physiology, genetics, agronomy, biotechnology, and materials science. Scientists are exploring ways to enhance node development, improve resource efficiency, and harness their potential for sustainable agriculture and industrial applications.
10. What are the prospects of rice node utilization?
The future of rice node utilization looks promising, with advancements in biotechnology, materials science, and environmental sustainability driving innovation and investment in value-added products and processes. Harnessing the potential of rice nodes can contribute to sustainable development, economic growth, and environmental stewardship on a global scale.
Read Also: The Different Types of Manure and How they Work









