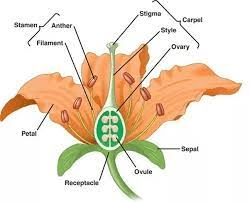
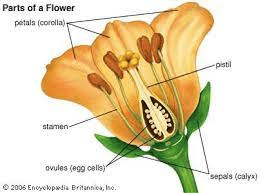
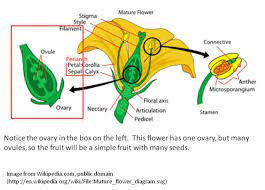
The arrowroot ovary refers to the female reproductive structure of the arrowroot plant, scientifically known as Maranta arundinacea. In botanical terms, the ovary is the part of the flower where ovules are produced, eventually developing into seeds after fertilization.
In the case of arrowroot, the ovary plays a crucial role in the plant’s reproductive process, ultimately leading to seed formation and propagation.
Within the arrowroot flower, the ovary is typically located at the base of the flower, beneath the petals and sepals. It is here that ovules, the precursor to seeds, are housed and protected.
Pollination, the process of transferring pollen from the male reproductive organ (anther) to the female reproductive organ (stigma), triggers the development of the ovules within the ovary. Once fertilized, the ovules undergo maturation, forming seeds within the ovary.
The arrowroot ovary is integral to the plant’s reproductive success, as it serves as the site for seed development. These seeds are essential for the propagation and continuation of the arrowroot plant species. Additionally, the ovary may undergo various developmental changes and adaptations to optimize seed production and dispersal, contributing to the plant’s reproductive strategy.
Beyond its botanical significance, the arrowroot ovary holds importance in agriculture and horticulture. Understanding the ovary’s structure, function, and reproductive mechanisms can inform cultivation practices and breeding programs aimed at enhancing crop yields, seed quality, and overall plant health. Furthermore, studying the ovary provides insights into the reproductive biology of arrowroot and related plant species, contributing to broader efforts in plant science and conservation.
The arrowroot ovary is a fundamental component of the plant’s reproductive system, playing a vital role in seed formation and propagation. Its structure and function are essential for the plant’s reproductive success and have implications for agriculture, horticulture, and botanical research.
Understanding the arrowroot ovary enriches our knowledge of plant biology and contributes to efforts aimed at sustainable cultivation and conservation of this valuable crop species.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Arrowroot Ovary
1. Culinary Applications: Arrowroot ovary is utilized in culinary applications as a natural thickening agent for soups, sauces, gravies, and desserts. Its high starch content makes it a popular choice for gluten-free and vegan recipes.
2. Pharmaceutical Industry: Arrowroot ovary is used in the pharmaceutical industry for its medicinal properties. It is a key ingredient in herbal remedies and dietary supplements known for its soothing effects on the digestive system.
3. Cosmetic Formulations: Arrowroot ovary extracts are incorporated into cosmetic formulations for their absorbent properties and skin-friendly nature. They are commonly used in talc-free body powders, dry shampoos, and facial masks to absorb excess oil and moisture from the skin.
4. Textile Sizing: Arrowroot ovary starch, derived from the ovary, is used as a natural sizing agent in the textile industry to improve the strength, smoothness, and crease resistance of fabrics during manufacturing.
5. Papermaking: Arrowroot ovary starch is employed in the papermaking process as an additive to enhance paper quality and performance. It improves the strength, opacity, and printability of paper, resulting in high-quality print results.
6. Industrial Applications: Arrowroot ovary extracts find applications in various industrial processes, including the production of adhesives, glues, and coatings. The bioactive compounds extracted from the ovary may serve as natural and eco-friendly alternatives to synthetic additives in industrial formulations.
7. Agricultural Practices: Arrowroot ovary cultivation supports sustainable agricultural practices by providing farmers with a low-input crop option that requires minimal water and fertilizer inputs. Arrowroot plants are resilient to pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemical inputs and promoting biodiversity in agroecosystems.
8. Livelihoods and Rural Development: Arrowroot ovary cultivation provides livelihood opportunities for smallholder farmers and rural communities in tropical regions. The cultivation, processing, and marketing of arrowroot products generate income and employment opportunities, contributing to poverty reduction and economic development in rural areas.
9. Export Industry: Arrowroot products, including arrowroot flour, starch, and extracts, contribute to the export industry in countries where arrowroot cultivation is prevalent. These products are exported to international markets for use in food, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and industrial applications.
