The Almond Seed Coat: Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products
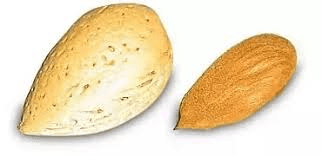
The almond seed coat, also known as the almond shell or hull, is the tough outer layer that encases the edible almond kernel inside the almond fruit. It serves as a protective barrier, shielding the delicate kernel from damage and environmental stressors.
The seed coat of the almond is quite hard and woody, providing sturdy protection for the kernel inside. It is typically brown or tan in color and has a rough texture. The seed coat is formed as the almond fruit matures, developing from the outer layers of the almond fruit.
To access the edible almond kernel, the almond seed coat must be cracked open. This can be done manually using nutcrackers or mechanized equipment in industrial processing facilities. Once the seed coat is cracked open, the almond kernel inside is revealed and can be consumed raw or used in various culinary applications.
While the almond seed coat itself is not typically consumed, it serves an important function in protecting the almond kernel during storage and transportation. It also provides a natural barrier against pests, diseases, and environmental elements, ensuring the viability and quality of the almond kernel.
In some cases, almond seed coats are removed during processing to produce blanched almonds, which have the outer skin removed. Blanched almonds are often used in baking and confectionery to achieve a smoother texture and appearance in finished products.
Overall, the almond seed coat is an integral part of the almond fruit, providing protection for the edible kernel inside. While not consumed directly, it plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality and integrity of almonds for consumption and various industrial applications.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Almond Seed Coat

1. Protection of Almond Seed: The almond seed coat serves as a protective layer surrounding the almond kernel, safeguarding it from environmental factors such as pests, pathogens, and mechanical damage during development and storage.
2. Moisture Regulation: The seed coat helps regulate moisture levels within the almond kernel, preventing dehydration and maintaining optimal hydration for seed viability and germination.
3. Germination Aid: The seed coat facilitates germination by regulating water absorption and oxygen exchange, creating favorable conditions for the emergence of the embryonic plant from the seed.
4. Nutrient Reserve: Almond seed coats contain reserves of nutrients and compounds that support seed development and early seedling growth, providing essential resources for the emerging plant.
5. Soil Enrichment: Almond seed coats, when naturally shed or incorporated into the soil, decompose and release organic matter and nutrients, enriching the soil and promoting fertility for subsequent plant growth.
6. Erosion Control: Seed coats contribute to soil stabilization and erosion control by anchoring seeds in place and reducing soil displacement caused by wind and water erosion.
7. Biomass Material: Almond seed coats, along with other agricultural residues, can be utilized as biomass material for energy production through combustion or conversion processes, contributing to renewable energy sources.
8. Soil Microbial Activity: The decomposition of almond seed coats in the soil supports microbial activity, enhancing soil biodiversity and nutrient cycling processes essential for ecosystem functioning.
9. Carbon Sequestration: Incorporating almond seed coats into the soil contributes to carbon sequestration, as organic matter from decomposed seed coats becomes part of the soil organic carbon pool, mitigating climate change impacts.
10. Soil Structure Improvement: Almond seed coats, when decomposed, improve soil structure by enhancing soil aggregation, porosity, and water infiltration rates, promoting better root development and plant growth.
11. Mulching Material: Ground almond seed coats can be used as mulch in agricultural and horticultural settings to conserve soil moisture, suppress weed growth, and regulate soil temperature.
12. Horticultural Applications: Almond seed coats can be utilized in horticulture for seed coating, seedling protection, and soil amendment purposes, supporting plant establishment and growth in nurseries and gardens.
13. Biochar Production: Almond seed coats can be converted into biochar, a stable form of charcoal used as a soil amendment to improve soil fertility, water retention, and nutrient availability for plants.
14. Organic Fertilizer: Decomposed almond seed coats serve as a source of organic matter and nutrients, contributing to the production of organic fertilizers used in sustainable agriculture and gardening practices.
15. Livestock Feed Additive: Ground almond seed coats can be incorporated into livestock feed as a fiber-rich additive, providing dietary benefits for ruminant animals and supporting digestive health.
16. Composting Material: Almond seed coats are suitable for composting, where they decompose alongside other organic materials to produce nutrient-rich compost for soil enrichment and plant nutrition.
17. Land Rehabilitation: Almond seed coats can be utilized in land rehabilitation projects to restore degraded soils, stabilize slopes, and revegetate barren areas, promoting ecosystem recovery and biodiversity conservation.
Read Also: 15 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Aleppo Pepper (Capsicum annuum var. annuum)
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Almond Seed Coat

