The Sugarcane Stigma: Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products
The sugarcane stigma, scientifically known as Saccharum officinarum, is a vital component of the sugarcane plant, playing a crucial role in its reproductive process.
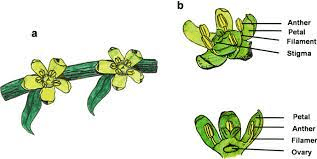
As a key part of the female reproductive organ, the stigma serves as the receptive surface for pollen grains during pollination. Located at the apex of the pistil, the stigma is often prominent in appearance, with a characteristic shape that facilitates the capture of pollen from visiting pollinators such as bees and wind-borne particles.
In the life cycle of sugarcane, the stigma emerges as an essential element in the sexual reproduction of the plant. When mature, the stigma secretes substances that attract pollen, aiding in the fertilization process.
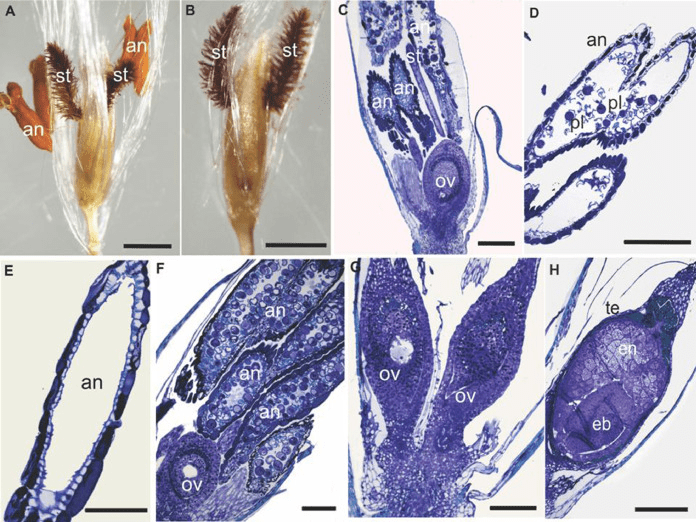
As pollen grains land on the stigma’s surface, they germinate, forming pollen tubes that extend down the style toward the ovary, where fertilization occurs. This intricate process ultimately leads to the development of seeds within the sugarcane flower, ensuring the continuation of the plant’s genetic lineage.
From a botanical perspective, the sugarcane stigma exhibits remarkable adaptations to enhance its effectiveness in attracting and capturing pollen. Its structure often features specialized cells and surface textures optimized for pollen adhesion and germination.
Additionally, the stigma’s positioning within the flower, typically elevated above other floral parts, maximizes its exposure to pollen-bearing agents, increasing the chances of successful pollination.
Beyond its biological significance, the sugarcane stigma holds economic importance due to its role in sugarcane cultivation. Successful pollination and seed development are crucial for maintaining genetic diversity within sugarcane crops, contributing to the resilience and productivity of commercial varieties.
Additionally, understanding the mechanisms underlying stigma function can inform breeding programs aimed at enhancing traits such as yield, disease resistance, and stress tolerance in sugarcane cultivars.
The sugarcane stigma represents a pivotal aspect of the plant’s reproductive biology, facilitating pollination and seed formation. Its specialized structure and function underscore the intricate adaptations that enable successful sexual reproduction in sugarcane.
Moreover, its relevance extends to agricultural practices, where knowledge of stigma physiology can inform strategies for improving sugarcane cultivation and breeding efforts.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Sugarcane Stigma
1. Pollination: Sugarcane stigma plays a crucial role in the pollination process of sugarcane plants. As the receptive part of the female reproductive organ, the stigma captures pollen grains, facilitating fertilization and seed formation, which is essential for crop yield and quality.
2. Seed Production: Sugarcane stigma contributes to seed production in sugarcane breeding programs. By enabling cross-pollination between different sugarcane varieties, stigma diversity enhances genetic variability, leading to the development of improved cultivars with desirable traits such as disease resistance, high yield, and quality.
3. Genetic Improvement: Sugarcane stigma is utilized in genetic improvement programs to develop new sugarcane varieties with enhanced characteristics. Through controlled pollination and selection of desirable traits, such as sugar content, fiber quality, and stress tolerance, stigma diversity drives genetic progress and innovation in sugarcane cultivation.
4. Research and Development: Sugarcane stigma serves as a valuable research resource for studying plant reproductive biology, genetics, and breeding. Scientific investigations into stigma morphology, physiology, and molecular mechanisms provide insights into sugarcane reproduction and contribute to advancements in crop improvement strategies.
