Plants are crucial to life on Earth. They are the backbone of all ecosystems, playing multiple roles that support and sustain life. Without plants, many of the processes that keep our planet healthy would not exist.
From producing oxygen to providing food, plants are fundamental to the survival of both humans and animals. This article will explore the key roles that plants play in ecosystems, helping you understand their importance in simple terms.
Photosynthesis: The Foundation of Life
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants make their own food. Using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide, plants produce glucose (a type of sugar) and oxygen. This process happens in the leaves, which contain a green pigment called chlorophyll. Chlorophyll captures the sunlight and starts the chemical reactions that turn carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
Photosynthesis is the foundation of life on Earth because it is the primary way that energy from the sun is captured and converted into a form that living organisms can use. The glucose produced during photosynthesis is used by the plant for growth, reproduction, and other vital functions. Moreover, the oxygen released as a byproduct is essential for the survival of most living creatures, including humans.
Photosynthesis plays a critical role in maintaining the balance of gases in the Earth’s atmosphere. By absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen, plants help regulate the levels of these gases, which is vital for a stable climate and a healthy environment.
Plants as Primary Producers
Primary producers are organisms that produce their own food. In most ecosystems, plants are the primary producers. They form the base of the food chain by creating energy-rich compounds through photosynthesis, which are then used by other organisms for nourishment.
Plants serve as the starting point in most food chains. Herbivores (animals that eat plants) rely directly on plants for their energy. In turn, carnivores (animals that eat other animals) rely on herbivores. Without plants, there would be no primary source of energy for these chains, leading to the collapse of entire ecosystems.
The energy captured by plants through photosynthesis is passed on to other organisms in the ecosystem when they are eaten. This flow of energy supports all life forms within the ecosystem. Thus, plants are crucial for maintaining the energy balance in ecosystems.
The Oxygen Cycle and Plants’ Contribution
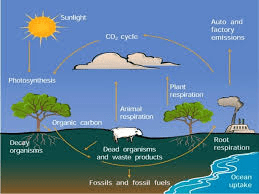
The oxygen cycle is the movement of oxygen between the atmosphere, biosphere (all living organisms), and the lithosphere (the Earth’s crust). Plants play a significant role in this cycle by producing oxygen during photosynthesis.
During photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen as a byproduct. This oxygen is then used by animals and humans for respiration. The continuous production of oxygen by plants ensures that there is always enough oxygen in the atmosphere for living organisms to breathe.
The oxygen cycle is crucial for maintaining the balance of gases in the atmosphere. Plants help keep this balance by absorbing excess carbon dioxide, which can contribute to global warming, and releasing oxygen, which is essential for life.
Plants in Food Chains and Webs
A food chain is a simple way to show how energy moves from one organism to another within an ecosystem. Plants are at the beginning of most food chains because they produce their own food through photosynthesis.
A food web is a more complex version of a food chain. It shows how different food chains in an ecosystem are interconnected. In a food web, plants are still the primary producers, but their role becomes even more crucial as they support multiple food chains simultaneously.
All animals, directly or indirectly, depend on plants for their survival. Herbivores eat plants, and carnivores eat herbivores. Even omnivores, which eat both plants and animals, rely on plants as a food source. Without plants, these food chains and webs would collapse, leading to the extinction of many species.
Habitat Formation: Plants as Ecosystem Architects
Plants create and shape habitats for a variety of organisms. Forests, grasslands, wetlands, and even deserts are all ecosystems where plants play a critical role in forming the environment. These habitats provide shelter, food, and breeding grounds for countless species.
Forests are among the most diverse ecosystems on Earth. Trees, as the dominant plants in forests, create a layered structure that supports different species at various levels—from the forest floor to the canopy. This layering allows for a wide range of biodiversity.
Aquatic plants, such as algae and water lilies, are vital in water ecosystems. They provide oxygen through photosynthesis, offer food for aquatic animals, and create habitats for fish, amphibians, and invertebrates. Without these plants, aquatic ecosystems would not be able to support life.