10. Agroecological Restoration: Arrowroot ovary cultivation supports agroecological restoration efforts by improving soil fertility, biodiversity, and ecosystem services in degraded or marginal lands. The cultivation of arrowroot plants helps rehabilitate disturbed soils, reduce erosion, and enhance nutrient cycling in agricultural landscapes, supporting landscape resilience and sustainability.
11. Food Industry: Arrowroot ovary is processed into arrowroot flour or starch, which serves as a versatile ingredient in the food industry. It is used as a thickening agent, binder, and stabilizer in a wide range of food products, including baked goods, sauces, and confectionery items.
12. Traditional Medicine: In traditional medicine systems, arrowroot ovary is valued for its medicinal properties and therapeutic effects. It is believed to have anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and antioxidant properties, which are beneficial for digestive health and overall well-being.
13. Animal Feed: By-products of arrowroot ovary processing, such as residual pulp and spent ovary, can be utilized as nutritious additions to animal feed formulations. These by-products provide essential nutrients and dietary fiber to support the health and growth of livestock, poultry, and pets.
14. Soil Amendment: Arrowroot ovary residues can be composted and recycled as organic soil amendments to improve soil fertility and structure. They contribute organic matter, essential nutrients, and beneficial microorganisms to the soil, enhancing its ability to support plant growth and productivity.
15. Botanical Research: Arrowroot ovary is of interest to botanists and researchers studying plant morphology and development. Studying the growth and anatomy of arrowroot ovary provides insights into seed development, flower morphology, and reproductive biology, informing agricultural practices and crop improvement strategies.
Raed Also: Aims and Objectives of Agriculture Department
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Arrowroot Ovary
1. Arrowroot Flour: Arrowroot ovary can be processed into arrowroot flour, a fine white powder with a neutral flavor and high starch content. Arrowroot flour is used as a gluten-free thickening agent in culinary applications and as a substitute for wheat flour in baking and cooking.
2. Arrowroot Starch: Arrowroot starch is extracted from the ovary and processed into a fine white powder with excellent thickening properties. It is used in food manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetic formulations as a natural and versatile ingredient.
3. Arrowroot Powder: Arrowroot powder is the dried and ground form of arrowroot ovary, commonly used in culinary and cosmetic applications. It serves as a thickening agent, absorbent, and texturizer in food products, body powders, and personal care items.
4. Arrowroot Extracts: Arrowroot ovary extracts contain bioactive compounds with potential medicinal properties, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial effects. These extracts are used in herbal remedies, dietary supplements, and natural health products for their therapeutic benefits.
5. Animal Feed: By-products of arrowroot ovary processing, such as residual pulp and spent ovary, can be utilized as nutritious additions to animal feed formulations. These by-products provide essential nutrients and dietary fiber to support the health and well-being of livestock, poultry, and pets.
6. Soil Amendment: Arrowroot ovary residues can be composted and recycled as organic soil amendments to improve soil fertility, structure, and health. They contribute organic matter, essential nutrients, and beneficial microorganisms to the soil, enhancing its ability to support plant growth and productivity.
7. Textile Sizing: Arrowroot starch, derived from the ovary, is used as a natural sizing agent in the textile industry to improve the strength, smoothness, and crease resistance of fabrics during manufacturing.
8. Papermaking: Arrowroot starch is employed in the papermaking process as an additive to enhance paper quality and performance. It improves the strength, opacity, and printability of paper, resulting in high-quality print results.
9. Industrial Applications: Arrowroot ovary extracts find applications in various industrial processes, including the production of adhesives, glues, and coatings. The bioactive compounds extracted from the ovary may serve as natural and eco-friendly alternatives to synthetic additives in industrial formulations.
10. Botanical Research: Arrowroot ovary is of interest to botanists and researchers studying plant morphology and development. Studying the growth and anatomy of arrowroot ovary provides insights into seed development, flower morphology, and reproductive biology, informing agricultural practices and crop improvement strategies.
11. Cosmetic Formulations: Arrowroot ovary extracts are incorporated into cosmetic formulations for their absorbent properties and skin-friendly nature. Arrowroot powder is commonly used in talc-free body powders, dry shampoos, and facial masks to absorb excess oil and moisture from the skin.
12. Traditional Medicine: In traditional medicine systems, arrowroot ovary is valued for its medicinal properties and therapeutic effects. It is believed to have anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and antioxidant properties, which are beneficial for digestive health and overall well-being.
13. Agroecological Restoration: Arrowroot ovary cultivation supports agroecological restoration efforts by improving soil fertility, biodiversity, and ecosystem services in degraded or marginal lands. The cultivation of arrowroot plants helps rehabilitate disturbed soils, reduce erosion, and enhance nutrient cycling in agricultural landscapes, supporting landscape resilience and sustainability.