5. Breeding Strategies: Sugarcane stigma diversity influences breeding strategies aimed at developing resilient and high-yielding cultivars. By selecting parent plants with compatible stigmas, breeders can optimize hybridization outcomes and accelerate the development of superior sugarcane varieties adapted to diverse agro-climatic conditions.
6. Crop Management: Sugarcane stigma characteristics influence crop management practices, including planting density, fertilization, irrigation, and pest control. Understanding stigma physiology and flowering patterns enables growers to implement effective agronomic strategies to maximize sugarcane yield, quality, and profitability.
7. Seedling Production: Sugarcane stigma contributes to seedling production through sexual propagation methods such as seed germination and embryo culture. Stigma-mediated pollination and seed set are essential steps in generating viable sugarcane seeds for establishing seedling nurseries and commercial plantations.
8. Genetic Diversity Conservation: Sugarcane stigma diversity is essential for conserving genetic resources and preserving biodiversity in sugarcane germplasm collections. Maintaining a diverse pool of stigmas ensures genetic resilience and adaptability, safeguarding against biotic and abiotic stresses and future breeding needs.
9. Crop Adaptation: Sugarcane stigma diversity drives crop adaptation efforts aimed at developing sugarcane varieties suited to changing environmental conditions and market demands. By selecting stigmas with traits such as drought tolerance, disease resistance, and early flowering, breeders can enhance crop resilience and sustainability.
10. Industrial Applications: Sugarcane stigma extracts are utilized in various industrial applications, including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food processing. Rich in bioactive compounds and antioxidants, stigma extracts exhibit potential health benefits and functional properties, contributing to product innovation and market diversification.
11. Soil Improvement: Sugarcane stigma residues contribute to soil improvement and fertility enhancement when incorporated into agricultural soils. Stigma biomass, after seed harvest, decomposes to organic matter, enriching soil organic carbon, nutrient availability, and microbial activity, thereby improving soil health and productivity.
12. Landscape Ornamentation: Sugarcane stigma diversity enhances landscape ornamentation and aesthetic appeal in botanical gardens, parks, and public spaces. Displaying diverse sugarcane cultivars with distinctive stigma colors, shapes, and sizes creates visual interest and educational opportunities for visitors, promoting botanical awareness and appreciation.
13. Culinary Uses: Sugarcane stigma fibers are utilized in culinary applications for their fibrous texture and nutritional properties. In traditional cuisines, stigma fibers are incorporated into recipes such as salads, stir-fries, and soups, adding dietary fiber, texture, and flavor to dishes.
Read Also: 17 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Apocynum cannabinum (Indian Hemp)
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Sugarcane Stigma
1. Sugarcane Seed: Sugarcane stigma facilitates pollination and seed formation, leading to the production of sugarcane seeds used in breeding programs to develop new cultivars with improved traits such as yield, quality, and disease resistance.
2. Genetic Variability: Sugarcane stigma diversity contributes to genetic variability in sugarcane breeding populations, enhancing the potential for selecting superior parent plants with desirable traits for hybridization and cultivar development.
3. Germplasm Conservation: Sugarcane stigma diversity is essential for conserving germplasm resources and preserving genetic diversity in sugarcane collections, ensuring resilience, adaptability, and sustainability in crop improvement programs.
4. Scientific Research: Sugarcane stigma serves as a valuable research material for studying plant reproductive biology, genetics, and breeding, providing insights into stigma morphology, physiology, and molecular mechanisms influencing sugarcane reproduction and genetic improvement.
5. Seedling Production: Sugarcane stigma-mediated pollination and seed set are essential steps in producing viable sugarcane seeds for establishing seedling nurseries and commercial plantations, supporting seedling production and crop propagation efforts.
6. Agronomic Practices: Sugarcane stigma characteristics influence agronomic practices such as planting density, fertilization, irrigation, and pest management, enabling growers to optimize crop management strategies for maximizing yield, quality, and profitability.
7. Industrial Applications: Sugarcane stigma extracts are utilized in industrial applications such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food processing, owing to their bioactive compounds, antioxidants, and functional properties, contributing to product innovation and market diversification.
8. Soil Enrichment: Sugarcane stigma residues contribute to soil enrichment and fertility enhancement when incorporated into agricultural soils, enriching soil organic carbon, nutrient availability, and microbial activity, thereby improving soil health and productivity.