1. Mulch: Ground almond seed coats can be used as mulch in agricultural and horticultural settings to conserve soil moisture and suppress weed growth.
2. Biochar: Almond seed coats can be converted into biochar, a stable form of charcoal used as a soil amendment to improve soil fertility and water retention.
3. Organic Fertilizer: Decomposed almond seed coats serve as a source of organic matter and nutrients for the production of organic fertilizers used in sustainable agriculture.
4. Livestock Feed Additive: Ground almond seed coats can be added to livestock feed as a fiber-rich supplement, supporting digestive health in ruminant animals.
5. Composting Material: Almond seed coats are suitable for composting, where they decompose alongside other organic materials to produce nutrient-rich compost for soil enrichment.
6. Land Rehabilitation: Almond seed coats can be used in land rehabilitation projects to restore degraded soils, stabilize slopes, and promote ecosystem recovery.
7. Soil Amendment: Decomposed almond seed coats enrich the soil with organic matter and nutrients, improving soil fertility and supporting plant growth.
8. Germination Aid: Almond seed coats facilitate seed germination by regulating water absorption and oxygen exchange, creating favorable conditions for seedling emergence.
9. Horticultural Applications: Almond seed coats are utilized in horticulture for seed coating, seedling protection, and soil amendment purposes, supporting plant establishment and growth.
10. Biomass Material: Almond seed coats, along with other agricultural residues, can be used as biomass material for energy production through combustion or conversion processes, contributing to renewable energy sources.
Read Also: Bedbugs: Description, Damages Caused, Control and Preventive Measures
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Almond Seed Coat

1. What is the almond seed coat?
The almond seed coat is the protective outer layer that encases the almond kernel within the almond drupe. It plays a crucial role in safeguarding the seed during development and storage.
2. What is the economic importance of the almond seed coat?
The almond seed coat contributes to soil health, erosion control, and biomass production, making it economically valuable in agricultural and environmental applications.
3. How does the almond seed coat benefit soil health?
The decomposition of almond seed coats enriches the soil with organic matter and nutrients, improving soil fertility, structure, and microbial activity.
4. Can almond seed coats be used as animal feed?
While almond seed coats are not commonly used as animal feed due to their fibrous and indigestible nature, they can be incorporated into livestock feed in limited quantities as a fiber source.
5. Are there any environmental benefits associated with almond seed coats?
Yes, almond seed coats contribute to soil stabilization, erosion control, carbon sequestration, and biodiversity conservation, supporting environmental sustainability and ecosystem health.
6. How are almond seed coats utilized in agriculture?
Almond seed coats are utilized as soil amendments, mulch, composting material, and erosion control measures in agricultural practices to improve soil quality, water retention, and crop productivity.
7. Can almond seed coats be used in gardening?
Yes, almond seed coats can be used in gardening for mulching, composting, and soil enrichment purposes to promote plant growth and sustainability.
8. Are there any safety considerations when using almond seed coats?
While almond seed coats are generally safe for agricultural and gardening purposes, precautions should be taken to avoid excessive dust inhalation during handling and processing.
9. How long does it take for almond seed coats to decompose in the soil?
The decomposition rate of almond seed coats depends on environmental conditions such as temperature, moisture, and microbial activity. Under favorable conditions, decomposition may take several months to a year.
10. Can almond seed coats be recycled or reused?
Yes, almond seed coats can be recycled or reused in various agricultural, horticultural, and environmental applications, contributing to waste reduction and resource conservation.
Read Also: How To Fix a Garbage Disposal Jam