Snakebites are a serious health issue in many parts of the world. Each year, millions of people are bitten by snakes, and some of these bites can be life-threatening. Knowing about snakebites, how to prevent them, and what to do if they occur can make a huge difference in handling such emergencies effectively.
Understanding Different Types of Venomous Snakes
Venomous snakes can be classified into different families. Here are some common ones:
1. Pit Vipers: These include rattlesnakes, copperheads, and cottonmouths. They are found mainly in the Americas. Pit vipers have a heat-sensing pit between their eyes and nostrils, which helps them detect warm-blooded prey.
2. Elapids: This group includes cobras, kraits, and sea snakes. Elapids are found in Africa, Asia, Australia, and the Pacific. They have fixed fangs and produce neurotoxins that affect the nervous system.
3. Colubrids: While many colubrids are non-venomous, some, like the boomslang, are venomous. They are widespread across the globe and can be less well-known.
Each type of venom causes different symptoms and requires specific treatments, making it important to identify the snake involved.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Snakebites

1. Be Cautious Outdoors: When hiking or walking in areas where snakes may live, wear long pants and sturdy boots. This provides a barrier between your skin and any potential snake bites.
2. Stay on Clear Paths: Stick to well-trodden trails and avoid tall grass, heavy underbrush, or areas with loose rocks where snakes might hide.
3. Watch Where You Step: Always look carefully before placing your hands or feet in areas where you cannot see clearly, such as under rocks or logs.
4. Avoid Provoking Snakes: Never try to handle or harass a snake. If you encounter one, give it space to move away.
5. Educate Yourself: Learn about the venomous snakes in your area and how to recognize them. Knowing what to look out for can help you avoid dangerous encounters.
Immediate Actions if Bitten by a Snake
1. Remain Calm: Keeping calm helps slow the spread of venom through your bloodstream. Panic can increase your heart rate and worsen the situation.
2. Get to Safety: Move away from the snake’s vicinity to avoid further bites. If possible, get to a safe place where you can seek help.
3. Seek Medical Attention: Go to the nearest hospital or medical facility immediately. Call emergency services if you cannot get there on your own.
4. Immobilize the Affected Area: Keep the bitten limb as still as possible to prevent the venom from spreading. Use a splint if available.
5. Do Not Attempt to Suck Out Venom: Avoid using any form of suction or cutting the bite area, as these methods are ineffective and can cause more harm.
Read Also: Trichomoniasis: Description, Damages Caused, Control and Preventive Measures
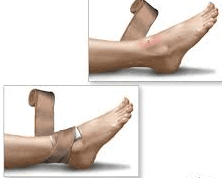
First Aid for Snakebites
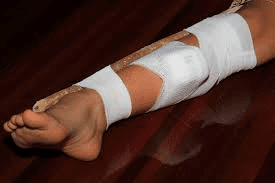
1. Call for Help: As soon as you are bitten, contact emergency services or get someone to help you seek medical care. Time is crucial in treating snakebites.
2. Keep the Bite Area Still: Immobilize the bitten limb with a splint or bandage to limit movement. Try to keep the affected area below the level of your heart.
3. Apply a Bandage: If instructed by medical professionals, use a bandage or cloth to apply gentle pressure above the bite site. This can help slow the spread of venom, but be careful not to cut off blood flow.
4. Avoid Ice or Heat: Do not apply ice, heat, or any form of ointment to the bite area. These methods can worsen the situation.
5. Monitor Symptoms: Keep track of symptoms such as swelling, pain, or difficulty breathing. Inform medical personnel about any changes.
6. Follow Medical Advice: Once you reach a medical facility, follow the instructions provided by healthcare professionals. They may administer antivenom and other treatments based on the type of snake and the severity of the bite.
When to Seek Medical Help
1. Immediate Care: Seek medical help immediately if bitten by a snake. The sooner you receive treatment, the better the chances of recovery.
2. Severe Symptoms: If you experience severe symptoms like difficulty breathing, severe swelling, or rapid spread of pain, seek emergency medical attention right away.
3. Signs of Infection: If you notice signs of infection at the bite site, such as increased redness, swelling, or pus, contact a healthcare provider as soon as possible.
Read Also: List of Diseases Ruminant Animals (Livestock) Get from Feeds and Water
Medical Treatment for Snakebites
1. Antivenom: The primary treatment for snakebites is antivenom. It neutralizes the venom and is specific to the type of snake that bit you.
2. Supportive Care: In addition to antivenom, treatment may include intravenous fluids, pain management, and medications to manage symptoms.
3. Monitoring: Medical staff will monitor your condition closely for any complications and adjust treatment as needed.
4. Wound Care: Proper care of the bite wound is essential to prevent infection and promote healing.
Recovery and Rehabilitation After a Snakebite
1. Follow-Up Appointments: Attend all follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider to ensure proper healing and recovery.
2. Physical Therapy: If the bite causes long-term damage or affects mobility, physical therapy may be necessary to regain function.
3. Mental Health Support: Snakebites can be traumatic. Seek mental health support if you experience anxiety, PTSD, or other psychological effects.
4. Avoid Repeated Exposure: Take steps to avoid future snakebites by following preventive measures and staying educated about snake safety.
Common Myths and Misconceptions About Snakebites
1. Myth: Sucking Out Venom Helps: It is a common misconception that sucking out venom can help. In reality, this is ineffective and can cause additional harm.
2. Myth: Ice Reduces Swelling: Applying ice to a snakebite can worsen the situation. It is better to avoid ice and heat altogether.
3. Myth: All Snakes are Deadly: Not all snakes are venomous or dangerous. Many snakes are harmless and play beneficial roles in their ecosystems.
4. Myth: Venomous Snakes Only Bite When Aggressed: Snakes may bite in self-defense, and it is not always due to provocation. It’s best to avoid contact with them.
Educational Resources and Support
1. Local Health Departments: Contact local health departments or poison control centers for information on snakebite treatment and prevention.
2. Educational Websites: Use reputable websites like the World Health Organization (WHO) or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for up-to-date information on snakebites.
3. Community Programs: Participate in community programs or workshops on snakebite prevention and first aid.
4. Support Groups: Join support groups for individuals recovering from snakebites to share experiences and receive emotional support.
Conclusion
Understanding when to seek medical help, the treatments available, and the recovery process after a snakebite is essential for effective management and recovery. By being aware of common myths and accessing educational resources, you can better protect yourself and others from snakebite risks. Always prioritize professional medical advice and support for the best outcomes.
Read Also: The Impact Of Hazardous Waste Disposal in Los Angeles
Frequently Asked Questions
We will update this section soon.