14. Food Industry: Arrowroot ovary is processed into arrowroot flour or starch, which serves as a versatile ingredient in the food industry. It is used as a thickening agent, binder, and stabilizer in a wide range of food products, including baked goods, sauces, and confectionery items.
15. Livelihoods and Rural Development: Arrowroot ovary cultivation provides livelihood opportunities for smallholder farmers and rural communities in tropical regions. The cultivation, processing, and marketing of arrowroot products generate income and employment opportunities, contributing to poverty reduction and economic development in rural areas.
Read Also: 10 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Contrayerva (Dorstenia contrajerva)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Arrowroot Ovary
1. What Is Arrowroot Ovary?
Arrowroot ovary refers to the reproductive structure of the arrowroot plant (Maranta arundinacea), containing seeds surrounded by a fleshy covering. The ovary is harvested for its starchy content, which is processed into arrowroot flour or starch.
2. How Is Arrowroot Ovary Used in Culinary Applications?
Arrowroot ovary is processed to extract arrowroot starch, which serves as a gluten-free thickening agent in culinary applications such as sauces, gravies, soups, and desserts. Arrowroot flour, derived from the ovary, is also used in gluten-free baking and cooking.
3. Is Arrowroot Ovary Nutritious?
Arrowroot ovary is low in calories and fat but contains moderate amounts of carbohydrates, fiber, and essential nutrients such as potassium and vitamin B6. It is a good source of resistant starch, which promotes digestive health and may support blood sugar management.
4. Can Arrowroot Ovary Be Eaten Raw?
Arrowroot ovary is typically consumed cooked rather than raw due to its starchy nature and mild flavor. It can be boiled, steamed, or roasted to soften the flesh and enhance its palatability.
5. Is Arrowroot Ovary Safe for Babies?
Arrowroot ovary is commonly used in baby food formulations due to its mild flavor, smooth texture, and digestibility. Arrowroot starch is used to thicken purees and porridges, providing a nutritious option for infants transitioning to solid foods.
6. Are Arrowroot Ovary and Arrowroot Powder the Same Thing?
Arrowroot ovary refers to the whole ovary structure containing seeds surrounded by flesh, while arrowroot powder refers to the dried and ground form of arrowroot ovary. Arrowroot powder is commonly used as a thickening agent in cooking and baking.
7. Is Arrowroot Ovary Cultivation Environmentally Friendly?
Arrowroot ovary cultivation is considered environmentally friendly due to its low-input requirements and minimal environmental impact. Arrowroot plants are perennial and resilient to pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemical inputs and promoting biodiversity in agroecosystems.
8. Can Arrowroot Ovary Be Grown at Home?
Arrowroot ovary can be grown at home in warm, humid climates with well-drained soil and adequate sunlight. It is propagated from rhizomes or seeds and requires regular watering and fertilization to thrive.
9. What Are Some Culinary Uses of Arrowroot Ovary?
Arrowroot ovary is used in various culinary preparations, including soups, sauces, gravies, and desserts, as a thickening agent. Arrowroot starch and flour derived from the ovary are popular ingredients in gluten-free baking and cooking.
10. Are Arrowroot Ovary and Tapioca the Same Thing?
Arrowroot ovary and tapioca are derived from different plant species and have distinct characteristics. Arrowroot ovary comes from the arrowroot plant (Maranta arundinacea), while tapioca is derived from the cassava plant (Manihot esculenta). Both are used as thickeners in cooking but have different textures and flavors.
11. How Should Arrowroot Ovary Products Be Stored?
Arrowroot ovary products, such as arrowroot flour and starch, should be stored in a cool, dry place away from moisture and direct sunlight to maintain their quality and freshness. They can be stored in airtight containers or sealed bags for extended shelf life.
12. Can Arrowroot Ovary Extracts Be Used in Skincare?
Arrowroot ovary extracts are commonly used in skincare formulations for their absorbent properties and skin-friendly nature. Arrowroot powder is used in talc-free body powders, dry shampoos, and facial masks to absorb excess oil and moisture from the skin.
13. Are Arrowroot Ovary Products Suitable for Individuals with Dietary Restrictions?
Arrowroot ovary products, such as arrowroot flour and starch, are gluten-free and suitable for individuals with gluten intolerance or celiac disease. They are also free from major allergens such as nuts, soy, and dairy, making them suitable for a wide range of dietary preferences and restrictions.
Raed Also: Practical Steps to Convert Used Cooking Oil Wastes into Soap

