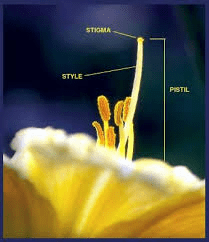
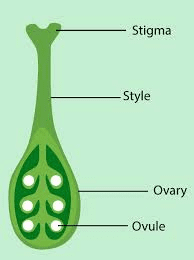
The Apricot Pistil (Prunus armeniaca) is the female reproductive organ crucial for the fertilization and fruit development processes. It consists of three main parts: the stigma, style, and ovary, each playing a specific role in the reproduction of the apricot tree.
The stigma is the uppermost part of the pistil and is designed to catch and hold pollen. It is typically sticky or feathery, which helps trap pollen grains that are transferred by pollinators or wind. In apricot flowers, the stigma is often located at the tip of the style and is somewhat shielded by the surrounding petals and stamens, ensuring effective pollen capture.
The style is the slender stalk that connects the stigma to the ovary. It serves as a conduit for pollen tubes to travel from the stigma to the ovary. After pollen lands on the stigma, it germinates and forms a pollen tube that grows down through the style to reach the ovary. The style’s length and structure are adapted to ensure that pollen tubes can navigate to the ovary efficiently.
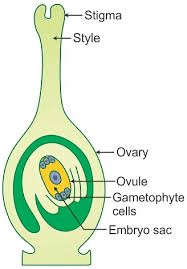
The ovary is the base of the pistil and contains one or more ovules. Each ovule has the potential to develop into a seed upon fertilization. Inside the ovary, fertilization occurs when the sperm cells from the pollen unite with the egg cells in the ovules. This process results in the formation of seeds, which eventually develop into new apricot fruits.
Apricot pistils begin developing early in the flower bud stage, along with other flower components. As the flower matures and opens, the pistil becomes fully functional and ready to receive pollen. The timing of pistil development is carefully synchronized with the flowering cycle to maximize the chances of successful fertilization.
In addition to their reproductive function, apricot pistils play a role in the overall health and productivity of the apricot tree. A healthy pistil is essential for producing viable seeds and high-quality fruit. Factors such as environmental conditions, pollinator activity, and the health of the tree can all influence the effectiveness of the pistil in supporting successful fertilization.
Understanding the function and development of apricot pistils provides valuable insights into both the biology of the apricot tree and the broader principles of plant reproduction. This knowledge is crucial for improving apricot cultivation practices, such as optimizing pollination strategies and enhancing fruit yield and quality.
The pistil of the apricot flower is a vital component of the plant’s reproductive system. Its role in pollen reception, fertilization, and seed development underscores its importance in the lifecycle of the apricot tree and its contributions to successful fruit production.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Apricot Pistil
1. Pollination: The apricot pistil is essential for the fertilization process. It receives pollen from the stamens and facilitates the development of the fruit.
2. Fruit Development: The pistil’s ovary develops into the apricot fruit after successful fertilization, making it crucial for fruit production.
3. Seed Production: The pistil’s ovary contains ovules that develop into seeds after fertilization, contributing to seed production and propagation of apricot trees.
4. Genetic Research: The pistil plays a key role in genetic research, helping scientists study plant reproduction, inheritance patterns, and the development of new apricot varieties.
5. Educational Tools: The pistil is used in educational settings to teach students about plant anatomy, specifically the structure and function of the pistil in reproduction.
6. Botanical Art: The pistil is featured in botanical art and illustrations, highlighting its role in the flowering and fruiting process.
7. Herbal Medicine: In some traditional medicine practices, the pistil is used for its potential health benefits, such as aiding in reproductive health and overall wellness.
8. Pollinator Attraction: The pistil, along with other flower parts, helps attract pollinators like bees and butterflies, which are essential for the pollination process.
9. Crop Yield Improvement: Understanding the pistil’s role in fruit development can lead to better crop management practices and improved apricot yields.
10. Plant Breeding: Knowledge of the pistil’s function aids in plant breeding programs aimed at developing apricot varieties with desirable traits.
11. Natural Fencing: In some cases, apricot pistils can be used in creating natural garden structures, though this is less common.
12. Research on Fertility: The pistil is studied to understand and address issues related to plant fertility and fruit set, which can improve agricultural practices.
13. Soil Enrichment: After harvest, pistils and other flower remnants can be composted to enrich soil with organic matter.