Raed Also: Blackleg (cruciferous plants): Description, Damages Caused, Control and Preventive Measures
Nutrient Cycling and Soil Health
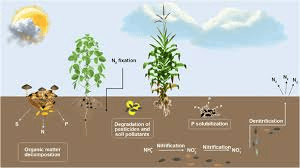
Plants play a key role in nutrient cycling, which is the movement and exchange of organic and inorganic matter back into the production of living matter. Through processes like photosynthesis, plants absorb nutrients from the soil and convert them into biomass, which is then returned to the soil when plants shed leaves or die.
Plants contribute to soil health by adding organic matter through fallen leaves, roots, and other plant parts. This organic matter is broken down by soil organisms, enriching the soil with nutrients. Healthy soil, in turn, supports plant growth, creating a sustainable cycle.
Plant roots help bind the soil, preventing erosion. In areas with rich plant cover, the soil is less likely to be washed away by rain or blown away by wind, maintaining soil fertility and preventing land degradation.
Plants’ Role in Climate Regulation
Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere during photosynthesis and store it in their biomass. This process, known as carbon sequestration, helps reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, which is a key factor in controlling global warming and climate change.
Plants, especially forests, help regulate temperature by providing shade and releasing moisture into the air through a process called transpiration. This can cool the surrounding area and influence local climate conditions.
Large plant communities, like forests, can affect rainfall patterns. Trees release water vapor into the air, which can contribute to cloud formation and precipitation. This process is essential for maintaining the water cycle and ensuring adequate rainfall for all forms of life.
Biodiversity Support through Plant Communities
Plant communities create diverse habitats that support a wide range of species. Different types of plants provide various resources, such as food, shelter, and breeding grounds, which allow multiple species to coexist in the same environment.
Plants are integral to the complex web of life. Many species depend on specific plants for survival, such as pollinators like bees relying on flowering plants for nectar. This interdependence ensures that biodiversity thrives within ecosystems.
Certain plant communities are critical for the survival of endangered species. Protecting these plants helps conserve the species that depend on them, preserving biodiversity and maintaining ecological balance.
Raed Also: Blackleg (cruciferous plants): Description, Damages Caused, Control and Preventive Measures
Plants in Water Cycles and Purification
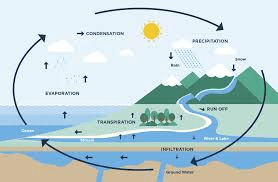
Plants play a vital role in the water cycle by absorbing water from the soil and releasing it into the atmosphere through transpiration. This process helps maintain the balance of moisture in the air, which is crucial for cloud formation and precipitation.
Wetlands and other plant-rich environments act as natural filters for water. Plants in these areas can absorb pollutants, sediments, and excess nutrients from water, purifying it before it enters rivers, lakes, and other bodies of water.
Plants help regulate water flow and reduce the risk of flooding. In forested areas, for example, trees and vegetation absorb large amounts of water, slowing down the runoff and decreasing the likelihood of floods.
Human Dependence on Plant Ecosystems
Humans rely on plants for food. Agriculture, which is the cultivation of plants for food, is the foundation of human civilization. From grains and vegetables to fruits and nuts, plants provide the essential nutrients that sustain human life.
Many medicines are derived from plants. Traditional remedies and modern pharmaceuticals alike depend on plant compounds to treat various ailments. The loss of plant biodiversity could mean the loss of potential cures for diseases.
Plants are a significant economic resource. They provide raw materials for industries such as timber, paper, textiles, and biofuels. Additionally, plants contribute to tourism and recreation, offering natural beauty and spaces for outdoor activities.
Plants hold cultural significance for many communities around the world. They are used in rituals, symbols, and traditional practices that are integral to cultural identity and heritage.
Conclusion
Plants are the foundation of life on Earth. They play a vital role in nutrient cycling, climate regulation, and supporting biodiversity. Plants are also crucial in water purification and in sustaining human life through food, medicine, and economic resources.
Understanding the role of plants in ecosystems is essential for appreciating their importance and the need to protect and preserve them for future generations.