9. Landscape Enhancement: Sugarcane stigma diversity enhances landscape ornamentation and botanical displays in gardens, parks, and public spaces, showcasing diverse sugarcane cultivars with unique stigma colors, shapes, and sizes for educational and aesthetic purposes.
10. Culinary Uses: Sugarcane stigma fibers are utilized in culinary applications for their fibrous texture and nutritional properties, adding dietary fiber, texture, and flavor to dishes such as salads, stir-fries, and soups in traditional cuisines.
11. Biofuel Production: Sugarcane stigma residues can be utilized in biofuel production processes such as bioethanol and biogas generation, contributing to renewable energy production and reducing reliance on fossil fuels in sustainable energy systems.
12. Waste Valorization: Sugarcane stigma residues can be valorized through processes such as composting, anaerobic digestion, and bioremediation, converting agricultural waste into valuable resources for soil improvement, energy generation, and environmental remediation.
13. Livestock Feed: Sugarcane stigma residues can be utilized as livestock feed or fodder for animals, providing dietary fiber, nutrients, and energy sources for livestock production systems, supporting animal nutrition and health.
Read Also: Bedbugs: Description, Damages Caused, Control and Preventive Measures
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Sugarcane Stigma
1. What is the role of sugarcane stigma in crop production?
The sugarcane stigma plays a crucial role in the pollination process of sugarcane plants, facilitating fertilization and seed formation, which are essential for crop yield and quality.
2. How does sugarcane stigma contribute to genetic improvement in sugarcane breeding programs?
Sugarcane stigma diversity enhances genetic variability in breeding populations, enabling the selection of parent plants with desirable traits for hybridization and the development of improved cultivars with traits such as yield, quality, and disease resistance.
3. What are some examples of industrial applications of sugarcane stigma extracts?
Sugarcane stigma extracts are utilized in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food processing industries for their bioactive compounds, antioxidants, and functional properties, contributing to product innovation and market diversification.
4. How can sugarcane stigma residues improve soil health and fertility?
Sugarcane stigma residues, when incorporated into agricultural soils, enrich soil organic carbon, nutrient availability, and microbial activity, promoting soil health, fertility, and productivity.
5. What are some agronomic practices influenced by sugarcane stigma characteristics?
Sugarcane stigma characteristics influence agronomic practices such as planting density, fertilization, irrigation, and pest management, enabling growers to optimize crop management strategies for maximizing yield, quality, and profitability.
6. Are there any culinary uses of sugarcane stigma fibers?
Yes, sugarcane stigma fibers are utilized in culinary applications for their fibrous texture and nutritional properties, adding dietary fiber, texture, and flavor to dishes such as salads, stir-fries, and soups in traditional cuisines.
7. How does sugarcane stigma contribute to landscape enhancement?
Sugarcane stigma diversity enhances landscape ornamentation and botanical displays in gardens, parks, and public spaces, showcasing diverse sugarcane cultivars with unique stigma colors, shapes, and sizes for educational and aesthetic purposes.
8. Can sugarcane stigma residues be utilized in biofuel production?
Yes, sugarcane stigma residues can be utilized in biofuel production processes such as bioethanol and biogas generation, contributing to renewable energy production and reducing reliance on fossil fuels in sustainable energy systems.
9. What role does sugarcane stigma play in seedling production?
Sugarcane stigma-mediated pollination and seed set are essential steps in producing viable sugarcane seeds for establishing seedling nurseries and commercial plantations, supporting seedling production and crop propagation efforts.
10. How does sugarcane stigma contribute to genetic diversity conservation?
Sugarcane stigma diversity is essential for conserving germplasm resources and preserving genetic diversity in sugarcane collections, ensuring resilience, adaptability, and sustainability in crop improvement programs.
11. Are there any emerging research areas related to sugarcane stigma?
Yes, emerging research areas related to sugarcane stigma include studies on stigma morphology, physiology, and molecular mechanisms influencing sugarcane reproduction, genetic improvement, and crop adaptation to changing environmental conditions.
12. Can sugarcane stigma residues be utilized as livestock feed?
Yes, sugarcane stigma residues can be utilized as livestock feed or fodder for animals, providing dietary fiber, nutrients, and energy sources for livestock production systems, supporting animal nutrition and health.
13. How can consumers support sustainable sugarcane production?
Consumers can support sustainable sugarcane production by choosing products certified as sustainably sourced, reducing food waste, and advocating for fair labor practices in the sugar industry.
Read Also: Practical Steps to Convert Wood Wastes into Mulch