14. Eco-Friendly Products: The pistil and other floral parts can be used in sustainable products like biodegradable garden supplies.
15. Educational Demonstrations: The pistil is used in demonstrations to show the reproductive processes of flowering plants.
16. Pollinator Conservation: Understanding the pistil’s role helps in efforts to conserve pollinator species by providing insights into their needs and behaviors.
17. Livelihood Opportunities: Harvesting and selling apricot pistils can create economic opportunities for local communities through the sale of botanical and educational products.
18. Fruit Quality Improvement: Research on the pistil can lead to improvements in fruit quality and characteristics, benefiting both growers and consumers.
Read Also: 17 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Guggul (Commiphora wightii)
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Apricot Pistil

1. Seed Production: The pistil’s ovary develops into seeds, which are essential for growing new apricot trees.
2. Botanical Art: The pistil is used in botanical illustrations and art, showcasing its role in the flowering process.
3. Educational Tools: The pistil is used in educational settings to teach about plant reproduction and anatomy.
4. Herbal Medicine: In traditional medicine, the pistil is used for its potential health benefits, particularly in relation to reproductive health.
5. Pollinator Habitat: The pistil helps attract pollinators, which are essential for maintaining biodiversity and supporting ecosystems.
6. Soil Enrichment: Pistils and other plant remnants are composted to improve soil fertility and structure.
7. Crop Management: Understanding the pistil’s function can lead to better crop management practices and increased apricot yields.
8. Plant Breeding: Knowledge of the pistil aids in developing new apricot varieties with improved traits.
9. Sustainable Products: The pistil can be used in eco-friendly products such as biodegradable garden supplies.
10. Research: The pistil is studied in research on plant reproduction and fertility, contributing to advancements in agriculture.
11. Pollinator Conservation: Insights into the pistil’s role help in efforts to conserve pollinator species by addressing their needs.
12. Educational Demonstrations: The pistil is used in demonstrations to illustrate plant reproductive processes.
13. Natural Fencing: While less common, pistils and other floral parts can sometimes be used in creating natural garden structures.
14. Livelihood Opportunities: Selling apricot pistils can provide economic opportunities for local communities through the sale of botanical and educational products.
15. Fruit Quality Improvement: Research on the pistil helps improve fruit quality and characteristics, benefiting growers and consumers.
16. Crop Yield Improvement: Understanding the pistil’s role contributes to better crop management and higher apricot yields.
Read Also: Rose Chafer: Description, Damages Caused, Control and Preventive Measures
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Apricot Pistil
1. What is the role of the apricot pistil in fruit development?
The apricot pistil plays a crucial role in fruit development. After receiving pollen from the stamens, the pistil’s ovary develops into the apricot fruit. This process is essential for the production of apricots.
2. How does the pistil contribute to seed production?
The pistil’s ovary contains ovules that develop into seeds after fertilization. These seeds are vital for the propagation of apricot trees and the continuation of the species.
3. How is the apricot pistil used in educational settings?
The pistil is used in educational settings to teach students about plant anatomy and reproduction. It helps illustrate the structure and function of the pistil in the flowering and fruiting process.
4. Can apricot pistils be used in traditional medicine?
Yes, in some traditional medicine practices, apricot pistils are used for their potential health benefits, such as supporting reproductive health and overall wellness.
5. How do apricot pistils support pollinators?
Apricot pistils, along with other flower parts, help attract pollinators like bees and butterflies. These pollinators are essential for transferring pollen and ensuring the fertilization of flowers.
6. What is the significance of studying the pistil in plant breeding?
Studying the pistil is important in plant breeding because it helps scientists understand plant reproduction and develop new apricot varieties with desirable traits, such as better fruit quality or higher yields.
7. How can apricot pistils be used to improve soil?
After harvest, apricot pistils and other flower remnants can be composted to enrich the soil with organic matter, improving soil fertility and structure.
8. Are apricot pistils used in making natural products?
Yes, apricot pistils can be used in eco-friendly products like biodegradable garden supplies, contributing to sustainable practices.
9. How does understanding the pistil benefit crop management?
Understanding the pistil’s role in fruit development and fertilization helps improve crop management practices, leading to increased apricot yields and better fruit quality.
10. Can harvesting apricot pistils create economic opportunities?
Yes, harvesting and selling apricot pistils can provide economic opportunities for local communities, supporting livelihoods through the sale of botanical and educational products.