The barley palea is a component of the barley flower, specifically a part of the outer whorl of floral organs called the lemma and palea. The palea is the inner of the two, located closest to the grain or seed. It is a thin, membranous structure that surrounds and protects the stamen, pistil, and other reproductive parts of the barley floret.
Economically, the barley palea plays a crucial role in seed development and grain quality. Along with the lemma, it helps to enclose and protect the developing grain, shielding it from damage, pests, and environmental stressors. This protection is essential for ensuring the viability and integrity of the grain, which directly impacts the yield and quality of the barley crop.
Additionally, the palea and lemma contribute to the dispersal of barley seeds and may influence seed dormancy and germination. Their structure and composition can affect seed shedding, seed longevity, and the ability of seeds to establish and grow under different environmental conditions. Understanding the biology of the palea and lemma is important for optimizing seed production, storage, and planting practices in barley cultivation.
Furthermore, the palea and lemma may have implications for barley breeding and genetic improvement. Traits related to seed size, shape, color, and dormancy are influenced by the structure and composition of these floral organs. Breeding programs often target genes associated with the palea and lemma to develop barley varieties with desirable agronomic traits, such as high yield, disease resistance, and stress tolerance.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Barley Palea
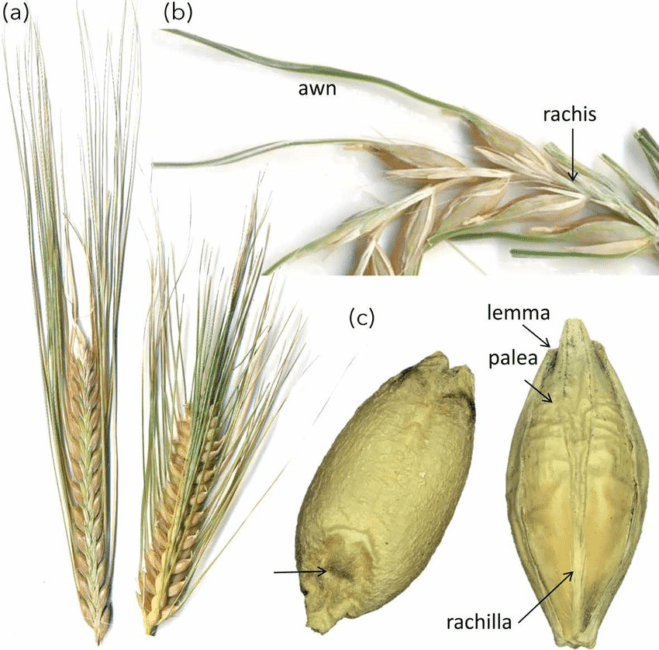
1. Seed Protection: Barley palea provides protection to the developing grain within the spikelet. It acts as a shield against environmental stresses such as moisture, pests, and diseases during the grain maturation process, ensuring seed viability and quality.
2. Grain Attachment: Barley palea aids in the attachment of grains to the spikelet structure, facilitating seed dispersal mechanisms. This attachment ensures that the grains remain intact during dispersal by wind, water, or passing animals, contributing to successful propagation.
3. Agricultural Cultivation: Barley palea influences agricultural practices such as seeding and crop management. Its presence affects seed placement, soil coverage, and water absorption, impacting crop establishment and yield in barley cultivation.
4. Animal Forage: Barley palea, along with other barley residues, is utilized in animal forage production. Barley straw, which includes palea structures, provides fiber and roughage in livestock diets, supporting digestion and nutrient utilization in ruminants.
5. Soil Erosion Control: Barley palea residues contribute to soil erosion control in agricultural fields. When left as crop residues or incorporated into the soil after harvest, they help stabilize soil structure, reduce water runoff, and prevent erosion, preserving soil fertility.
6. Composting: Barley palea residues are valuable components of composting systems. Their decomposition adds organic matter and nutrients to compost piles, enriching the compost for soil amendment and improving soil health in agricultural and horticultural applications.
7. Biodegradable Packaging: Barley palea is explored as a raw material for biodegradable packaging products. Its natural biodegradability makes it suitable for use in environmentally friendly packaging solutions, reducing plastic waste and environmental pollution.
8. Crafts and Decor: Dried barley palea is used in crafts and decor for its rustic and natural aesthetic appeal. It is incorporated into floral arrangements, wreaths, and seasonal decorations, adding texture and visual interest to home decor items.
9. Wildlife Habitat: Barley palea residues provide habitat and food sources for wildlife in agricultural landscapes. They support insect populations, small mammals, and birds, contributing to biodiversity conservation and ecological balance.
10. Soil Fertility: Barley palea residues contribute to soil fertility by adding organic matter and nutrients to the soil. Their decomposition enhances soil structure, nutrient cycling, and microbial activity, promoting healthy plant growth and crop yields.
Read Also: How to Control Feeding Struggle among Fishes in the same Pond
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Barley Palea
1. Biodegradable Mulch Films: Barley palea residues can be processed into biodegradable mulch films used in agricultural fields and gardens. These films suppress weed growth, retain soil moisture, and degrade naturally over time, reducing plastic pollution.
2. Animal Bedding: Barley palea, along with other barley straw, is used as animal bedding material in livestock farming operations. Its absorbent properties provide comfort and hygiene for animals in barns and stables, improving welfare and productivity.
3. Bioplastics: Barley palea residues can be utilized in the production of bioplastics and packaging materials. Their natural biodegradability makes them attractive alternatives to conventional petroleum-based plastics, reducing environmental impact and plastic waste.
4. Compost: Barley palea residues are valuable additions to compost piles and bins. Their decomposition adds organic matter and nutrients to the compost, enriching the soil for plant growth and improving soil health in agricultural and horticultural applications.
5. Erosion Control Mats: Barley palea residues can be incorporated into erosion control mats used in land restoration projects. These mats stabilize soil, prevent erosion, and promote vegetation establishment in erosion-prone areas, supporting environmental conservation efforts.
6. Biofuel Feedstock: Barley palea residues are potential feedstocks for biofuel production. Their cellulose and lignin content can be converted into biofuels such as ethanol and biogas through biochemical and thermochemical processes, contributing to renewable energy production.
7. Papermaking: Barley palea fibers can be processed into pulp for papermaking. Their cellulose content provides strength and durability to paper products, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional wood-based paper production.
8. Soil Amendment: Barley palea residues, when incorporated into the soil, contribute to soil organic matter and nutrient content. Their decomposition enhances soil fertility, improves soil structure, and promotes healthy plant growth in agricultural systems.
9. Biogas Production: Barley palea residues can be anaerobically digested to produce biogas. Biogas production from agricultural residues helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels for energy, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
10. Wildlife Habitat Enhancement: Barley palea residues provide habitat and food sources for wildlife in agricultural landscapes. They support insect populations, small mammals, and birds, contributing to biodiversity conservation and ecological balance.
Read Also: 10 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Convolvulus prostratus (Bindweed)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Barley Palea
1. Are barley palea structures important for seed protection?
Yes, barley palea structures play a crucial role in protecting developing grains within the spikelet, ensuring seed viability and quality.
2. Can barley palea residues be used as animal bedding?
Yes, barley palea residues, along with other barley straw, are commonly used as animal bedding material in livestock farming operations due to their absorbent properties and availability as agricultural residues.
3. Do barley palea residues contribute to soil erosion control?
Yes, barley palea residues help control soil erosion by stabilizing soil structure, reducing water runoff, and preventing erosion when left as crop residues or incorporated into the soil after harvest.
4. Can barley palea residues be composted?
Yes, barley palea residues are valuable additions to composting systems and contribute to the decomposition process, producing nutrient-rich compost for soil enrichment and plant growth.
5. Are barley palea residues utilized in biodegradable materials production?
Yes, barley palea residues can be processed into biodegradable materials such as mulch films and packaging products, offering environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional plastics.
6. Do barley palea structures affect agricultural cultivation practices?
Yes, barley palea structures influence seed drilling, germination, and crop establishment in agricultural cultivation, impacting crop yield and uniformity.
7. Can barley palea residues be used in biofuel production?
Yes, barley palea residues are potential feedstocks for biofuel production, contributing to renewable energy production and reducing dependence on fossil fuels for energy.
8. Are barley palea residues suitable for papermaking?
Yes, barley palea fibers can be processed into pulp for papermaking, providing a sustainable alternative to traditional wood-based paper production.
9. Do barley palea residues contribute to soil fertility?
Yes, barley palea residues contribute to soil fertility by adding organic matter and nutrients to the soil, improving soil structure and nutrient availability for plant growth.
10. Are barley palea residues important for wildlife habitat enhancement?
Yes, barley palea residues provide habitat and food sources for wildlife in agricultural landscapes, supporting biodiversity conservation and ecological balance.
Read Also: How to Build a Raised Bed Garden





